What is the future of the construction industry?
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
Unlike other industries, the Engineering and Construction (E&C) sector has been slow to adopt new technologies, and has certainly never undergone a major transformation. As a result, productivity has stagnated over the last 40 years, or in some cases, even declined.
This unimpressive record looks set to change very soon, and very dramatically. In fact, profound changes are already taking place – though not yet on a sufficiently wide scale – in many aspects of the construction industry. The writer William Gibson’s famous phrase fits the industry perfectly - 'the future is here today – it is just not evenly distributed.'
The key is digitalisation. More and more construction projects are incorporating systems of digital sensors, intelligent machines, mobile devices, and new software applications – increasingly integrated with a central platform of Building Information Modelling (BIM).
The challenge now is to achieve widespread adoption and proper traction. Wherever the new technologies have properly permeated this fragmented industry, the outlook is an almost 20% reduction in total life-cycle costs of a project, as well as substantial improvements in completion time, quality, and safety.
[edit] Construction reconstructed in all its phases
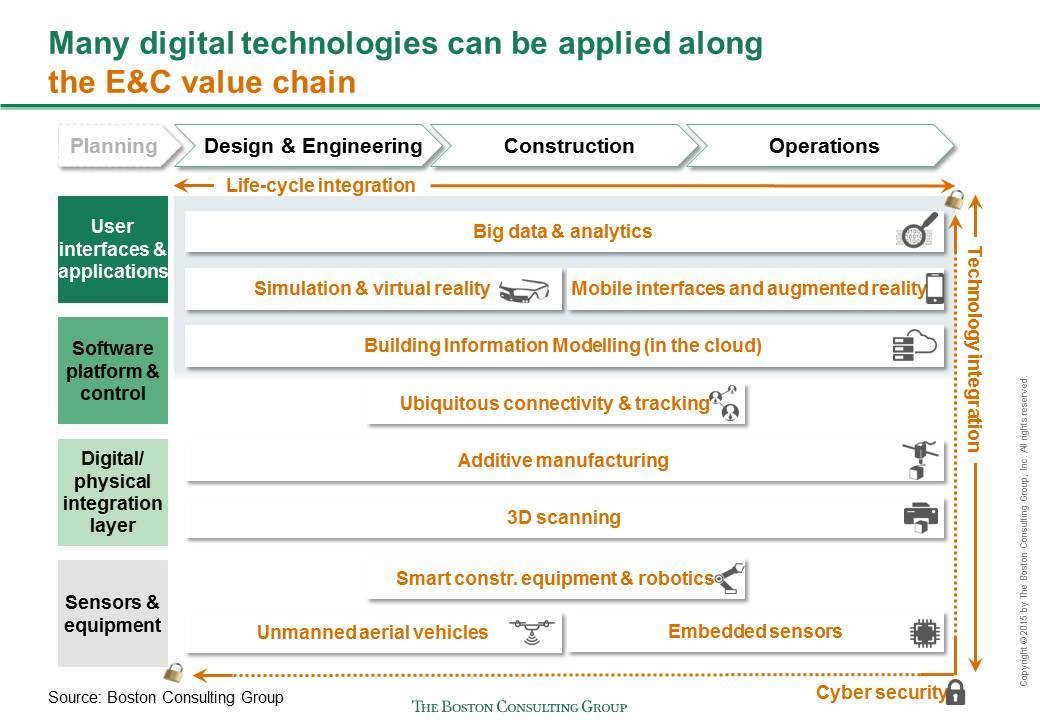
Technological advances are now revolutionising almost all points in the lifecycle of a built asset, from conceptualisation to demolition. The chart below shows the relevance of digital technologies along the engineering and construction industry’s value chain.
Digitalisation is transforming all three major lifecycle phases of construction projects. Consider the following scenario – no longer futuristic, but 'here today', though its building blocks are still distributed patchily over disparate projects.
During the Design & Engineering phase, BIM identifies potential design clashes and constructability issues, thereby averting costly corrective rework; and it improves the tendering process by making the information more transparent and accessible.
An interesting example is that of Crossrail – one of the world’s largest and most complex infrastructure projects, building a major new underground line across London: the designers and engineers are using a centralised set of linked BIM databases to integrate about 1.7 million CAD files into a single information model.
During the actual construction phase, drones survey and inspect the construction site. 3D printers prefabricate many of the building components. GPS and radio-frequency identification (RFID) are used for tracking the materials, equipment, and workers, in order to then optimise flows and inventory levels. Robots and autonomous vehicles do much of the actual building work. 3D laser scanning or aerial mapping is used for comparing work-in-progress against a virtual model, thereby enabling prompt course corrections and minimising corrective work.
Take the case of a Japanese equipment manufacturer that has developed fully autonomous bulldozers, led by drones that map the area in real-time to provide data on the workload.
During the operations phase, embedded sensors continue to monitor any given part of an asset, checking for deterioration, facilitating predictive maintenance, and continually updating a central database. Augmented reality is used for guiding maintenance crews.
Big data – on traffic movements, electricity consumption, and so on – are collected digitally, and are subjected to advanced analytics, in order to optimise decision-making and generally boost operational efficiency.
By way of illustration, consider the approach taken by the Japanese building service provider NTT Facilities to the inspection, maintenance and repair of their R&D premises: by integrating the BIM model into the building’s facility- and asset-management system, and making intelligent use of this combined resource, the company was able to reduce the cost of operations and maintenance by an estimated 20%.
[edit] Gathering momentum
On average, uptake of these transformative technologies has been slow initially. They have faced some resistance to adoption, and some companies that do deploy them have struggled to capture all the potential benefits.
However, the obstacles are being overcome. More and more companies are now embracing the opportunities, with productivity starting to rise and promising to soar.
Within ten years, according to our estimates, full-scale digitalisation will lead to huge annual global cost savings. For non-residential construction, those savings will be $0.7 trillion to $1.2 trillion (13% to 21%) in the Design & Engineering and Construction phases; and $0.3 trillion to $0.5 trillion (10% to 17%) in the Operations phase.
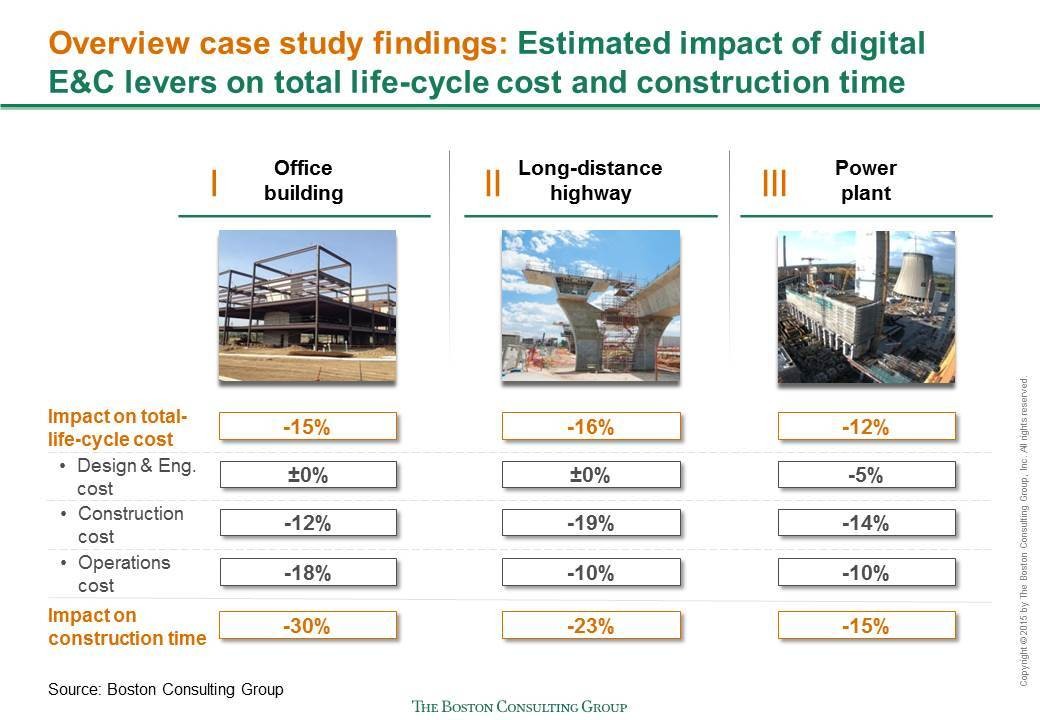
Note that the productivity gains will vary not only across the life-cycle phases but also across the sub-sectors: vertical, industrial, and infrastructure. The chart below, based on a study of construction projects from each of the sub-sectors, shows the variation in detail.
The gap between digital leaders and laggards is widening – for construction companies themselves, for technology providers, and also for governments in their role as project owners and regulators. All these stakeholders need to master the dynamics, upgrade their competencies and investments, and adapt their processes and attitudes, or risk losing out competitively.
Post originally published on weforum.org.
This article was written by Christoph Rothballer, Santiago Castagnino, Philipp Gerbert.
This article was also published on the Future of Construction Knowledge Sharing Platform and the WEF Agenda Blog.
--Future of Construction 15:54, 16 Jun 2017 (BST)
[edit] Find out more
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- 10 construction industry trends to watch in 2017.
- Construction innovation.
- Eight ways to win the fight for talent in construction.
- Shaping the Future of Construction: Inspiring innovators redefine the industry.
- Tackling the construction skills shortage.
- The future of the built environment in a revolutionary age.
- The transformative power of BIM.
- Top 4 challenges facing the construction industry.
- Unprecedented Innovation and New Technologies on the Horizon.
Featured articles and news
The Association of Consultant Architects recap
A reintroduction and recap of ACA President; Patrick Inglis' Autumn update.
The Home Energy Model and its wrappers
From SAP to HEM, EPC for MEES and FHS assessment wrappers.
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.