What are The Important Features of Diamond Drilling?
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
Diamond Drilling is an innovative technique in many situations, demanding precise holes for different purposes. The introduction of diamond drilling has made it easier to create holes and openings in the hardest surfaces, including concrete, asphalt, tile, metal, stone, and glass.
From extracting oil and gas and mining industry to creating large openings for ducts, creating holes for placing or anchoring bolts, and concrete analysis- Diamond Drilling in London is the optimal method to create holes of almost unlimited depth. In addition, Diamond is the hardest material on the Earth, making Diamond Drilling in Kent a world-popular drilling technique.
The market size of diamond core drilling in the UK is expected to reach US$ 110.5 million by 2033. The application of diamond core drilling equipment in the mining industry is the primary reason to drive market growth over the coming years.
This article will inform you everything about Diamond Drilling- what it is, how it works, the latest technological innovations, and essential features.
[edit] What Do You Mean by Diamond Drilling?
Diamond drilling is a unique technique to create holes and openings in different hard surfaces. Diamond Drilling uses a rotary drilling non-percussive method of drilling, and the drilling system often comprises 110v powered motors, but can also use 415v motors and air or hydraulic driven systems.
This specific drilling technique uses drill bits that are made of diamonds. These drill bits are designed to penetrate the strongest surfaces and create holes. They cut through reinforced concrete, stone, glass, tile, asphalt, etc.
The non-percussive cutting processes of diamond drilling help maintain the structural integrity at a low sound frequency while creating a clean and accurate hole. The holes created by diamond drilling usually range from 10mm to 15mm in diameter, and diamond drill bits can drill virtually any depth.
[edit] How Diamond Drilling Works?
Knowing the components of a Diamond Drilling system can help better understand how diamond drilling is carried out. These components include the mounted rig, diamond bit, and the electric or hydraulic-powered drill.
The rotary drill is used to power the diamond drilling system secured to the surface being cut while being mounted on a rig. Then it is fitted with an appropriate-sized diamond drill bit.
Talking about the diamond drill bit is a cylindrical tool featuring an open centre section. The diamond bit comprises a steel tube and diamond segments welded to the cutting face that is secured to the drilled surface. During the Diamond Drilling in London, the diamond drill bit rotates with gentle pressure to penetrate the hardest surface. Water is used to lubricate and cool the face of the drill bit. Moreover, it flushes away the material that is being cut.
The professional carrying out the Diamond Drilling in Kent adjusts the pressure and rotary speed of the drill bit and water circulation depending on several factors, such as the type of surface being drilled, the drilling conditions, etc.
Many different factors are to be considered by experts to carry out diamond drilling effectively. These are
- The type of material and surface that is to be drilled
- The size and diameter of the hole that is to be created
- Structural resistance of the material that is to be cut
- The matching suitable diamond compounds to get the job done efficiently
[edit] Latest Technologies in Diamond Drilling
Diamond Drilling is a years-old technique in the offshore industry, but recent advancements are changing the face of this particular sector. Furthermore, ongoing technological improvements are necessary to enhance diamond drilling's operational efficiency.
Multiple technological innovations are being made in diamond drilling, and some of these are
[edit] Polycrystalline Diamond Compact (PDC) Technology:
Polycrystalline Diamond Compact (PDC) Technology: Diamond drilling is well known for use in the mining industry. Although the basic technology is likely to look the same, PDC (polycrystalline diamond compact) technology is particularly designed for the oil and gas industry. With the increase in the demand for easy-to-reach oil, the demand for effective, reliable, and cost-sensitive equipment is also grown.
PDC bits are so advanced that their designs are specialised to address different oil and gas wells' formations and reduce vibration. The most significant technological development is improving the PDC's cutter design, which increases the life of PDC cutters and bits. PDC works by scrapping the surface and is now used in areas traditionally dominated by tri-cone technology.
[edit] Thermally Stable Polycrystalline (TSP) Technology
Thermally stable polycrystalline (TSP) is a diamond hard-facing material. It is introduced to increase the life of drilling tools that operate in highly abrasive environments by almost ten times and reduce the cost of drilling operations.
This new material constitutes Hardide-D. It is the metallurgically bonded coating for thermally stable polycrystalline (TSP) diamonds. Additionally, it is suitable for brazing, aggressive media, and extreme loads.
Moreover, the new TSP Xtreme inserts offer a 200 times improvement compared to tungsten carbide inserts. In addition, they can be secured with downhole tools needing gauge protection, including stabilisers, logging while drilling tools, rotary steerable tools, bent housings and downhole motor bearings.
[edit] Important Features of Diamond Drilling
Since Diamond Drilling is crucial for mining oil and gas in the UK, knowing the features of diamond drilling can help make a better decision. Here listed are the significant features of an efficient diamond drilling method:
[edit] Maintenance of Structural Integrity
Maintaining structural integrity is essential for the safety of people who will use the structure being drilled. A critical factor distinguishing Diamond Drilling in London is that this drilling technique uses minimal vibration. Little to no vibration means there will be no structural disturbance, and the risk of structural damage is reduced.
Unlike conventional drilling methods, diamond drilling doesn't compromise the structure's stability. Chips and cracks are the common damages caused by drilling methods alternative to the diamond drilling technique. The latter technology ensures efficient drilling with no chips or cracks to be repaired.
[edit] Minimal Dust
Highly accurate drilling bit causes minimal spalling, i.e., breaking down construction material into tiny pieces. This feature enables experts to create clean openings on a hard surface, eliminating the post-reinstatement work. In addition, with minimal dust, there is no need for the workers to spend their valuable time cleaning the construction site, and they can move on to the next task.
[edit] Minimal Noise
According to Diamond Drilling experts, conventional drilling techniques can be harsh on workers' ears, forcing them to wear ear defenders during work. Fortunately, diamond drilling produces little to no noise. In addition, the high-speed diamond drilling method leads to less resonance while drilling the surface, eliminating the risk of ear damage.
[edit] Best for Restricted Spaces
It is possible to carry out Diamond Drilling in Kent using automatic feed systems, making it the most suitable option for working within restricted spaces.
[edit] High Precision and Cost Effective
Diamond drill bits have higher strength, making diamond drilling a high-precision technique to create accurate holes and openings. In addition, precise drilling minimizes the risk of accidental structural damage, making it an ideal method for different types of surfaces.
Diamond drilling is one of the most cost-effective, regardless of using multiple layers of diamonds for manufacturing drill heads. It is because diamond drills reduce structural damage while creating openings in the surface. Therefore, there is no need for the property owners to spend a fortune on repairs, making diamond drilling a cheaper drilling technique.
[edit] How Working with Professional CA Drillers Can be Beneficial?
The United Kingdom is an essential European mining country. Significant mineral resources mined here are hard coal, diamond, and crude oil. Over the next few years, the UK's building and mining industries will witness more use of diamond core drilling equipment and boost output. With the increased application, it is only wise to work with professional service providers offering efficient Diamond Drilling in London.
CA Drillers is one of the most trusted companies in the UK and provides premium quality diamond drilling services with trained and experienced specialists. In addition, this ISO-certified company has in-depth experience in handling small electrical wiring and plumbing projects to large construction projects.
CA Drillers ensures timely delivery of Diamond Drilling in Kent services. It uses robust, portable diamond drilling machines that are versatile enough for application in massive and compact spaces. The company operates all over the UK, including London, Kent, Essex, and Surrey, while offering highly precise and seamless diamond drilling services at a fair price.
[edit] Wrapping It Up
Diamond Drilling is a non-percussive core drilling form that integrates diamond segments into the blades. It is one of the best drilling methods that support the creation of precisely measured holes and openings. Minimal noise, high precision, minimal dust, cost-effectiveness, and structural integrity are the top features of diamond drilling.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- A Guide to Diamond Blades
- Compressed air plant.
- Diamond stitch drilling.
- Driven piles.
- Geotechnical engineering.
- Piling equipment.
- Structural engineer.
- Types of excavation.
- Reasons for using diamond stitch drilling in construction
- What are The Important Features of Diamond Drilling?
Featured articles and news
Exchange for Change for UK deposit return scheme
The UK Deposit Management Organisation established to deliver Deposit Return Scheme unveils trading name.
A guide to integrating heat pumps
As the Future Homes Standard approaches Future Homes Hub publishes hints and tips for Architects and Architectural Technologists.
BSR as a standalone body; statements, key roles, context
Statements from key figures in key and changing roles.
ECA launches Welsh Election Manifesto
ECA calls on political parties 100 day milestone to the Senedd elections.
Resident engagement as the key to successful retrofits
Retrofit is about people, not just buildings, from early starts to beyond handover.
Plastic, recycling and its symbol
Student competition winning, M.C.Esher inspired Möbius strip design symbolising continuity within a finite entity.
Do you take the lead in a circular construction economy?
Help us develop and expand this wiki as a resource for academia and industry alike.
Warm Homes Plan Workforce Taskforce
Risks of undermining UK’s energy transition due to lack of electrotechnical industry representation, says ECA.
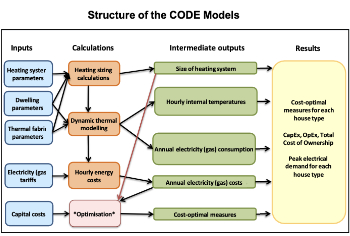
Cost Optimal Domestic Electrification CODE
Modelling retrofits only on costs that directly impact the consumer: upfront cost of equipment, energy costs and maintenance costs.
The Warm Homes Plan details released
What's new and what is not, with industry reactions.
Could AI and VR cause an increase the value of heritage?
The Orange book: 2026 Amendment 4 to BS 7671:2018
ECA welcomes IET and BSI content sign off.
How neural technologies could transform the design future
Enhancing legacy parametric engines, offering novel ways to explore solutions and generate geometry.
Key AI related terms to be aware of
With explanations from the UK government and other bodies.
From QS to further education teacher
Applying real world skills with the next generation.