Strut
|
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
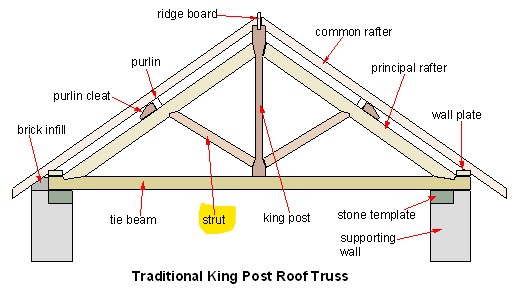
A strut is a structural component that has compression acting upon it - pushing it together. Struts are most frequently made from timber or metal.
[edit] Struts and ties
The counterpart of a strut is a tie, which is a structural element that has tension acting upon it - stretching it apart. For more information, see Ties.
Struts and ties are common components of structural elements such as trusses. The two components work together to support the weight of other parts of the structure and any imposed load. The struts provide resistance to compression and sometimes contribute to tension resistance. Ties perform the opposite function.
As a component of a moveable bridge, the strut can work in conjunction with other mechanisms to open and close the bridge.
|
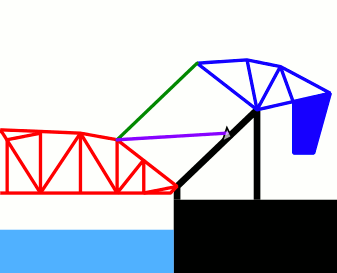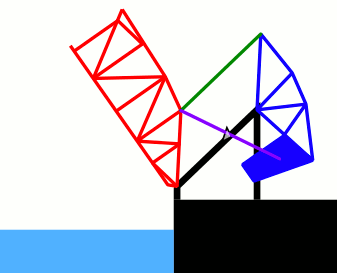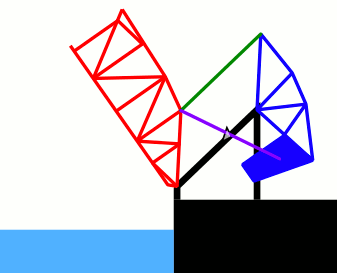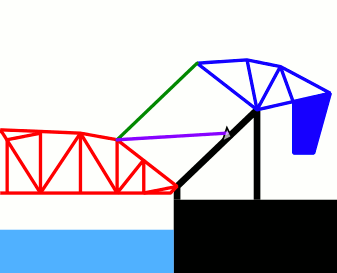
This animated GIF depicts the opening and closing of the Henry Ford bridge - a double-leaf bascule bridge built in 1924. For each leaf, the operating strut (in purple) is drawn back using a pinion gear on the fixed structure. This brings the counterweight structure (in blue) down while raising the bridge truss (in red). A parallelogram link (green) means the rotation of the counterweight is synchronised with the rotation of the truss structure. |
[edit] Strutting and strut channels
Strutting is a method of providing temporary support to the side of a trench. It is sometimes called timbering and planking. Strutting can also be used between floor joists to increase the strength of flooring systems. In this instance, it may also be referred to as blocking.
Strut channels (also referred to as channel struts) are components that support cable management and plumbing systems. They are made from steel, aluminium or plastic and can be used to connect pipes, wire, threaded rods or bolts to walls.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
Featured articles and news
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.
The 2025 draft NPPF in brief with indicative responses
Local verses National and suitable verses sustainable: Consultation open for just over one week.
Increased vigilance on VAT Domestic Reverse Charge
HMRC bearing down with increasing force on construction consultant says.
Call for greater recognition of professional standards
Chartered bodies representing more than 1.5 million individuals have written to the UK Government.
Cutting carbon, cost and risk in estate management
Lessons from Cardiff Met’s “Halve the Half” initiative.
Inspiring the next generation to fulfil an electrified future
Technical Manager at ECA on the importance of engagement between industry and education.
Repairing historic stone and slate roofs
The need for a code of practice and technical advice note.
Environmental compliance; a checklist for 2026
Legislative changes, policy shifts, phased rollouts, and compliance updates to be aware of.