Data analytics

|
Analytics is a method which uses logical analysis to interpret large quantities of data to help with prediction and decision making. The analysis of data may include discerning trends and patterns, their interpretation and communication. Analytics is therefore the link between the data and making informed decisions. Organisations can use analytics to gain a predictive intelligence that can help shape their future plans.
Data used for analytics can be structured or unstructured. Structured data, for example, might be formatted into a table; whereas unstructured data cannot be tabulated e.g some documents or hearsay.
There are two main types of data:
- Descriptive data – this is data which describes things in the past e.g customer records, past performance, purchase history etc.
- Predictive data – this is closely linked to machine learning and looks at the future, and how to make predictions based on past events.
Once descriptive data has been gathered, it can be processed by algorithms (mathematical formulas or models) to create a model that identifies relationships in variables existing in the data and allows predictions to be made. Uncertain data for which the answers are not known e.g the type of goods that certain people in a geographical area might be interested in, can then be fed into the model which subsequently outputs what their preferences might be. This can then be reported or communicated in various formats such as tables, bar and line charts, etc.
The important result of the process is the creation of the model. Once established, data can be inputted to produce a prediction. This is the basis of machine learning which can lead to the attainment of artificial intelligence (AI).
Data analytics is useful in all walks of life but particularly in marketing where possible future consumer preferences can be predicted and therefore accommodated in campaigns. It can blend into performance analytics which may help a company measure its progress toward specific goals and to determine which actions will help achieve them.
Data analytics can be used for digital management to help construction firms to win projects and deliver them more efficiently. This is particularly apposite for large capital projects, for example, providing analysis to challenge trends in low-performance, getting a better understanding of project performance, root causes and prioritising daily activities.
Analytics will become increasingly important with the growth of big data, the internet of things and the use of sensors in the built environment.
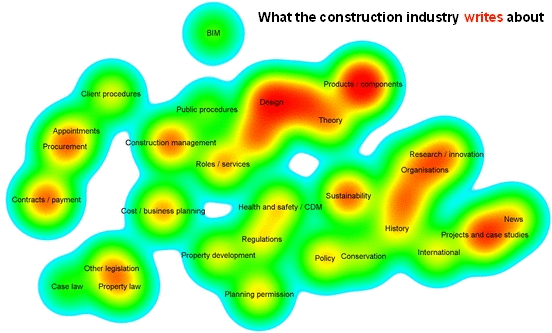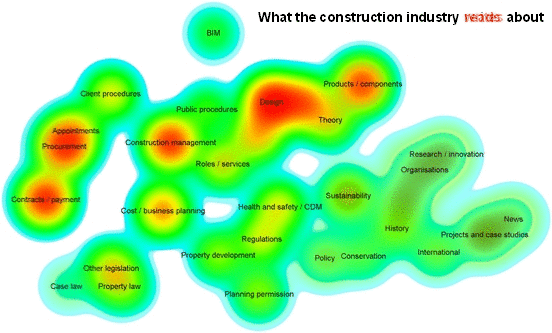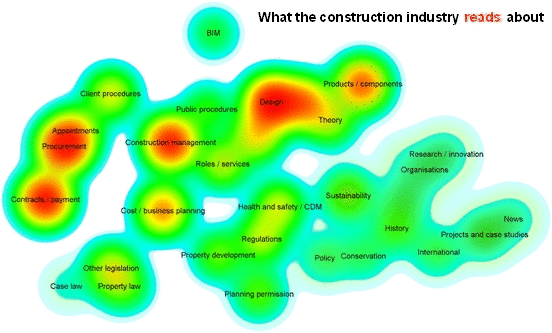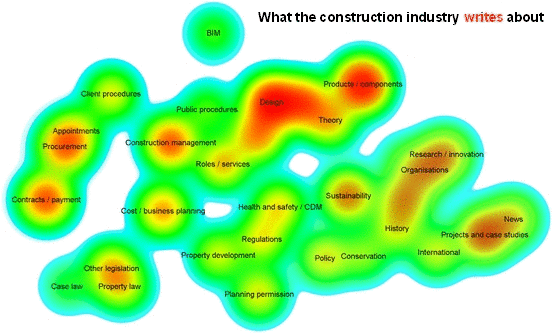
Analyics were used by Designing Buildings Wiki to assess the relationships between subjects on the website, and the difference between what authors write about and what users read about. For more information see: Fit for purpose - Big data reveals the construction knowledge gap
NB PwC Global, Digital procurement survey 2022, defines Data analytics as: ‘…the science of analyzing raw data to make conclusions about that information.’
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Asset information model.
- Big data.
- Building data exchange.
- Clustering.
- Common data environment.
- Data-centric business model.
- Data-driven mobility.
- Data and behaviours in construction.
- Data and infrastructure productivity.
- Data collection strategies.
- Data drop.
- Data manager.
- How data can stop waste.
- Interoperability.
- Internet of things.
- Making the most of big data.
- Open data - how can it aid the development of the construction industry?
- Predictive analytics.
- Procurement analytics.
- Top big data tools used to store and analyze data.
- Treating data as part of infrastructure
- Virtual reality and big data disrupting digital construction.
Featured articles and news
The Architectural Technology podcast: Where it's AT
Catch up for free, subscribe and share with your network.
The Association of Consultant Architects recap
A reintroduction and recap of ACA President; Patrick Inglis' Autumn update.
The Home Energy Model and its wrappers
From SAP to HEM, EPC for MEES and FHS assessment wrappers.
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.