Drawing projections
There are a number of techniques of projection that can be used to represent three-dimensional objects in two-dimensions by 'projecting' their image onto a planar surface.
Drawing projections should comply with relevant standards (such as British Standards) to prevent misunderstanding and avoid errors in interpreting the drawing.
See also projections detailing, projections measurement and projections dataset.
Contents |
[edit] Orthographic projection
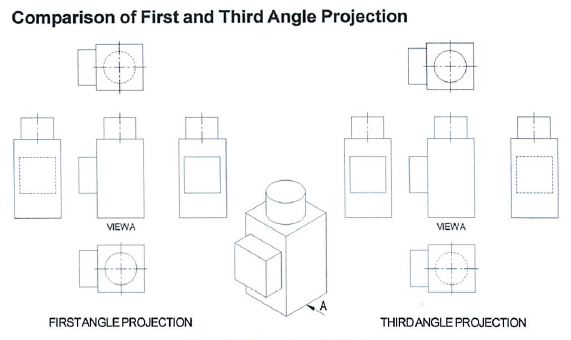
Orthographic projection is a type of 'parallel' projection in which the four orthogonal views of an object are shown. The orthographic projection commonly used in the UK is called first angle projection.
[edit] Axonometric projection
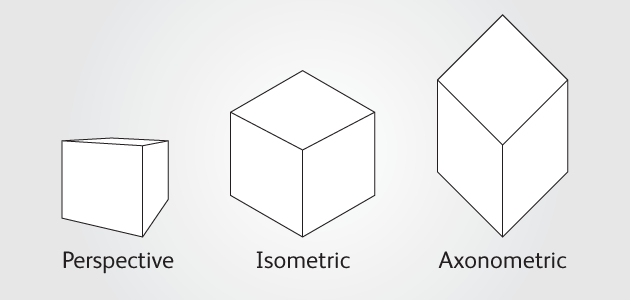
Axonometric projection creates a true plan set at 45º, which retains the original orthogonal geometry of the plan. It is particularly suitable for representing interior designs, such as kitchen layouts. Planning drawings can also be effective represented as axonometric projections, showing the relationships between buildings and topography.
The axonometric method became increasingly popular in the 20th century as a formal presentation technique, but recently has become less widely used due to the emergence of CAD programmes and building information modelling.
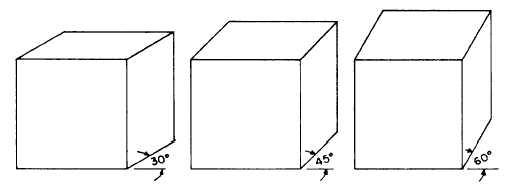
NB Drawing for Understanding, Creating Interpretive Drawings of Historic Buildings, published by Historic England in 2016 suggests that axonometric projection: 'Is a type of parallel projection used for creating a drawing where the plan is drawn to scale but rotated at an angle of 60° or 30°along one or more of its axes relative to the normal axis.'
[edit] Isometric projection
The isometric was the standard view until the mid-20th century. Unlike the axonometric projection, the isometric plan view is slightly distorted, using a plan grid at 30º from the horizontal in both directions. It can be used to show the nature of the design and explain construction details more clearly than an orthographic projection. It is sometimes used during concept design to help the client grasp the mass of the proposal.
[edit] Oblique projection
When primary information is drawn in elevation, the interpretation can be enhanced by an oblique projection. This is a simple method of producing two-dimensional images of three-dimensional objects. The differentiating characteristic of oblique projection is that the drawn objects are not in perspective, and so do not correspond to any actual obtainable view.
[edit] Parallel projection
'Parallel projections have lines of projection that are parallel both in reality and in the projection plane.' Ref Drawing for Understanding, Creating Interpretive Drawings of Historic Buildings, published by Historic England in 2016.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Architectural reprography.
- As-built drawings and record drawings.
- Assembly drawing.
- Augmented reality in construction.
- Bill of quantities.
- Blueprint.
- Building information modelling.
- CAD layer.
- Component drawing.
- Computer aided design.
- Concept drawing.
- ConTech.
- Detail drawing.
- Elevations.
- Engineering drawing.
- Exploded view.
- General arrangement drawing.
- Geometric form.
- How to draw a floor plan.
- Installation drawings.
- Manual drafting techniques.
- North American Paper Sizes
- Notation and symbols.
- Orthogonal plan.
- Paper sizes (ISO 216 A, B and C series)
- Production information.
- Section drawing.
- Shop drawings.
- Site plan.
- Specification.
- Technical drawing.
- Types of drawings.
- Working drawing.
Featured articles and news
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help the homebuilding sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.