Centre Pompidou
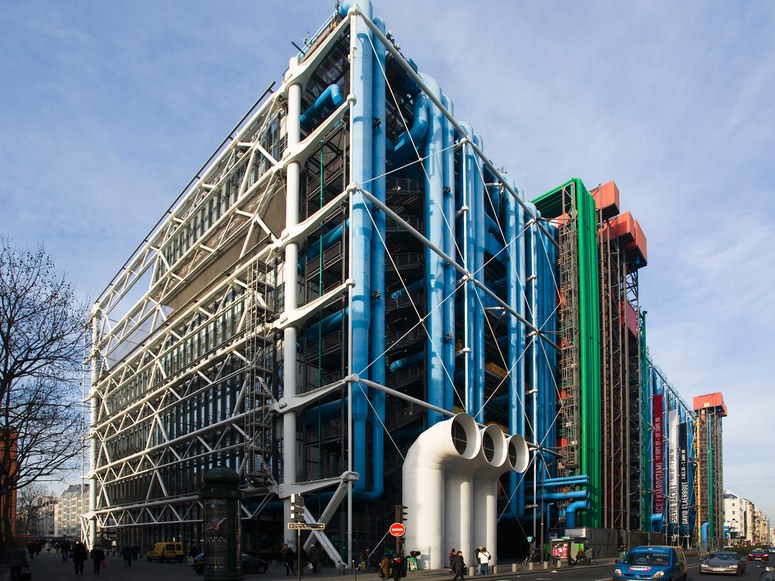
Centre Georges Pompidou (popularly known as Centre Pompidou) is a complex high-tech building in the Beaubourg area of Paris. It was designed by the architectural team of Richard Rogers and Renzo Piano, along with Gianfranco Franchini, and was completed in 1977, becoming one of the most famous and provocative buildings of the 20th century.
It houses the Bibliothèque publique d'information (Public Information Library), a vast public library, the Musée National d'Art Moderne, which is the largest museum for modern art in Europe, and IRCAM, a centre for music and acoustic research.
The design created a flexible and a dynamic communications centre. A large piazza for public activities and glazed street animate the façade of one of the most visited cultural centres in the world.
The Centre Pompidou brings together the themes which have characterised Rogers’ architecture from the mid 1960s – skin and structure, technology and flexibility, movement and anti-monumentalism. The building was envisaged as a cross between ‘an information-oriented computerised Times Square and the British Museum’, a democratic place for all people and the centrepiece of a regenerated quarter of the city.
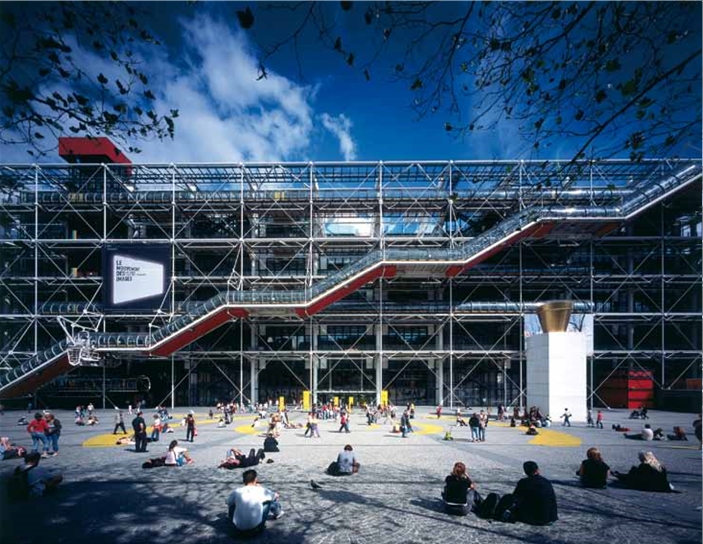
Half of the total available site area was set aside as a public square, therefore the Centre had to be tall enough to accommodate 90,000 m2 (one million ft2) of space. The decision to place structure and services on the outside was driven by the need for internal flexibility, as a result providing huge expanses of uninterrupted space on massive, open floors – the staggering scale of these internal spaces is free from the intrusion of services and stairs.
The structural system provided for a braced and exposed steel superstructure with reinforced concrete floors. External services give scale and detail to the façades, while celebration of movement and access is provided by lifts and escalators. The result is a highly expressive, strongly articulated building that has come to be seen as a Parisian landmark.
Yet the achievement at Beaubourg is urbanistic as much as architectural. The building and great public square were intended to revitalise an area of Paris that had been in decline. The neighbouring Marais district, now vibrant and multicultural, underlines the success of the Pompidou’s role as a catalyst for urban regeneration.
The Pompidou’s radicalism is still striking and has proved attractive to a vast public: more than seven million people visit the building every year. The building and its extraordinary contents remain as popular as ever, while crowds fill the square, clustering around musicians, acrobats and fire-eaters. Beaubourg – inside and out – remains as magnetic as ever.
- Place/Date: Paris, France 1971—1977
- Client: Ministère des Affaires Culturelles, Ministère de l’Education Nationale
- Architect: Piano + Rogers
- Cost: £58 million
- Gross Internal Area: 100,000m²
- Structural Engineer: Ove Arup & Partners
- Services Engineer: Ove Arup & Partners
- Quantity Surveyor: Ove Arup & Partners
- Mechanical Services & Superstructure: Laurie Abbott with Shunji Ishida, Hiroshi Naruse, Hiroyuki Takahashi
- Mechanical Engineer: Walter Zbinden with Hans-Peter Bysaeth, Johanna Lohse, Peter Merz, Philippe Dupont
- Site Management: Bernard Plattner
- Main Contractor: Grands Travaux de Marseilles
- Internal & External Systems/Audio Visual: Alan Stanton with Michael Dowd, William Logan, Noriaki Okabe, Rainer Verbizh
- Interior Design: Gianfranco Franchini
Click here to see the full job sheet.

 --Rogers Stirk Harbour + Partners 11:36, 11 March 2015 (UTC)
--Rogers Stirk Harbour + Partners 11:36, 11 March 2015 (UTC)
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- Archigram.
- Dali Theatre and Museum.
- Eiffel Tower.
- Engineering the World - VandA Museum.
- Exoskeleton.
- Guggenheim Museum, Bilbao.
- High-tech architecture.
- Lloyds of London.
- McArthurGlen Designer Outlet Ashford.
- Renzo Piano.
- Richard Rogers.
- Richard Rogers - A Place for all People.
- Robot Building, Bangkok.
- RSHP.
- Solomon R. Guggenheim Museum.
- Switch House, Tate Modern.
- Titanic Belfast.
Featured articles and news
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.
The 2025 draft NPPF in brief with indicative responses
Local verses National and suitable verses sustainable: Consultation open for just over one week.
Increased vigilance on VAT Domestic Reverse Charge
HMRC bearing down with increasing force on construction consultant says.
Call for greater recognition of professional standards
Chartered bodies representing more than 1.5 million individuals have written to the UK Government.
Cutting carbon, cost and risk in estate management
Lessons from Cardiff Met’s “Halve the Half” initiative.
Inspiring the next generation to fulfil an electrified future
Technical Manager at ECA on the importance of engagement between industry and education.
Repairing historic stone and slate roofs
The need for a code of practice and technical advice note.
Environmental compliance; a checklist for 2026
Legislative changes, policy shifts, phased rollouts, and compliance updates to be aware of.





















