Long span roof
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
Long span roofs are generally defined as those that exceed 12 m in span. Long span roofs can create flexible, column-free internal spaces and can reduce substructure costs and construction times. They are commonly found in a wide range of building types such as factories, warehouses, agricultural buildings, hangars, large shops, public halls, gymnasiums and arenas.
Their primary functions are, similar to normal roofs, typically, protecting against the weather, restricting the spread of fire, providing sound and thermal insulation and so on. However, as they may offer the only structural system other than the perimeter walls, they may also have to provide support for building services, access routes, lifting equipment, lighting, and so on.
[edit] Materials
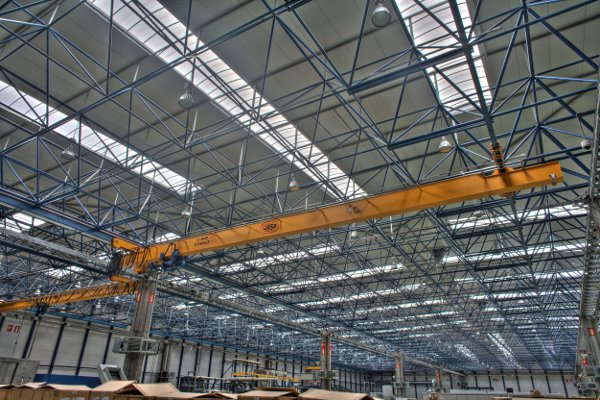
Long span roofs can be fabricated in from a number of materials, such as steel, aluminium alloy, timber, reinforced concrete and prestressed concrete. Steel is often preferred due to its high strength and because it will not spread fire over its surface. The design of long span steel and (steel-concrete) composite beams is generally carried out in accordance with BS 5950, BS EN 1993 or BS EN 1994.
[edit] Roof forms
[edit] Portal frame
Portal frames are a type of structural frame, that, in their simplest form, are characterised by a beam (or rafter) supported at either end by columns, however, the joints between the beam and columns are 'rigid' so that the bending moment in the beam is transferred to the columns. This means that the beam can be reduced in sectional size and can span large distances.
Typically, the joint between the beam and the columns is made 'rigid' by the addition of a haunch, bracket, or by a deepening of the section at the joints. Portal frames are generally fabricated from steel, reinforced precast concrete, or laminated timber sometimes referred to as 'glulam'.
See Portal frame for more information.
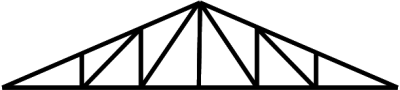
[edit] Pitched truss
Pitched trusses are triangulated plane frames spaced at suitable centres. To prevent spreading, the rafters, which form the top edge of the truss are connected at their feet by a tie member. Bracing is provided within the basic triangle by using struts and ties. Purlins are fixed between the trusses to which roof coverings can be attached.
Pitched trusses allow for good rainwater run off, reasonable daylight spreads from rooflights, and high roof volume due to the triangulated format.
They are often made from steel sections, connected together with bolts or by welding to shaped plates called gussets. Steel truss members are usually angle sections since they are economic and accept both tensile and compressive stresses. Alternatively, timber members may be used, joined with bolts and timber connectors.
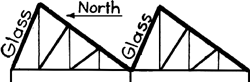
[edit] Saw-tooth roof
Saw-tooth roofs comprise a series of ridges, with one pitch much steeper than the other – similar in profile to the teeth of a saw. They allow a pitched roof to be constructed over a large span without creating a very high apex. The steeper surfaces often face north and are glazed to admit natural light into a deep plan building or factory, hence they are also known as 'north light roofs'.
They were historically used in industrial and manufacturing buildings before electric light was introduced and when daylight strategies were essential. Although these went into decline with the advent of artificial lighting, architects and designers have begun to reintroduce them because of their environmental efficiency and the fact that their shape offers good potential for solar panel installation.
[edit] Trussed rafter
Trussed rafters can be designed for very long spans, ranging from 15-45 m. They are usually fabricated from timber or steel, and are spaced at suitable centres to carry purlins. They typically have a low pitch to give acceptable rainwater run off and can give reasonable daylight spread from rooflights. While they have the advantage of reducing roof volume, the depth, and hence volume, increases with the span.
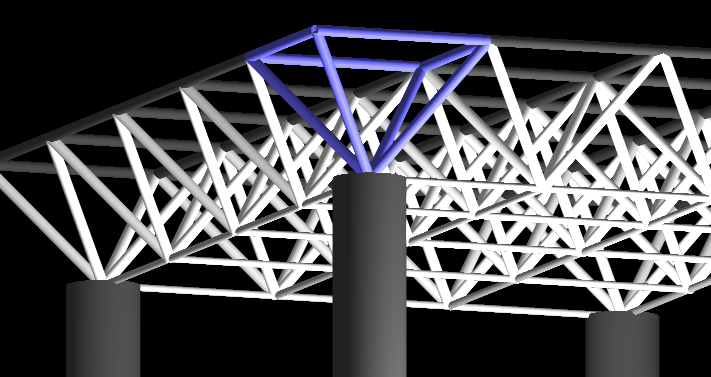
[edit] Space deck
This is a modular structural roofing system based on a simple pyramidal unit typically fabricated using tubular diagonals welded to a forming tray and apex boss. Single span designs can provide large clear spans of up to 22 m, while two-way span designs can provide up to 33 m.
The component parts can be easily transported to site and assembled into beams, the whole space deck being constructed at ground level before being hoisted into position on top of perimeter supports. Any lightweight structural decking is appropriate as a roof covering. Rooflights can also be mounted directly onto the square top space deck units.
[edit] Space frame
This is similar in concept to a space deck, but has greater design and layout flexibility. Space frames are lightweight rigid roofing systems consisting of a series of connectors that join together the chords (or struts) and bracing members. Their strength derives from the rigidity of the triangle, with the flexing loads being transmitted as tension and compression loads along the length of each chord. Most space frames are fabricated from structural steel or aluminium alloy tubes.
Buckminster Fuller pioneered the use of space frames in the 1960s for his geodesic dome structures.
[edit] Fabric structures
Architectural fabrics such as PTFE glass and PVC polyester are extremely strong in tension, and can span very large areas with the minimum of material. They can be pushed into tension by supporting structures, pulled by structural cables, or inflated by air pressure. They are generally translucent, and so provide good natural daylight.
See The history of fabric structures for more information.
[edit] Monitor roofs
A monitor roof is a flat roof with glazed portions that are raised, called 'monitors'. They allow for a good even spread of daylight from the monitor lights which is not affected by the building's orientation. They can be constructed with light long span girders that support the monitor frames, or a precast concrete portal frame.
[edit] Long span arch
Long span arches are entirely self-supporting, with no trusses, frames, support posts, or purlins. They are also known as shell roofs. They are a structural curved skin covering a given plan shape and area where the forces in the shell or membrane are compressive and in the restraining edge beams are tensile.
See Barrel vault for more information.
[edit] Suspension structures
Suspended structures are those where the main elements that support the load, such as wires, cables, chains, and so on, are subject only to extension forces. Plane (horizontal) structures use a wire fastened to supports from which are suspended elements that take the local stress. These are used mainly in bridges and roofs.
[edit] Cable stayed structures
This is a structural system derived from bridge building, where a flat roof structure is supported from above by steel cables radiating downward from masts that rise above roof level. The cables behave as simple suspension elements, while the roof structure behaves like a normal load-resisting unit, subject to moments, shears and other kinds of action effect. Even under wind uplift, due to the dead weight of the roof, it is expected that the suspending elements remain in tension.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Arches.
- Barrel vault.
- Braced frame.
- Conoid shell.
- Concrete-steel composite structures.
- Cool roofs.
- Domestic roofs.
- Dormer window.
- Failure of cast iron beams.
- Flat roof.
- Flat roof defects.
- Geodesic dome.
- Green roofs.
- Guidance for construction quality management professionals: Structural Steelwork.
- Hammerbeam roof.
- Hyperbolic paraboloid.
- Major cast metal components.
- Megastructure.
- Metal roofing.
- Pitched roof.
- Portal frame.
- Prestressed concrete.
- Shell roof.
- Structural steelwork.
- Rafter.
- Roofing defects.
- Tensile structures.
- Tension cable and rod connectors.
- The development of structural membranes.
- The history of fabric structures.
- Truss.
- Types of frame.
- Types of roof.
[edit] External references
- 'Building Construction Handbook' (6th ed.), CHUDLEY, R., GREENO, R., Butterworth-Heinemann (2007)
Featured articles and news
UK Net Zero Carbon Buildings Standard V1 published
Free-to-access technical standard to enable robust proof of a decarbonising built environment.
Prostate Cancer Awareness Month
Why talking about prostate cancer matters in construction.
The Architectural Technology podcast: Where it's AT
Catch up for free, subscribe and share with your network.
The Association of Consultant Architects recap
A reintroduction and recap of ACA President; Patrick Inglis' Autumn update.
The Home Energy Model and its wrappers
From SAP to HEM, EPC for MEES and FHS assessment wrappers.
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.