Waterproofing
Waterproofing is a process that ensures a structure or object is able to keep out 100% of any water that comes into contact with it. In construction, waterproofing can increase the life of common materials like concrete, iron, paint and more. Although it is not common to refer to a building as being 'waterproof' (although it would not be wrong and would be understood by most), it is more common to use the term ‘watertight’ or 'weatherproof'.
A new building will reach a stage in construction where it is made watertight to prevent water from penetrating into internal areas. Alternatively, an existing building may undergo remedial works to make its basement watertight, to prevent penetrating damp or rising damp and so on. For more information see: Damp proofing.
However, the term waterproof can be applied to particular elements of the building fabric that are designed to keep out water. For example, although high-grade concrete can be highly impervious to moisture this is difficult to achieve in practice due to a number of construction reasons. But when PVC or copper water bars are incorporated at joints (the weak points) and a waterproofing agent is added to the mix, a waterproof construction can be achieved.
Similarly, a synthetic roofing membrane may be termed waterproof not only because water is unable to penetrate the molecular structure of the material but also because it can form a continuous, seamless roof surface that can be waterproof when properly installed.
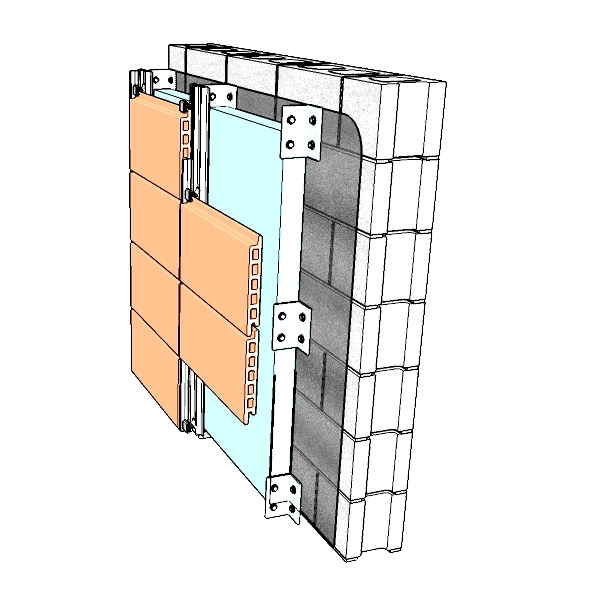
In contrast, a slate roof may be termed watertight as it will generally do an excellent job of keeping water out. However, in severe weather conditions (such as wind driven rain) it may not be waterproof since water ingress may occur through joints. Cladding systems such as rainscreen cladding may allow water to penetrate through a first layer of defence, but this is then drained away before reaching the interior.
Cementitious waterproofing is a method of waterproofing used in wet areas like toilets and bathrooms. This is a semi-flexible or rigid type of waterproofing, and material should not be exposed to weathering or sunlight.
More flexible than cementitious waterproofing, liquid membrane waterproofing is a thin coating of primer and two top coats.The liquid cures into a rubbery coating on surfaces and can provide high elongation. The durability of the coating depends on what type of polymer is used.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
Featured articles and news
UK Net Zero Carbon Buildings Standard V1 published
Free-to-access technical standard to enable robust proof of a decarbonising built environment.
Prostate Cancer Awareness Month
Why talking about prostate cancer matters in construction.
The Architectural Technology podcast: Where it's AT
Catch up for free, subscribe and share with your network.
The Association of Consultant Architects recap
A reintroduction and recap of ACA President; Patrick Inglis' Autumn update.
The Home Energy Model and its wrappers
From SAP to HEM, EPC for MEES and FHS assessment wrappers.
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.





















Comments
Waterproofing is the process of making a surface or structure resistant to the penetration of water. It is commonly applied to various areas in buildings or structures to prevent water ingress, leakage, and potential damage. Waterproofing is essential in areas that are exposed to moisture, such as basements, roofs, bathrooms, balconies, and foundations.
There are different methods and materials used for waterproofing, depending on the specific requirements and the location being treated. Here are some common waterproofing techniques:
Thanks for your comment, maybe you want to create a new article covering your points above, perhaps called "common waterproffing techniques", We could then cross link it to the above. Best regards. Editor