Capillary action
|
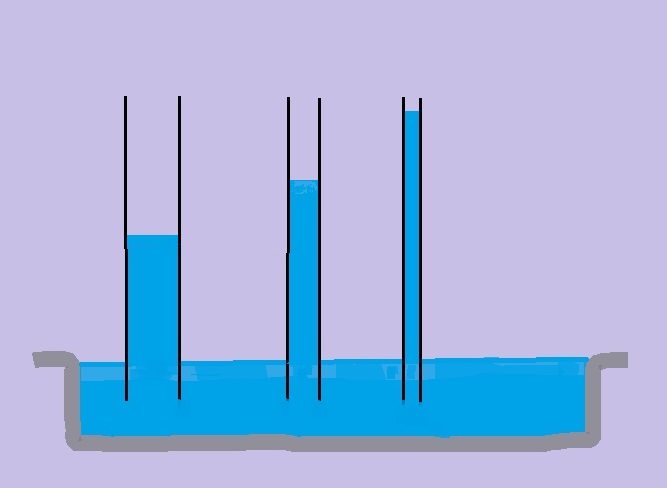
| Capillary action causes the water in the thinnest tube to rise to a higher level than in the other tubes |
[edit] Introduction
Capillary action is a phenomenon associated with surface tension, whereby liquids can travel – horizontally or vertically (against the force of gravity) in small spaces within materials. It is sometimes referred to as capillary attraction, capillarity or wicking.
The movement is due to the surface tension that results when liquid or moisture is contained within very fine spaces or tubes (capillaries). Essentially, the liquid is attracted to the sides of the container; the smaller the space, the greater the attraction. Examples of capillarity include the action observed when a paper towel or blotting paper absorb water, and the way oil travels up a wick in oil lamps.
[edit] Rising damp
Rising damp in concrete and masonry is also the result of capillary action. When building materials such as most brick types, some stones, concrete blocks and plaster come into contact with moisture, the water adheres to the pores of the material’s capillaries. If the adhesive force between the water molecules and the material is greater than the cohesive force existing between the water molecules themselves, the water rises up the tube through capillary action.
Typically, damp can rise up to around 1m above its source. It is usually prevented from doing so by the installation of a damp-proof course (DPC), typically a polymerised rubber material such as bitumen polymer. Installed as the brickwork goes up and bedded both sides with mortar, the bond between DPC, mortar and walling material creates a barrier to moisture rising through capillary action.
Capillary action is also seen in many plants and trees.
Leonardo da Vinci is regarded as being the first person to observe and record capillary action.
Technical paper 35: Moisture measurement in the historic environment, published by Historic Environment Scotland in 2021, defines capillarity as: ‘The tendency of a liquid in an absorbent material to move as a result of surface tension.’ It suggest that capillary rise is: ‘...controlled by capillarity - the rise of a liquid in an absorbent material above the level that would be influenced solely by atmospheric pressure.’
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Blockwork.
- Building damp-free cavity walls.
- Building science.
- Capillary active material.
- Capillary break.
- Chemical injected DPC.
- Damp.
- Damp proof membrane.
- Defects in brickwork
- Defects in stonework.
- Penetrating damp.
- Rising damp.
- Rising damp in walls - diagnosis and treatment (DG 245).
- Tempering heating.
- Vapour barrier.
Featured articles and news
UK Net Zero Carbon Buildings Standard V1 published
Free-to-access technical standard to enable robust proof of a decarbonising built environment.
Prostate Cancer Awareness Month
Why talking about prostate cancer matters in construction.
The Architectural Technology podcast: Where it's AT
Catch up for free, subscribe and share with your network.
The Association of Consultant Architects recap
A reintroduction and recap of ACA President; Patrick Inglis' Autumn update.
The Home Energy Model and its wrappers
From SAP to HEM, EPC for MEES and FHS assessment wrappers.
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.




















