Visualisation in the construction industry
|

|
|

|
Visualisation refers to the physical or mental representation of an object, situation, or information as an image.
The construction industry relies heavily on visualisation to investigate and communicate complex situations and objects, in particular relating to the design and construction buildings and other built assets such as bridges, tunnels and so on. It is widely used as part of the design process, and as a way of describing construction works and components to contractors, subcontractors and suppliers. It is also used to communicate proposed solutions to clients, local authorities and other stakeholders.
This means that visualisations can range from very simple block diagrams at the early stages of a project, to highly-technical representations of construction information or visually realistic representations that can be useful for communicating to non-expert stakeholders.
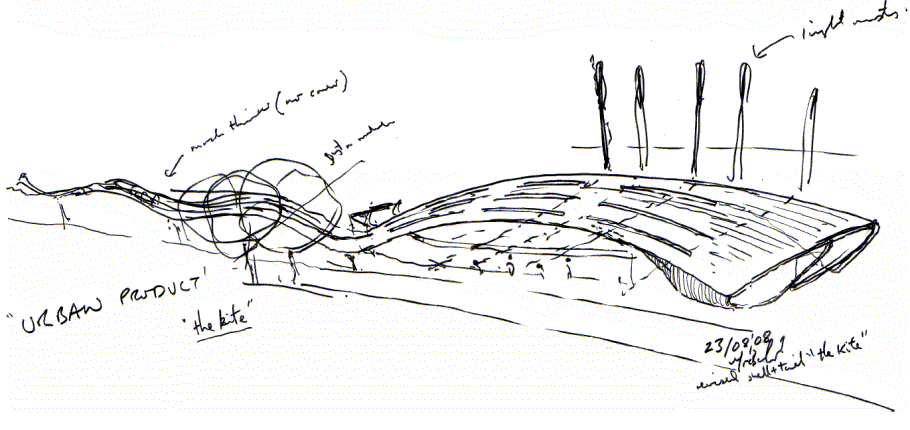
Traditionally visualisations were prepared by hand as sketches, diagrams, technical drawings and 3D renderings. For more information see: Manual drafting techniques and Types of drawings.
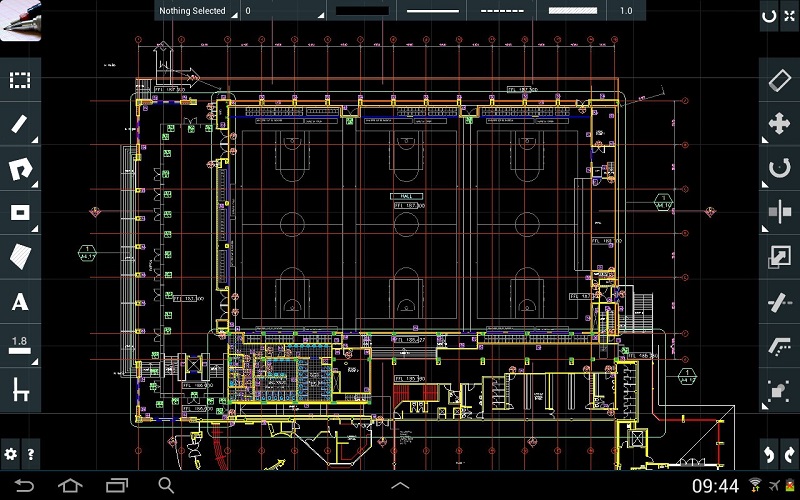
The development of computers resulted in the emergence of computer aided design (CAD) techniques that allowed two-dimensional visualisations to be create, changed and duplicated more easily. However, there was some criticism that the expression and artistry that was possible with hand drawn visualisation was lost. For more information see: Computer aided design.
More recently Building Information Modelling has allowed 3D modelling of design proposals, constructed parametrically and including 4D (time), 5D (cost) and 6D (facilities management) information. For more information see: Building Information Modelling.
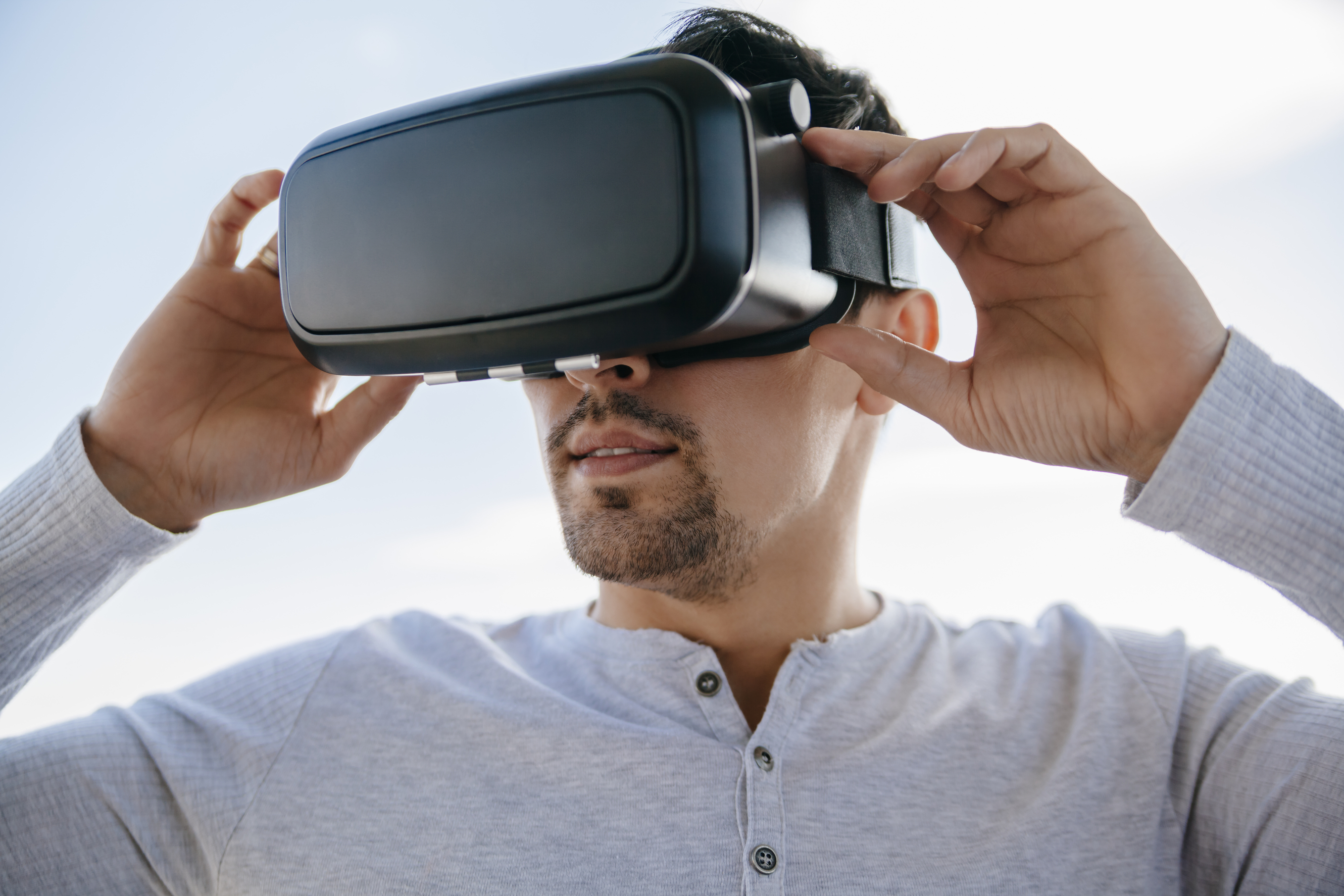
Specialist software has also been developed that allows more realistic computer generated imagery (CGI) to be created, including perspective views, daylight, shadows, complex textures and so on. It is possible to make 3D fly-throughs of proposals, and real time models that allow viewers to experience proposals as if they were completed. This has been supplemented with virtual reality and augmented reality techniques. For more information see: Computer generated imagery, Virtual reality and Augmented reality.
Three dimensional physical models are also commonly used to communicated proposals. Traditionally these would have to be created by hand, but increasingly, 3D printing techniques are able to automate some or all of the process. For more information see: Models.
Other techniques include:
- Immersive hybrid reality.
- Mixed reality.
- Photography.
- Samples and mock-ups.
- Mood boards.
- Digital twins.
- Virtual construction models.
Visualisations may contain standard notations and symbols that offer simplified representations of common situations and components. For more information see: Notation and units on drawings and Symbols on architectural drawings.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Assisted reality aR.
- Augmented reality.
- Building Information Modelling.
- Computer aided design.
- Computer generated imagery.
- Models.
- Manual drafting techniques.
- Notation and units on drawings.
- Shaping Space - Architectural Models Revealed.
- Symbols on architectural drawings.
- Types of drawing.
- Virtual reality.
- Immersive Hybrid Reality IHR.
- Mixed reality.
Featured articles and news
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help the homebuilding sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.
























