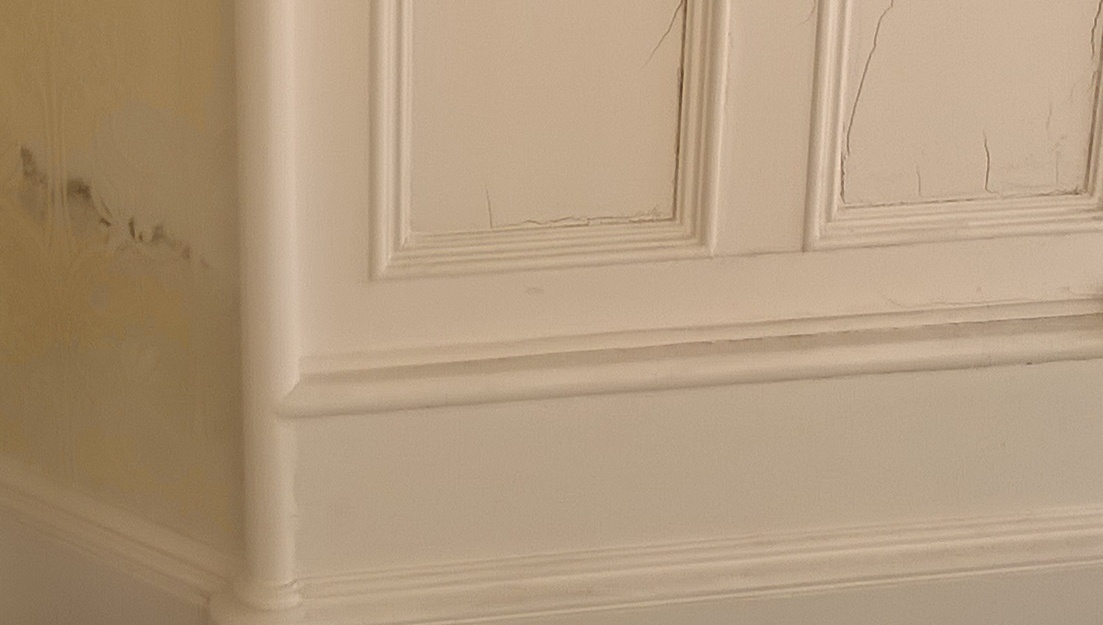
Rising damp
Excess moisture is a common problem in buildings, and may be apparent from; damp patches, mould growth, mildew, salts, staining, ‘tide marks', blistering paint, bulging plaster, and so on.
The most common causes of persistent damp in buildings are:
- Condensation (surface or interstitial).
- Penetrating damp.
- Rising damp.
Rising damp is said to be caused by capillary action drawing moisture up through porous elements of a building’s fabric.
Rising damp might be apparent from:
- Condensation or damp patches (typically up to 1 m above the floor).
- Corrosion of metal elements such as beading.
- Damp odours.
- Timber decay, such as skirting boards.
- Damage to surface finishes.
- Tide marks and staining (typically up to 1 m above the floor).
- The presence of white salts.
- Health problems.
It should be noted that these problems are common to other sorts of damp, such as; cold bridges, lateral penetrating damp, surface condensation and interstitial condensation. It is claimed capillary action can only cause damp to rise approximately a meter above the source of the damp (depending on the nature of the materials, the presence of salts and the rate of evaporation), and so problems above this height probably have a different cause.
Dampness can be measured with electrical resistance meters, either on the surface, or within the building fabric itself. Generally, if the meter reading indicates that the fabric is dry, then it is dry. However, electrical resistance meters were developed for use in timber, and if the reading indicates the fabric is wet, this does not necessarily mean that it is wet, as the presence of other substances such as soluble salts will give a similar reading, and in older walls, salts may be present even where damp is not.
Carbide meters are likely to give a more accurate measure of moisture content, and this can be further enhanced by testing samples drilled from the building fabric and tested for hygroscopic moisture content. This may require appointing a specialist.
Further information about testing techniques, the cause of dampness and remedies is available from BRE Digest 245, Rising damp in walls - diagnosis and treatment.
Rising damp has been attributed to faults in, or the absence of, a damp proof course (DPC). This can be exacerbated by:
- The moisture content of the building fabric itself.
- Raised ground water levels.
- Raised ground levels around a building.
- Leaks to pipework or guttering.
- Flooding.
- The presence of salts in the building fabric.
- Crystallisation of salts on surfaces resulting in reduced evaporation.
- Cool internal temperatures or internal humidity reducing the rate of evaporation.
The height of rising damp depends on:
- Temperature gradients in walls - the coldest area typically being near ground level.
- The rate of evaporation from the wall.
- The porosity of the wall.
- The salt content of the wall and soil.
- Heating in the building.
If there is a specific source of damp, this should be corrected before treating rising damp, for example, fixing leaking pipes, altering ground levels, installing drainage, and so on.
Treatment of rising damp involves creating a moisture impermeable layer within the building fabric, either by the insertion of a damp proof course, or by injection of water-repellent chemicals. Treatment generally also involves remedial work to any corroded or decayed elements of the building fabric, as well as hacking off and replacing existing plaster to a height of 1 m. This can be disruptive as it involves removing skirting, sockets, and so on.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Assessing moisture in porous building materials.
- Capillary action.
- Carbide meter.
- Chemical injected DPC.
- Cold bridge.
- Condensation.
- Damp.
- Damp-proof course.
- Damp proof membrane.
- Damp proofing.
- Dehumidification.
- Dew point.
- Diagnosing the causes of dampness (GR 5 revised).
- Does damp proofing work?
- Efflorescence.
- Electrical resistance meters.
- Flashing.
- Humidity.
- Interstitial condensation.
- Mould growth.
- Penetrating damp.
- Psychometric chart.
- Rising damp in walls - diagnosis and treatment (DG 245).
- Sleeper wall.
- Sling psychrometer.
- Spalling.
- Tanking.
- Tempering heating.
- Treating brickwork with sealant or water repellent.
- Types of damp-proof courses.
- Understanding dampness.
[edit] External references
Featured articles and news
CIOB Apprentice of the Year 2025/26
Construction apprentice from Lincoln Mia Owen wins this years title.
Insulation solutions with less waste for a circular economy
Rob Firman, Technical and Specification Manager, Polyfoam XPS explains.
Recycled waste plastic in construction
Hierarchy, prevention to disposal, plastic types and approaches.
UK Net Zero Carbon Buildings Standard V1 published
Free-to-access technical standard to enable robust proof of a decarbonising built environment.
Prostate Cancer Awareness Month
Why talking about prostate cancer matters in construction.
The Architectural Technology podcast: Where it's AT
Catch up for free, subscribe and share with your network.
The Association of Consultant Architects recap
A reintroduction and recap of ACA President; Patrick Inglis' Autumn update.
The Home Energy Model and its wrappers
From SAP to HEM, EPC for MEES and FHS assessment wrappers.
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.