Laser Scanning for 3D Modeling in Building Information Modeling
Contents |
[edit] Introduction:
Laser scanning has emerged as a powerful technology in the field of Building Information Modelling (BIM). It allows for the accurate and efficient capture of as-built conditions, enabling the creation of highly detailed and realistic 3D models. This article explores the process of laser scanning to 3D modelling in BIM, highlighting its benefits, challenges, and applications.
[edit] Laser Scanning: A Brief Overview
Laser scanning, also known as 3D scanning or LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), is a technology that uses laser beams to capture the geometry and spatial information of objects or environments. It involves the use of a laser scanner, which emits laser pulses and measures the time it takes for the pulses to bounce back, thereby creating a point cloud of data.
[edit] Laser Scanning Process
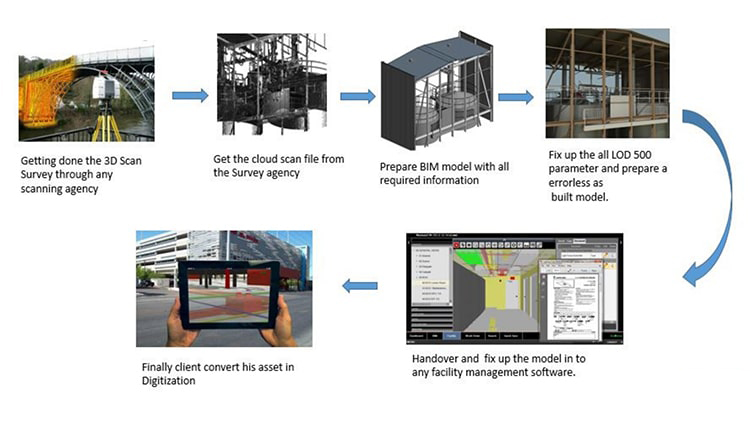
The laser scanning process involves several key steps:
a) Pre-Scanning Planning: Before commencing the scanning process, it is essential to plan the project scope, determine the required level of detail, and establish scan positions for optimal coverage.
b) Data Acquisition: During the scanning phase, laser scanners are deployed at strategic positions to capture the desired areas. The scanners emit laser beams and record millions of points per second, creating a dense and accurate point cloud representation.
c) Point Cloud Registration: After acquiring multiple scans, the individual point clouds are registered together using common reference points. This process aligns the scans into a unified coordinate system, creating a seamless representation of the entire scanned area.
d) Data Processing: Once the registration is complete, the point cloud data is processed to remove any noise, outliers, or unwanted artefacts. Filtering techniques are employed to enhance the quality and accuracy of the point cloud.
[edit] 3D Modelling in BIM
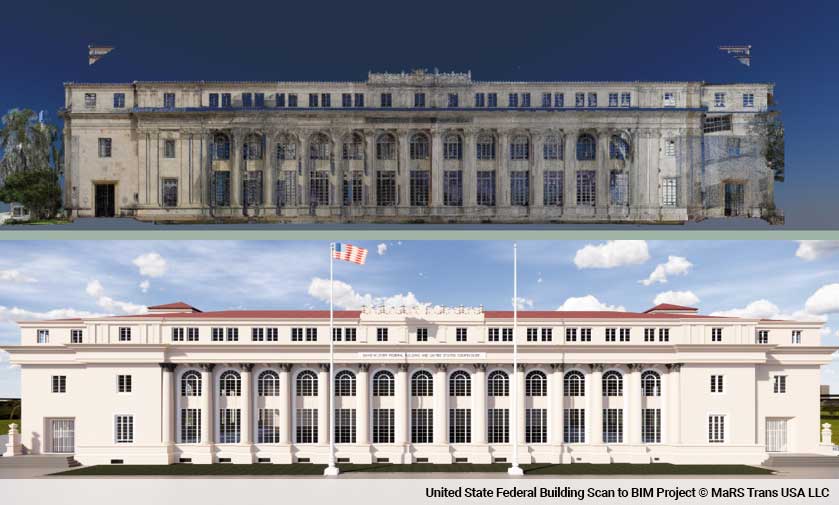
The processed point cloud data serves as the foundation for creating a 3D model in the BIM environment. The point cloud is imported into specialised BIM software, which allows for the extraction of precise geometric information and the creation of detailed models.
a) Model Creation: Using BIM software tools, the point cloud is used as a reference to generate 3D elements such as walls, floors, ceilings, and structural components. These elements are accurately positioned and aligned within the model.
b) Visualisation and Analysis: The 3D model derived from the point cloud provides an immersive visual representation of the as-built conditions. It enables architects, engineers, and construction professionals to visualise, analyse, and simulate various scenarios, improving decision-making processes.
c) Clash Detection and Coordination: BIM models facilitate clash detection by identifying conflicts between different building systems, such as mechanical, electrical, and plumbing. By identifying clashes early on, costly on-site rework can be minimised.
[edit] Benefits of Laser Scanning in BIM
The integration of laser scanning into the BIM workflow offers numerous advantages:
- Accurate As-Built Documentation: Laser scanning provides highly accurate and detailed representations of existing conditions, reducing errors and uncertainties during the design and construction phases.
- Time and Cost Savings: Laser scanning enables faster and more efficient data capture compared to traditional surveying methods. It helps expedite the modeling process, leading to cost savings and improved project timelines.
- Improved Collaboration: Laser scanning promotes collaboration and communication among project stakeholders. The 3D models derived from scans can be easily shared and accessed by architects, engineers, contractors, and facility managers, fostering a more integrated approach to construction and facility management.
- Enhanced Facility Management: 3D Laser scanning solutions allows for the creation of as-built models that can be utilized for facility management purposes. These models provide valuable information for maintenance, renovations, and future expansions.
[edit] Challenges and Considerations
While laser scanning offers numerous benefits, certain challenges should be taken into account:
a) Data Processing and Management: The large volume of data generated by laser scanning requires efficient processing and storage capabilities. Adequate hardware and software solutions must be in place to handle the data effectively.
b) Accuracy and Limitations: Although laser scanning provides high accuracy, certain factors such as reflectivity, occlusions, and environmental conditions can affect data quality. Careful consideration must be given to these limitations during the scanning process.
c) Skill and Expertise: Laser scanning requires specialized knowledge and expertise. Trained professionals are needed to operate the equipment, conduct scans, and interpret the data accurately.
[edit] Conclusion:
Laser scanning plays a crucial role in the creation of detailed 3D models for BIM applications. It enables accurate as-built documentation, improves collaboration, and enhances the overall efficiency of the design and construction processes. As the technology continues to evolve, laser scanning is expected to become an increasingly indispensable tool in the field of BIM, revolutionizing the way we design, construct, and manage buildings.
https://www.marsbim.com/services/bim/scan-to-bim.html
https://www.marsbim.com/services/laser-scanning-services-in-india.html
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- 3D city model.
- 3D printer.
- BIM for heritage asset management.
- Building information modelling.
- Building survey.
- Construction cameras.
- Construction drones.
- Desk study.
- Development appraisal.
- Drones as a Service DaaS.
- Geophysical survey.
- Global positioning systems and global navigation satellite systems.
- Ground control point GCP.
- How can drones transform construction processes?
- How to layout a building.
- Impulse radar.
- Innovation and investigation at the Hill House.
- Interview with David Southam about laser scanning in construction.
- Laser.
- Pre-construction information.
- Radar.
- Site information.
- Site surveys.
- Surveying instruments.
- Surveyor.
- Technical due diligence.
- Uses of drones in construction.
- Vendor survey.
- Laser scanning for building design and construction.
[edit] External links
https://www.marsbim.com/services/bim/scan-to-bim.html
https://www.marsbim.com/services/laser-scanning-services-in-india.html
BIM Directory
[edit] Building Information Modelling (BIM)
[edit] Information Requirements
Employer's Information Requirements (EIR)
Organisational Information Requirements (OIR)
Asset Information Requirements (AIR)
[edit] Information Models
Project Information Model (PIM)
[edit] Collaborative Practices
Industry Foundation Classes (IFC)