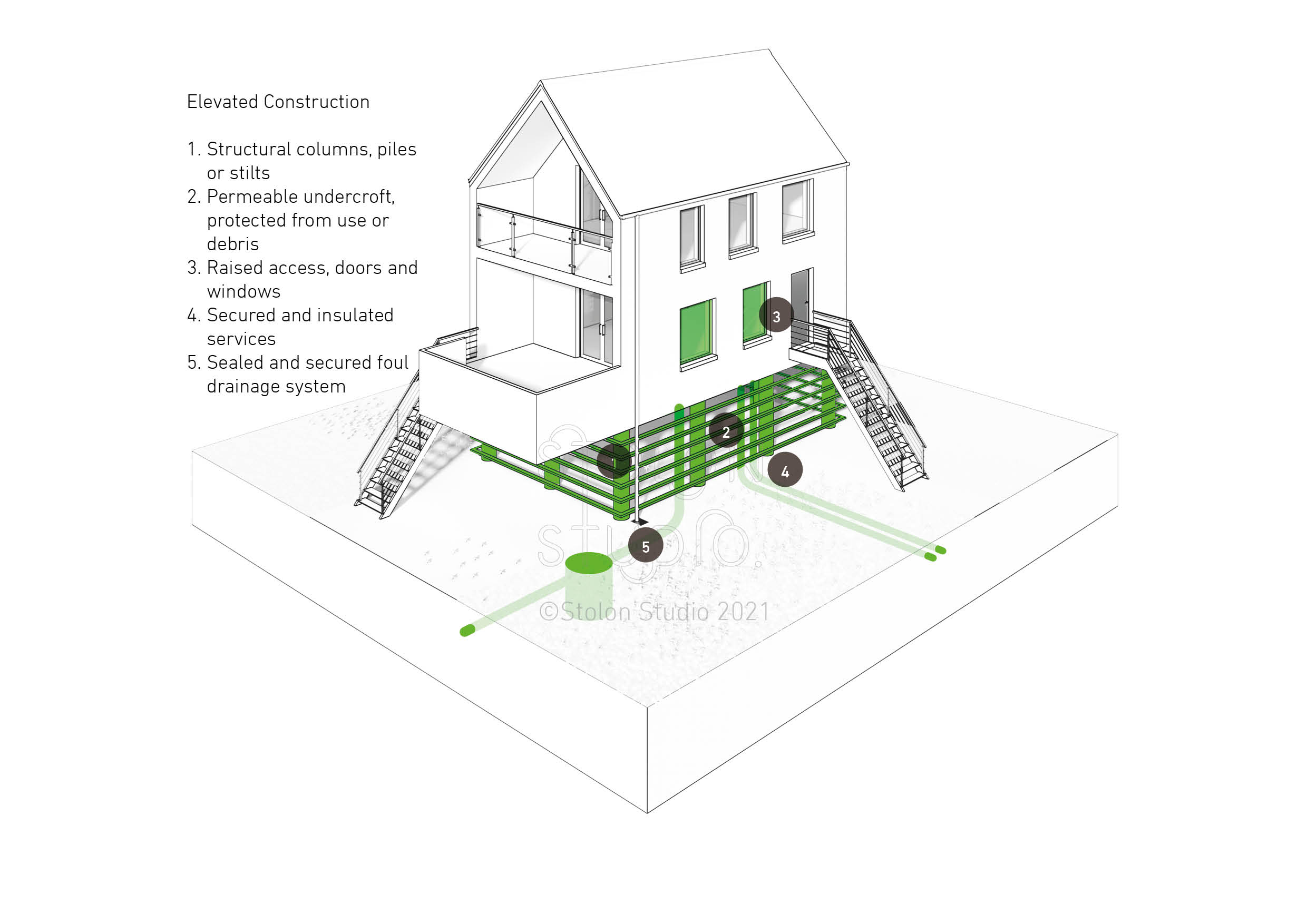
Elevated Construction
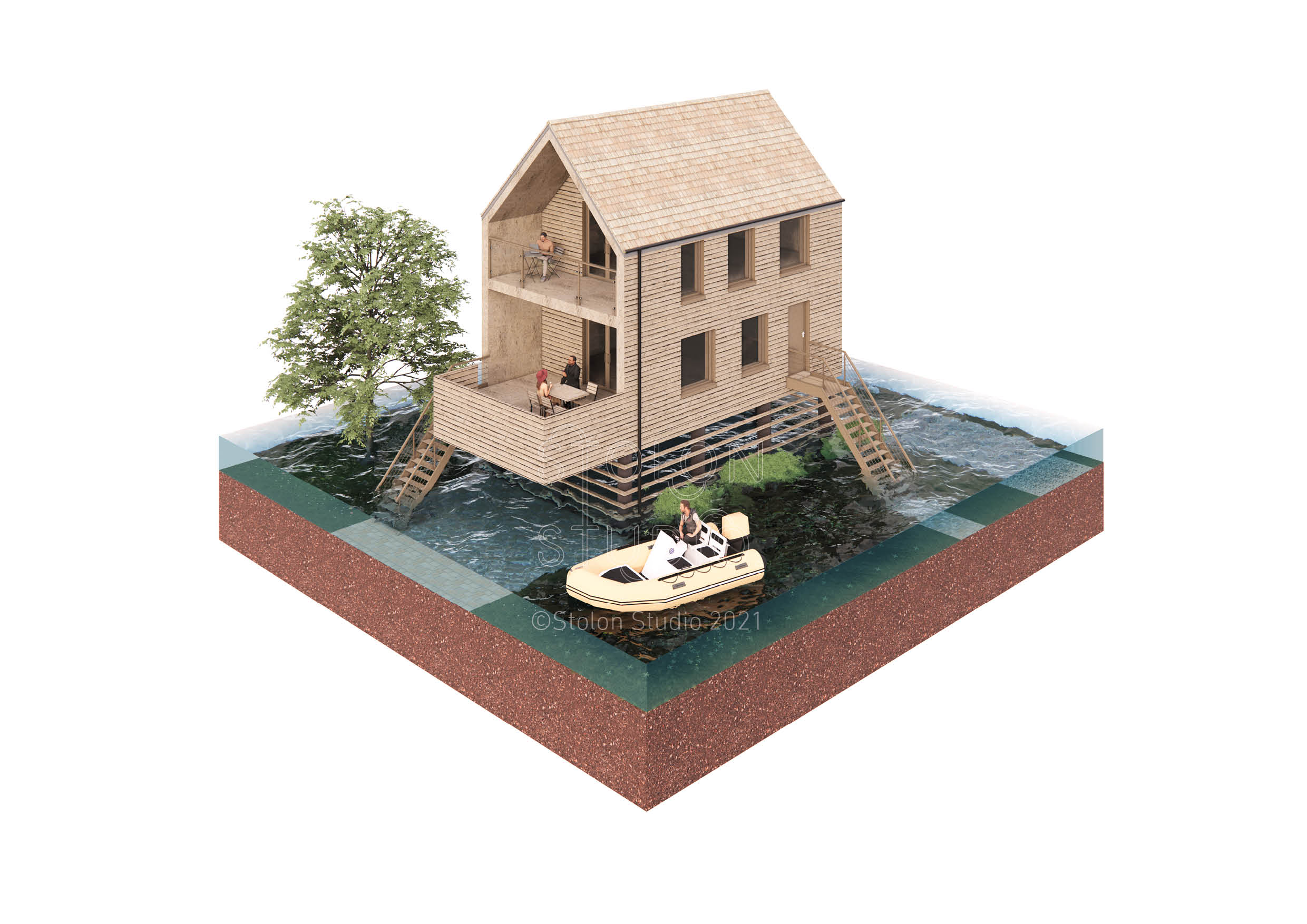
An elevated building, with regards to flooding, is a building that is raised on columns (or stilts) so that the floor level is higher than the potential level of the flood water. This is a simple and logical way to protect a property from flooding but it is reliant on accurate predictions of flood levels.
There are many examples of this type of construction across the world, ranging from traditional timber or bamboo houses to modern steel and concrete structures. Some structures may be raised only a few centimetres above the ground, while others are raised meters in the air, such as hurricane homes in the south east of the USA or lake side houses in Tonle Sap, Cambodia. A more extreme example of a structure elevated above water ingress is an oil rig.
Elevated buildings maybe constructed from many different materials, such as brick, concrete, steel and wood. The actual construction materials used may be influenced by the local vernacular or may be determined by the flood hazard. Deep and/or fast flowing water can be a hazard to buildings. In some cases the structure required to resist the hydrostatic pressure can be considerable.
One of the main issues with an elevated building is access and the potential disconnection with the ground plane. Whilst the building may be protected from flooding, if it is elevated above the ground plane, it may not be able to provide easy access for people, particularly those with mobility difficulties. If it is elevated more than half a storey above ground, the access is more challenging, the engagement with the surrounding environment may be diminished, and natural surveillance becomes less effective. This may result in increased antisocial behaviour and less community interaction or reduced social cohesion.
One should not design to reduce flood-risk yet compromise other important aspects of design. A good design solution to flooding should not result in detrimental social effects for all the rest of the time the building is in use.
In cases where flood depths may be more extreme, it may be preferential to raise the primary floor of the building a storey above the ground and use the ground level for other uses such as parking, bin/bike storage or for less vulnerable uses such as commercial or residential amenity spaces, such as you might find in choosing schemes.
Key components of elevated construction include:
- Structural columns, piles or stilts
- Permeable undercroft, protected from use or debris
- Raised apertures, doors and windows
- Raised, secured and insulated services
- Sealed and secured foul drainage system
--Robert Barker, Stolon 02:14, 30 Jan 2021 (BST)
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- Amphibious construction.
- BRE flood resilient repair project.
- BREEAM Flood risk management.
- Building flood resilience.
- Changing attitudes to property flood resilience in the UK.
- Fighting flooding in the 21st century.
- Flood defences.
- Flood resilient construction.
- Flood resilient house.
- Pitt Review Lessons learned from the 2007 floods.
- Planning for floods.
- Property flood resilience.
- Pumps and dewatering equipment.
- Temporary flood defences.
- Ten years on - Lessons from the Flood on building resilience.
- Thames barrier.
- Workplace design – flood protection.
Featured articles and news
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.
The 2025 draft NPPF in brief with indicative responses
Local verses National and suitable verses sustainable: Consultation open for just over one week.