Aluminium
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
Aluminium makes up more than 8% of the Earth’s core mass and is the most widespread metal. It is also the third most common chemical element after oxygen and silicon. It is the 13 element on the Periodic Table and has a silvery-white appearance.
Pure aluminium does not occur in nature because it binds very easily with other elements. It is because of this that aluminium was only discovered in the 19th century when scientists were able to break down chemical compounds into their elements.
Because of the high costs of the extraction process, it wasn't until the late 19th century that it was possible to produce aluminium on an industrial scale for use in construction and other industries.
[edit] Extraction process
Aluminium is relatively expensive because of the amount of energy required for its extraction. It is extracted from aluminium oxide, a white powder which is purified from aluminium ore (bauxite).
The aluminium oxide is dissolved in molten cryolite (an aluminium compound that has a lower melting point than aluminium itself). Aluminium is then extracted by a process of electrolysis or electrolytic reduction. Electricity is passed through the liquid, and aluminium forms at the negative electrode. It then sinks to the bottom of the tank, where it can be tapped off.
[edit] Properties of aluminium
One of the main reasons for aluminium’s widespread application is its combination of properties:
- Lightweight: Almost three times lighter than iron.
- Durable: Almost as durable as steel.
- Ductile: Extremely flexible and easily processed using pressure when hot or cold.
- Corrosion-resistant: Its surface is protected by an extremely thin yet very strong layer of aluminium oxide.
- Non-magnetic.
- Excellent conductivity.
- Fire-resistant.
- Non-toxic.
- Bonds with other elements relatively easily, enabling the formation of a wide variety of aluminium alloys.
- Re-usable: Aluminium and its alloys can be melted down and reused without any impact on their mechanical properties. Estimates suggest that around 75% of all aluminium produced is still in use in some form.
[edit] Aluminium in construction
As the extraction process is relatively expensive, aluminium was generally not used in construction until the early-20th century. In the 1920s, it began to be used primarily for decorative detailing and Art Deco structures. In the 1930s, a breakthrough was achieved when the Empire State Building used aluminium for much of its interior structures and its famous spire. Subsequently, it began to be used for roofing, flashing, wall panels, spandrels, and so on.
Today, aluminium is the second most used metal in buildings after steel.
Because of its ductility, aluminium can be formed into many shapes and profiles. Aluminium wall cladding systems are commonly used for building exteriors, with large wall panels requiring fewer joints, resulting in time-efficient installation.
Some of the most common applications for aluminium are:
- Window and door frames.
- Rolling shutters and sun shading elements.
- Long-span roof systems covering large areas such as halls and auditoriums.
- Structures located in inaccessible places where the economy of transport and ease of installation are important, such as electrical transmission towers.
- Structures in corrosive or humid environments, such as swimming pools, bridges, hydraulic structures, offshore superstructures, and so on.
- Structures with moving sections, such as moving bridges.
- Structures to which access for maintenance is limited, such as masts, lighting towers, antenna towers, and so on.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Alloy.
- Aluminium decking.
- Bauxite.
- Cast iron.
- Copper.
- Failure of metals.
- Flashing.
- Galvanised steel.
- Iron.
- Lead.
- Metal.
- Metal fabrication.
- Metal roofing.
- Stainless steel.
- Types of metal.
- Zinc.
[edit] External resources
- Aluminium Leader - What is aluminium?
Featured articles and news
What they are, how they work and why they are popular in many countries.
Plastic, recycling and its symbol
Student competition winning, M.C.Esher inspired Möbius strip design symbolising continuity within a finite entity.
Do you take the lead in a circular construction economy?
Help us develop and expand this wiki as a resource for academia and industry alike.
Warm Homes Plan Workforce Taskforce
Risks of undermining UK’s energy transition due to lack of electrotechnical industry representation, says ECA.
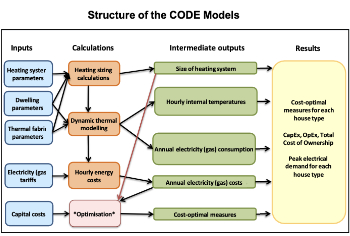
Cost Optimal Domestic Electrification CODE
Modelling retrofits only on costs that directly impact the consumer: upfront cost of equipment, energy costs and maintenance costs.
The Warm Homes Plan details released
What's new and what is not, with industry reactions.
Could AI and VR cause an increase the value of heritage?
The Orange book: 2026 Amendment 4 to BS 7671:2018
ECA welcomes IET and BSI content sign off.
How neural technologies could transform the design future
Enhancing legacy parametric engines, offering novel ways to explore solutions and generate geometry.
Key AI related terms to be aware of
With explanations from the UK government and other bodies.
From QS to further education teacher
Applying real world skills with the next generation.
A guide on how children can use LEGO to mirror real engineering processes.
Data infrastructure for next-generation materials science
Research Data Express to automate data processing and create AI-ready datasets for materials research.
Wired for the Future with ECA; powering skills and progress
ECA South Wales Business Day 2025, a day to remember.
AI for the conservation professional
A level of sophistication previously reserved for science fiction.
Biomass harvested in cycles of less than ten years.
An interview with the new CIAT President
Usman Yaqub BSc (Hons) PCIAT MFPWS.
Cost benefit model report of building safety regime in Wales
Proposed policy option costs for design and construction stage of the new building safety regime in Wales.
Do you receive our free biweekly newsletter?
If not you can sign up to receive it in your mailbox here.
























Comments