Damp-proof course DPC
Contents |
[edit] What are the causes of damp in buildings?
The most common causes of persistent damp in buildings are:
- Condensation (surface or interstitial).
- Penetrating damp.
- Rising damp.
For more information see: Damp in buildings.
Rising damp is caused by capillary action drawing moisture up through the porous elements of a building’s fabric. Rising damp, and some penetrating damp, can be caused by faults to, or the absence of a damp-proof course (DPC) or damp-proof membrane (DPM).
[edit] What problems does damp cause?
Damp in buildings can cause a number of serious problems, such as:
- Damp patches.
- Mould growth, which is a cause of respiratory allergies.
- Mildew, salts, staining and ‘tide marks’.
- Damage to surface finishes.
- Corrosion and decay of the building fabric.
- Slip hazards.
- Frost damage.
- Poor performance of insulation.
- Damage to equipment, or electrical failure.
[edit] What is a damp-proof course?
A damp-proof course is a barrier, usually formed by a membrane, built into the walls of a property, typically 150 mm above ground level, to prevent damp rising through the walls. Historically, damp-proof courses may have been formed using bitumen, slates, lead, pitch, asphalt or low absorption bricks. They emerged during the Victorian era and are commonly found in buildings from around 1900.
For more information, see Types of damp-proof courses.
[edit] Are damp-proof courses required?
Damp-proof courses are now required in the construction of new buildings to prevent rising damp and in some situations to prevent penetrating damp. Approved document C of the Building Regulations, Site preparation and resistance to contaminants and moisture, suggests that a damp-proof course may be a, ‘…bituminous material, polyethylene, engineering bricks or slates in cement mortar or any other material that will prevent the passage of moisture.’
Approved document C requires that, to prevent rising damp, a damp-proof course should be:
- Continuous with any damp-proof membrane in the floor.
- At least 150 mm above the level of the adjoining ground if it is in an external wall.
- If it is in an external cavity wall, the cavity should extend at least 225 mm below the damp-proof course, or a cavity tray should be provided with weep holes every 900 mm so that water running down the cavity cannot pass to the inner leaf.
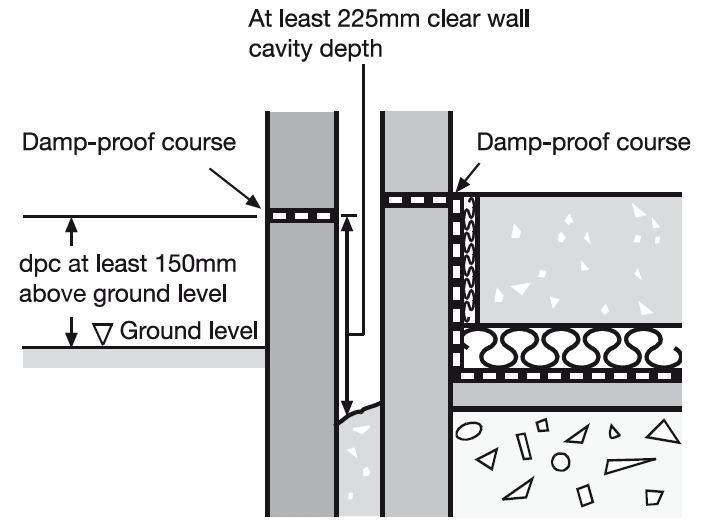 [image source Approved document C, Site preparation and resistance to contaminants and moisture]
[image source Approved document C, Site preparation and resistance to contaminants and moisture]
A damp-proof course may also be required:
- In masonry walls below a coping, where the coping is constructed from a material that is not impervious to water.
- In the joints between walls and door and window frames.
- In suspended timber ground floors between the timber and materials that can carry moisture from the ground.
Standards for damp-proof courses are provided in BS 8215:1991 Code of practice for design and installation of damp-proof courses in masonry construction.
[edit] Inserting a damp-proof course in an existing building
The absence of a damp-proof course in older buildings can be rectified by creating a moisture-impermeable layer, either by the insertion of a damp-proof course, or by the injection of water-repellent chemicals. Treatment generally also involves remedial work to any corroded or decayed elements of the building fabric, as well as hacking off and replacing existing plaster to a height of 1 m.
For more information see: Chemical injected DPC.
However, damp in older buildings is actually often caused by a leak or a defect in the wall construction, such as a cracking, rather than by rising damp, and this may not be rectified by the insertion of a damp-proof course. It is important therefore that any defects are properly identified and corrected first before accepting the cost and disruption of inserting a damp-proof course.
Where it is not possible to insert a damp-proof course 150 mm above the external ground level, for example if the building has a solid external wall and the internal floor level is less than 150 mm above the external ground level, external drainage solutions may be necessary, such as the installation of a french drain.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Breather membrane.
- Building damp-free cavity walls.
- Cavity tray.
- Cavity wall.
- Chemical injected DPC.
- Condensation.
- Damp.
- Damp proof membrane.
- Dew point.
- Does damp proofing work?
- Flashing.
- French drain.
- Humidity.
- Interstitial condensation.
- Penetrating damp.
- Rising damp.
- Rising damp in walls - diagnosis and treatment (DG 245).
- Types of damp-proof courses.
- Vapour barrier.
- Weep hole.
Featured articles and news
The UK's Modern Industrial Strategy: A 10 year plan
Previous consultation criticism, current key elements and general support with some persisting reservations.
Building Safety Regulator reforms
New roles, new staff and a new fast track service pave the way for a single construction regulator.
Architectural Technologist CPDs and Communications
CIAT CPD… and how you can do it!
Cooling centres and cool spaces
Managing extreme heat in cities by directing the public to places for heat stress relief and water sources.
Winter gardens: A brief history and warm variations
Extending the season with glass in different forms and terms.
Restoring Great Yarmouth's Winter Gardens
Transforming one of the least sustainable constructions imaginable.
Construction Skills Mission Board launch sector drive
Newly formed government and industry collaboration set strategy for recruiting an additional 100,000 construction workers a year.
New Architects Code comes into effect in September 2025
ARB Architects Code of Conduct and Practice available with ongoing consultation regarding guidance.
Welsh Skills Body (Medr) launches ambitious plan
The new skills body brings together funding and regulation of tertiary education and research for the devolved nation.
Paul Gandy FCIOB announced as next CIOB President
Former Tilbury Douglas CEO takes helm.
UK Infrastructure: A 10 Year Strategy. In brief with reactions
With the National Infrastructure and Service Transformation Authority (NISTA).
Ebenezer Howard: inventor of the garden city. Book review.
The Grenfell Tower fire, eight years on
A time to pause and reflect as Dubai tower block fire reported just before anniversary.
Airtightness Topic Guide BSRIA TG 27/2025
Explaining the basics of airtightness, what it is, why it's important, when it's required and how it's carried out.
Construction contract awards hit lowest point of 2025
Plummeting for second consecutive month, intensifying concerns for housing and infrastructure goals.
Understanding Mental Health in the Built Environment 2025
Examining the state of mental health in construction, shedding light on levels of stress, anxiety and depression.






















Comments
[edit] To make a comment about this article, click 'Add a comment' above. Separate your comments from any existing comments by inserting a horizontal line.
Please note that retrofitting damp proof courses does not work in solid walled constructed buildings and can cause more harm than good. Simply direct water away from the building by having lower external ground levels than internal floor levels where possible and install free flowing land drains around the building.
Can you explain why you think it doesn't work?
Solid walled structures are designed to operate differently from modern buildings. Solid walled structures are designed to allow moisture to freely flow within the brickwork and evaporate naturally. The application of a modern material/ damp proofing will prohibit this transfer of moisture and lead to interstitial condensation.
I have retrofitted a DPC to a Georgian house, and it did work with no condensation problems.
Good injected DPC companies give a ten year guarantee for their work.