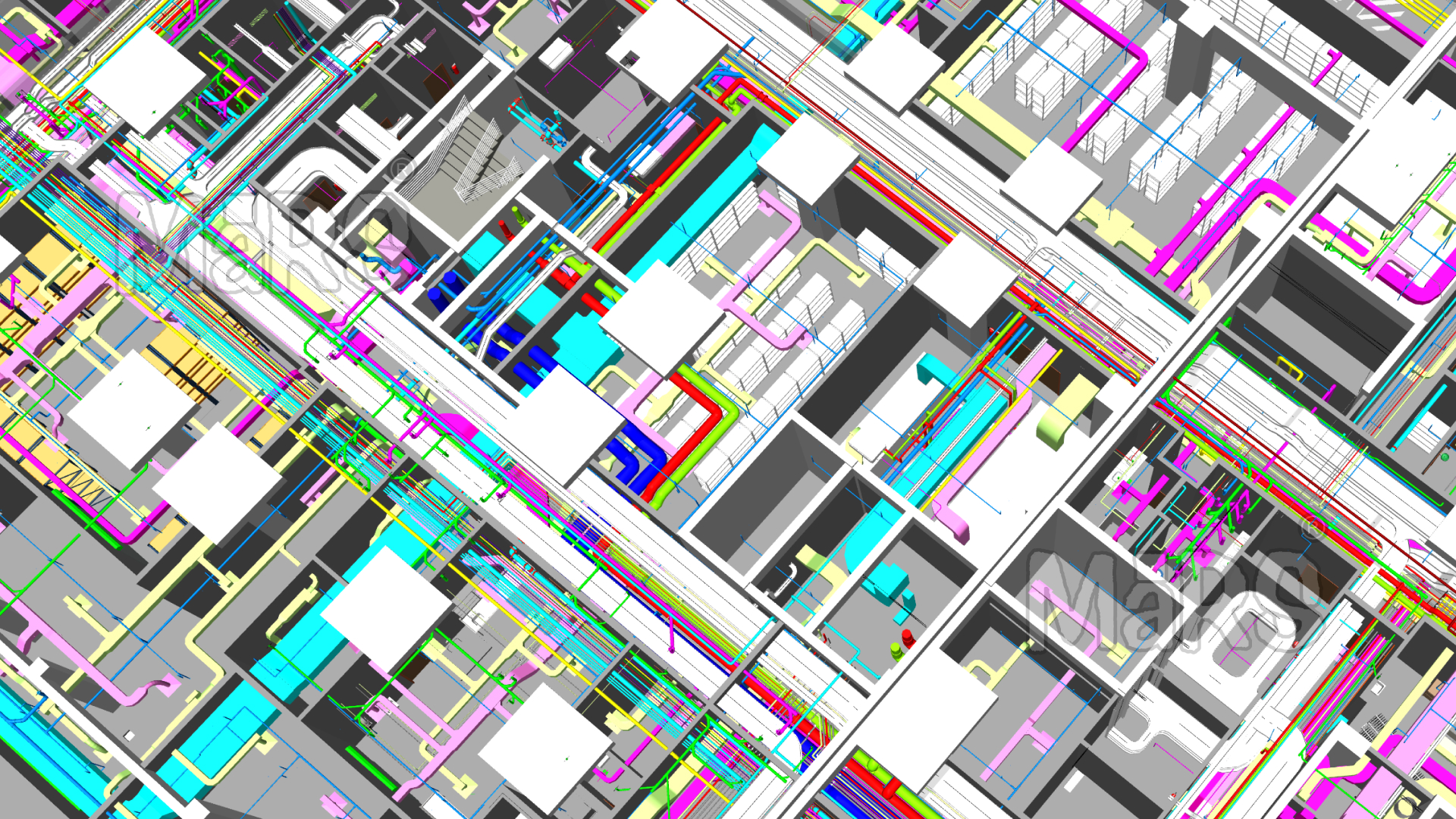
MEP 3D Modelling
[edit] Introduction of MEP 3D Modelling:
When we talk about creating buildings that are functional, comfortable, and safe, the significance of MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing) systems cannot be understated. Imagine a building without heating, air conditioning, electrical wiring, or running water pretty impossible, right? This is where MEP design comes into play, ensuring that all these systems work seamlessly together. Traditionally, the design and installation of MEP systems could be challenging, with frequent misalignments and clashes between different systems. But MEP 3D modelling is transforming this process, ensuring better accuracy and project delivery.
In this blog, we’ll dive deep into MEP 3D modelling, breaking down its core elements, benefits, and technical considerations that are essential for modern construction projects.
[edit] What is MEP 3D Modelling?
MEP 3D modelling is the process of creating a detailed digital representation of a building’s mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems using specialised BIM (Building Information Modelling) software tools like Revit MEP, AutoCAD MEP, or Navisworks. It’s essentially a virtual prototype that enables designers, engineers, and contractors to visualise and coordinate complex systems before actual construction begins. This digital twin includes parametric data, spatial coordination, and detailed fabrication elements, making it a comprehensive solution for effective MEP design and execution.
[edit] Core Components of MEP 3D Modelling:
An MEP 3D model is constructed by integrating the following systems:
- Mechanical Systems: Includes HVAC components such as air handling units (AHUs), chillers, boilers, VAV (Variable Air Volume) boxes, ductwork, and exhaust systems. These elements are connected through a series of supply, return, and exhaust ducts. The mechanical system model also accounts for CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute) calculations and duct sizing for optimal airflow distribution.
- Electrical Systems: Involves creating conduit and cable tray layouts, lighting systems, electrical equipment like transformers, switchgear, and distribution boards. Electrical modelling incorporates load calculations, voltage drop analysis, and circuiting, ensuring accurate power distribution throughout the building.
- Plumbing Systems: Covers water supply piping, sanitary waste systems, vent stacks, and storm water drainage. Key aspects include pipe routing, pipe sizing, and pressure loss calculations to maintain adequate flow rates and pressure levels in different systems.
- Fire Protection Systems: Includes sprinkler heads, piping networks, and fire suppression equipment. Accurate representation of these systems in the model ensures compliance with fire safety standards like NFPA (National Fire Protection Association) codes.
[edit] Levels of Development (LOD) in MEP 3D Modelling:
The Level of Development (LOD) is a standard that defines the complexity and amount of information contained in the MEP model. This ranges from basic geometry to a highly detailed model, depending on the project’s stage:
- LOD 100 (Conceptual Design): Minimal geometric representation with basic placement information.
- LOD 200 (Schematic Design): Includes approximate geometry, system connections, and spatial coordination.
- LOD 300 (Design Development): Detailed model with precise dimensions, component specifications, and annotations.
- LOD 400 (Fabrication Details): Contains comprehensive information required for fabrication, including detailed spool drawings, material specifications, and assembly information.
- LOD 500 (As-built Model): Represents the final constructed state of the building, incorporating all modifications and changes made during construction.
[edit] Key Advantages of MEP 3D Modelling: From Clash Detection to Constructibility
The transition from 2D design to 3D modelling has introduced several benefits, fundamentally changing the way MEP systems are designed and managed:
- Spatial Coordination and Clash Detection: The MEP 3D model integrates with architectural and structural models to identify and resolve clashes early in the design phase. By running clash detection and interference checks, software tools like Navisworks and Revit ensure there are no conflicts, such as HVAC ductwork intersecting with a structural beam or electrical conduits colliding with plumbing pipes.
- Accurate Quantity Take-off (QTO) and Scheduling: MEP 3D models provide precise quantity take-offs for materials like pipes, fittings, conduits, and ductwork, enabling accurate cost estimation and scheduling. This reduces the risk of over- or under-ordering materials and helps in creating a more efficient project schedule.
- Enhanced System Performance Analysis: MEP models can be used for simulations, such as CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics) for airflow analysis in HVAC systems or load flow analysis for electrical systems. These simulations help validate system performance and ensure compliance with design requirements.
- Fabrication and Prefabrication Benefits: LOD 400 models are used for fabrication-level details, enabling prefabrication of MEP components off-site. This reduces installation time and minimises errors during the construction phase.
- Improved Project Collaboration: Cloud-based BIM platforms like Autodesk BIM 360 enable project teams to collaborate in real-time, sharing model updates, clash reports, and design changes seamlessly. This enhances communication between teams, reducing the risk of miscommunication and ensuring that everyone is on the same page.
[edit] Software Tools for MEP 3D Modelling
Different software tools are used for MEP modelling depending on the project’s complexity, requirements, and desired outputs:
- Revit MEP: A BIM software widely used for designing complex MEP systems, offering tools for parametric modelling, clash detection, and automatic documentation. It supports integration with energy analysis tools for performance evaluation.
- AutoCAD MEP: Ideal for creating 2D and 3D MEP designs with precise placement and annotation capabilities. It’s often used for schematic designs and early-stage layouts.
- Navisworks Manage: Typically used for model coordination, clash detection, and project review. It combines MEP models with architectural and structural models to provide a comprehensive view of the project, making it easier to identify and resolve conflicts.
[edit] Standardisation and Compliance
MEP systems must comply with specific industry standards to ensure safety, reliability, and energy efficiency. Some key standards include:
- ASHRAE (American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air-Conditioning Engineers): Regulates HVAC system design and energy efficiency.
- NEC (National Electrical Code): Governs electrical system design, installation, and safety standards.
- IPC (International Plumbing Code): Provides guidelines for plumbing system design, installation, and water conservation.
Adherence to these standards is crucial for meeting regulatory requirements and ensuring the safety and efficiency of the MEP systems.
[edit] Collaboration and Coordination: The Backbone of Successful MEP Modelling
MEP modelling isn’t just about creating detailed designs; it’s also about effective collaboration between various teams such as architects, structural engineers, MEP designers, and contractors. Tools like Revit and BIM 360 facilitate interdisciplinary coordination, allowing all stakeholders to review, comment, and make updates to the model in real-time. This collaborative approach minimises discrepancies, enhances constructibility, and ensures that the project stays on track.
[edit] Future Trends
MEP 3D modelling is no longer just an industry trend. it’s a standard practice that’s pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in building design and construction. With its ability to enhance project coordination, optimise system performance, and ensure constructibility, MEP 3D modelling is revolutionising how buildings are designed and built. Investing in the right software tools, adopting standardised workflows, and fostering collaboration across disciplines are key to leveraging this technology to its fullest potential.
--Snehal Dodha 09:44, 27 Sep 2024 (BST)
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
BIM Directory
[edit] Building Information Modelling (BIM)
[edit] Information Requirements
Employer's Information Requirements (EIR)
Organisational Information Requirements (OIR)
Asset Information Requirements (AIR)
[edit] Information Models
Project Information Model (PIM)
[edit] Collaborative Practices
Industry Foundation Classes (IFC)