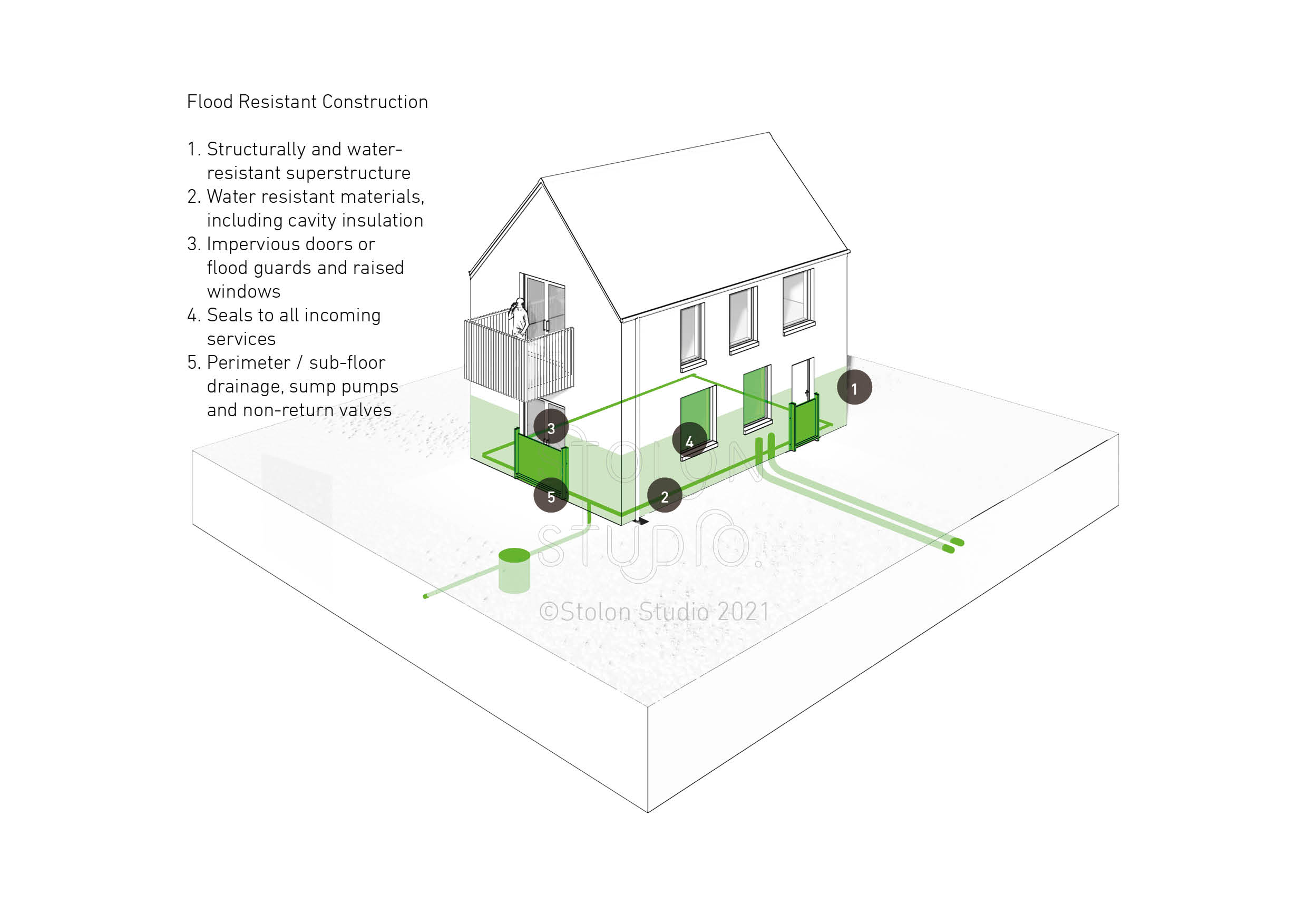
Flood Resistant Construction
A flood resistant building is one that is designed to resist flood water ingress. That means that the building is designed to prevent flood water from entering through the walls, floor and any apertures. The deeper the flood water and the higher the velocity, the more difficult it is to keep water out. As water rises on the outside of the building it creates a force on the ground floor and outside walls including any windows and doors at that level.
Flood resistant buildings are typically constructed using concrete or steel and concrete but may also be made with masonry provided there is an impervious layer, such as water-resistant render or asphalt. Typically, frame buildings are more difficult to make flood resistant without a concrete or masonry layer due to the number of potential pathways for water around junctions. Masonry is generally permeable, as is concrete unless to a certain specification. Therefore, water can seep through walls and floors unless designed properly. Cavity walls may need to be filled with water resistant insulation below the flood level to prevent the passage of water and to prevent contamination within the cavity.
The ground floor is a potential pathway for floodwater to enter, particularly if flood water remains present outside for a period of time. This is because the water will seek to reach an equilibrium inside and outside the building. If the pressure from the rising water is substantial it will apply an upward force to the floor potentially causing structural damage, water penetration or the floor to rise, particularly if light.
Concrete floors may need to be reinforced to prevent the risk of fracture from the water pressure. Beam and block floors are likely to require additional waterproofing to prevent water ingress. The membrane is also likely to need to be weighed down to prevent it being forced up by the water.
Where flood depths can be greater than a few hundred millimetres (in the order of 0.5m) it may become expensive to make a building resistant to floodwater. In this case it may be more cost effective to make a building resilient to flooding. This may also be more appropriate for existing buildings.
Because most doors and windows would not prevent the ingress of water, specialist flood resistant doors and windows are required, or flood barriers located infront of ordinary doors and windows.
Special care and attention to the detailing of jambs and thresholds is required to prevent water ingress and to ensure the integrity is maintained under the pressure of water.
Where floodwater is likely to remain for several days, such as areas with relatively flat topography, it may be better to consider flood resilient construction, to reduce the reliance on the structural and waterproofing measures.
The key components of flood resistant construction are:
- Structurally and water-resistant superstructure
- Water resistant materials, including cavity insulation
- Impervious doors or flood guards and raised windows
- Seals to all incoming services
- Perimeter / sub-floor drainage, sump pumps and non-return valves
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- Amphibious construction.
- BRE flood resilient repair project.
- BREEAM Flood risk management.
- Building flood resilience.
- Changing attitudes to property flood resilience in the UK.
- Elevated Construction.
- Fighting flooding in the 21st century.
- Flood defences.
- Flood resilient house.
- Pitt Review Lessons learned from the 2007 floods.
- Planning for floods.
- Property flood resilience.
- Pumps and dewatering equipment.
- Temporary flood defences.
- Ten years on - Lessons from the Flood on building resilience.
- Thames barrier.
- Workplace design – flood protection.
--Robert Barker, Stolon 23:48, 02 Nov 2021 (BST)
Featured articles and news
UK Net Zero Carbon Buildings Standard V1 published
Free-to-access technical standard to enable robust proof of a decarbonising built environment.
Prostate Cancer Awareness Month
Why talking about prostate cancer matters in construction.
The Architectural Technology podcast: Where it's AT
Catch up for free, subscribe and share with your network.
The Association of Consultant Architects recap
A reintroduction and recap of ACA President; Patrick Inglis' Autumn update.
The Home Energy Model and its wrappers
From SAP to HEM, EPC for MEES and FHS assessment wrappers.
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.