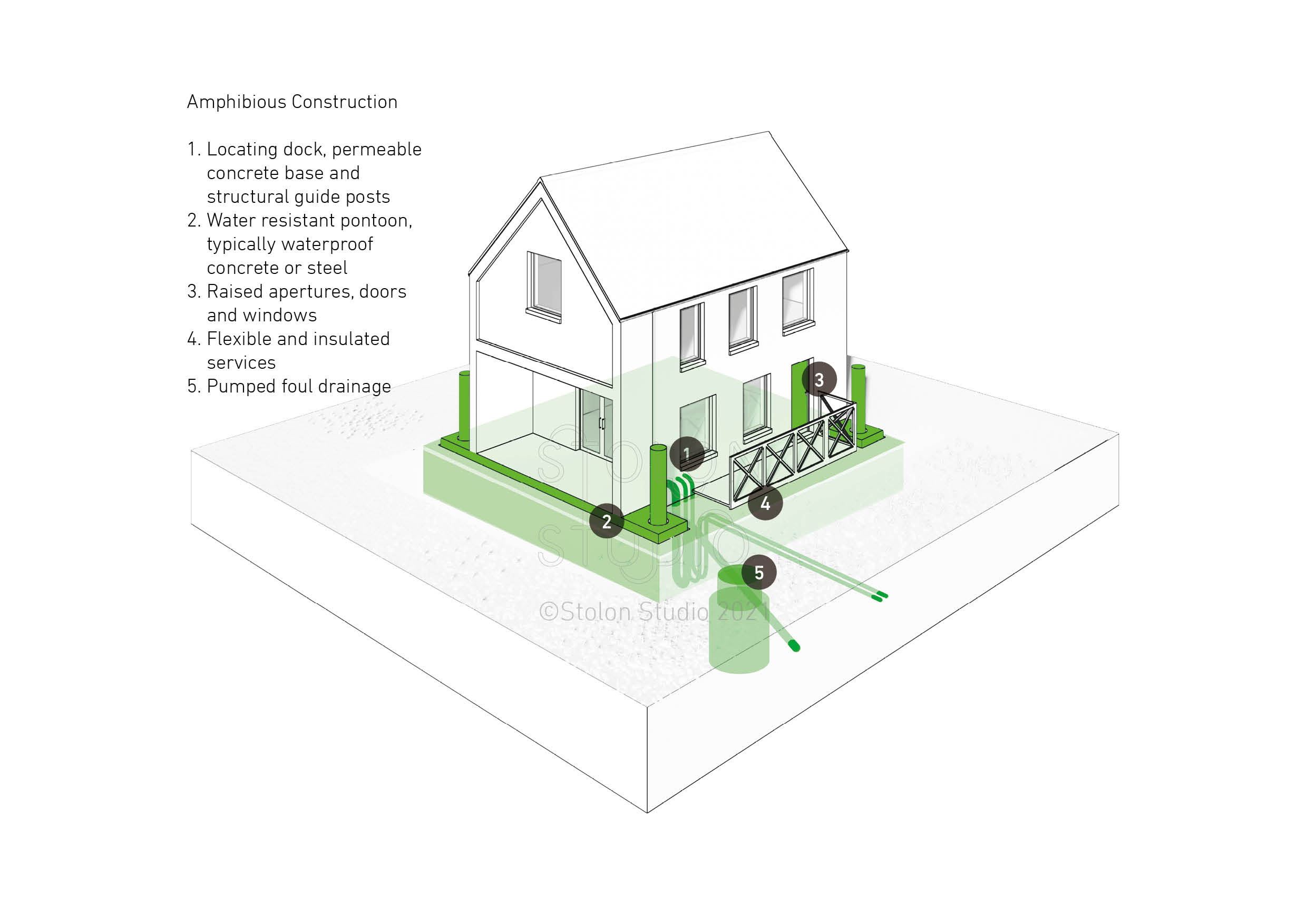
Amphibious Construction
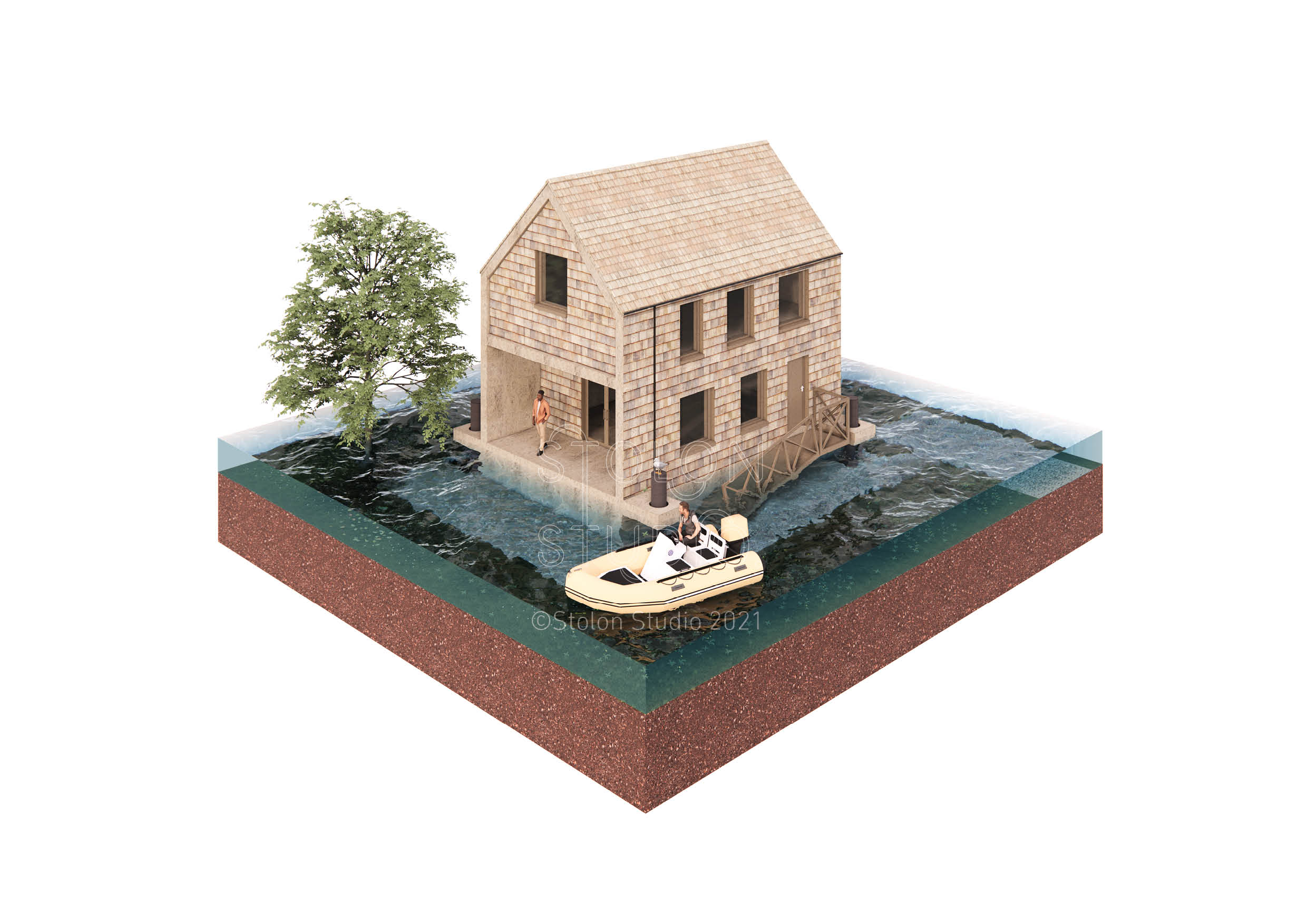
An amphibious building, or can-float building, is one that is designed to float in the event of a flood, but to rest on solid foundations at other times. This unusual hybrid building typology has an express purpose to protect the property from flooding by floating when water levels rise.
Amphibious buildings are typically designed as to be conventional fixed buildings but constructed with technology also used in floating buildings. They are not designed to float continuously, instead, they float when flood levels reach a certain level, hence the alternative name - can-float.
To make any object float it requires buoyancy. As buildings are heavy, water levels need to be sufficient to provide the buoyancy to enable them to float.
Unlike a floating home which requires a permanent deep body of water, an amphibious house only needs to float when water levels rise, and reach the sufficient depth to provide buoyancy, i.e. during a flood. This means that an amphibious building may be bigger and heavier than a floating one, which may be limited in size by the depth of water.
Most amphibious buildings use a concrete pontoon base, rather like the hull of a boat, where the height of the pontoon is determined based on the level of water required to make the structure buoyant. From experience a single storey height concrete pontoon can support a light weight 2 storey building above. This has the added advantage that the space within the pontoon can be used as accommodation rather like a traditional basement.
Steel pontoons, which are lighter than concrete pontoons, may support larger buildings than those using similar sized concrete pontoons. However, in addition to buoyancy the issue of balance must be considered. A boat is made stable by its keel. A floating structure is reliant on maintaining a low centre of gravity. The heavier the base the lower the centre of gravity. Therefore, a building supported by a steel, plastic or timber pontoon may be less stable than a concrete one.
A further consideration is the tethering. Whilst a floating structure can rise and fall, held roughly in place by a mooring post, like a boat; this may not be suitable for a building where it may need to land in exactly the same place that it floated from. In this situation, complicated control measures may be required to restrain the structure.
Whilst there are other issues, the most challenging is servicing. Like a moored boat: electricity, water, waste, and telecom connections need to be flexible. This in itself is not complicated but the distance of travel during a flood can be substantial, so the location of pipes needs to be carefully considered. From experience the waste water discharge is simplest when pumped, thereby facilitating a useable connection at all times regardless of flood levels.
Key components of amphibious construction include:
- Locating dock, permeable concrete base and structural guide posts
- Water resistant pontoon construction, such as waterproof concrete or steel
- Raised apertures, doors and windows
- Flexible and insulated services
- Pumped foul drainage
For further information about this type of construction please refer to the case study in the RIBA book ‘aquatecture’.
--Robert Barker, Stolon 01:41, 30 Jan 2021 (BST)
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- BRE flood resilient repair project.
- BREEAM Flood risk management.
- Building flood resilience.
- Changing attitudes to property flood resilience in the UK.
- Elevated Construction.
- Fighting flooding in the 21st century.
- Flood defences.
- Flood resilient construction.
- Flood resilient house.
- Pitt Review Lessons learned from the 2007 floods.
- Planning for floods.
- Pontoon bridge.
- Property flood resilience.
- Pumps and dewatering equipment.
- Temporary flood defences.
- Ten years on - Lessons from the Flood on building resilience.
- Thames barrier.
Featured articles and news
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help the homebuilding sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.