Damp proof membrane DPM
Contents |
[edit] What problems does damp cause in buildings?
Damp in buildings can cause a number of serious problems, such as:
- Damp patches.
- Mould growth, which is a cause of respiratory allergies.
- Mildew, salts, staining and ‘tide marks’.
- Damage to surface finishes.
- Corrosion and decay of the building fabric.
- Slip hazards.
- Frost damage.
- Poor performance of insulation.
- Damage to equipment, or electrical failure.
[edit] What are the causes of damp in buildings?
The most common causes of persistent damp in buildings are:
- Surface condensation.
- Interstitial condensation (condensation within the fabric of a building's construction, either on the surfaces of components that make up the fabric, or sometimes within the components themselves).
- Penetrating damp.
- Rising damp.
[edit] What regulates the requirement for a damp proof membrane?
Approved document C, Site preparation and resistance to contaminants and moisture, requires that (where appropriate) floors next to the ground should:
- Resist the passage of ground moisture to the upper surface of the floor.
- Not be damaged by moisture from the ground.
- Not be damaged by groundwater.
- Be designed and constructed so that their structural and thermal performance are not adversely affected by interstitial condensation.
- Should not promote surface condensation or mould growth.
[edit] What is a damp proof membrane?
A damp proof membrane (DPM) is a thin, sheet material used to prevent moisture transmission. Typically, a damp proof membrane is a polyethylene sheet laid under a concrete slab to prevent the concrete from gaining moisture from the ground by capillary action.
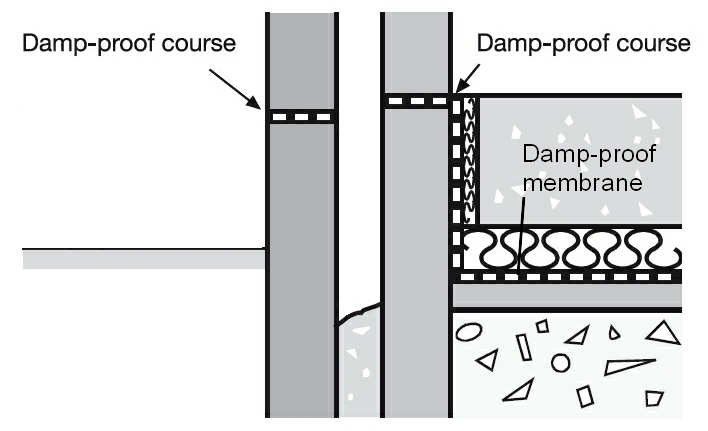
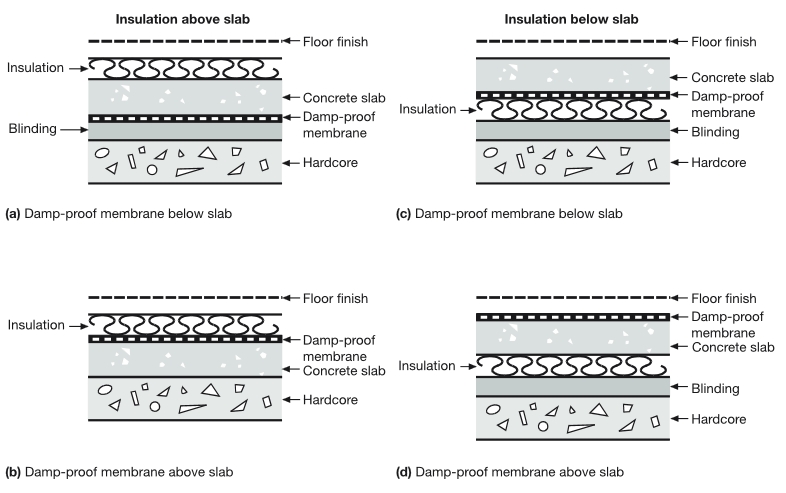
The approved document suggests that a ground-supported floor will meet these requirements if the ground is covered with dense concrete laid on a hardcore bed and a damp proof membrane is provided. It suggests that the damp proof membrane may be above or below the concrete, and continuous with the damp proof courses (DPCs) in walls, piers, and other structures.
If the ground could contain water soluble sulphates, or there is any risk that sulphate or other deleterious matter could contaminate the hardcore, the membrane should be placed at the base of the concrete slab.
The approved document proposes that:
- A membrane below the concrete could be formed with a sheet of polyethylene, which should be at least 300μm thick (1200 gauge) with sealed joints and laid on a bed of material that will not damage the sheet.
- A membrane laid above the concrete may be either polyethylene sheet as described above (but without the bedding material) or three coats of cold applied bitumen solution or similar moisture and water vapour resisting material. It should be protected by either a screed or a floor finish, unless the membrane is pitchmastic or similar material which will also serve as a floor finish.
In order to resist degradation, insulation placed below the damp proof membrane should have low water absorption. If necessary the insulant should be resistant to contaminants in the ground.
A timber floor finish laid directly on concrete may be bedded in a material which may also serve as a damp-proof layer. Timber fillets laid in the concrete as a fixing for a floor finish should be treated with an effective preservative unless they are above the damp-proof membrane.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Basement waterproofing.
- Bitumen.
- Blinding.
- Breather membrane.
- Capillary action.
- Cavity tray.
- Chemical injected DPC.
- Damp.
- Damp proof course.
- Damp proofing.
- Does damp proofing work?
- Dew point.
- Humidity.
- Insulation.
- Interstitial condensation.
- Penetrating damp.
- Polyethylene.
- Rising damp.
- Types of damp-proof courses.
- Vapour barrier.
Featured articles and news
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.
The 2025 draft NPPF in brief with indicative responses
Local verses National and suitable verses sustainable: Consultation open for just over one week.
Increased vigilance on VAT Domestic Reverse Charge
HMRC bearing down with increasing force on construction consultant says.
Call for greater recognition of professional standards
Chartered bodies representing more than 1.5 million individuals have written to the UK Government.
Cutting carbon, cost and risk in estate management
Lessons from Cardiff Met’s “Halve the Half” initiative.
Inspiring the next generation to fulfil an electrified future
Technical Manager at ECA on the importance of engagement between industry and education.
Repairing historic stone and slate roofs
The need for a code of practice and technical advice note.
Environmental compliance; a checklist for 2026
Legislative changes, policy shifts, phased rollouts, and compliance updates to be aware of.




















Comments
[edit] To make a comment about this article, or to suggest changes, click 'Add a comment' above. Separate your comments from any existing comments by inserting a horizontal line.