Cavity tray
The external masonry walls of modern buildings are generally cavity walls, that is, they are formed by an inner leaf and an outer leaf of masonry, tied together, but separated by an air gap or ‘cavity’.
The cavity prevents moisture transmitting from the outer leaf to the inner leaf. It can also provide a ventilation space, allowing moisture within the wall construction to vent to the outside, and can provide a space for the installation of cavity wall insulation.
It is only since the 1920s that external masonry walls in the UK have widely adopted a cavity construction. Before this, they were generally a solid construction.
Cavity trays are included in cavity wall constructions where there are penetrations across the cavity, such as:
- At an abutment with a roof.
- Above openings such as doors and windows.
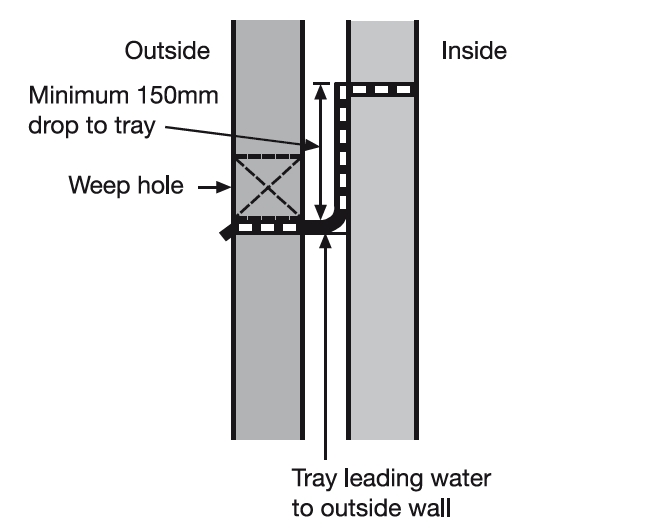
- Where extensions are constructed against existing walls.
- Above concrete slabs or beams.
- Above airbricks, ducts and pipes.
- At the bottom of a wall, if the cavity does not extend 225 mm below the damp-proof course.
Cavity trays prevent moisture being carried to the inner leaf. Very broadly, cavity trays tend to prevent moisture that is travelling downwards from being carried to the inner leaf, whereas damp-proof courses tend to be used to prevent rising damp.
Approved document C of the Building Regulations, Site preparation and resistance to contaminants and moisture, suggests that a cavity tray (or damp-proof course or closer) should be provided to ensure water drains outwards:
- Where the downward flow will be interrupted by an obstruction such as a lintel.
- Under openings, unless there is a sill and the sill and its joints will form a complete barrier.
- At abutments between walls and roofs.
 [Image source: Approved document C, Site preparation and resistance to contaminants and moisture]
[Image source: Approved document C, Site preparation and resistance to contaminants and moisture]
Cavity trays can be formed using a pliable material such as lead, but more commonly they are pre-formed, with a wide range of shapes allowing for different cavity widths, corners, stop ends, steps, lintel shapes, arch shapes and sometimes incorporating external flashing.
Cavity trays must always be bedded onto fresh mortar.
Weep holes must be provided in the external leaf of the wall to allow moisture to drain to the outside. Weep holes are generally created by omitting mortar from the vertical joint between bricks, typically at 450-900 mm centres. They may include plastic weep vents which incorporate a baffle structure to prevent rain from penetrating through the hole and preventing insects from entering the cavity and provide a drip at the front lip to aid drainage.
Care must be taken where there is insulation in the cavity to ensure that both the insulation and the cavity tray continue to function correctly. This can be particularly problematic where blown insulation is retrofitted in to existing cavities.
Where it is necessary to insert cavity trays into existing walls, for example, if an extension is being built against an existing wall, this can be done by removing brickwork a section at a time, or by inserting self-supporting cavity trays through slots cut in the wall.
Standards for cavity trays are described in BS 5628 Code of practice for the use of masonry and BS 8215 Code of practice for design and installation of damp-proof courses in masonry construction.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Building damp-free cavity walls.
- Cavity wall.
- Cavity wall insulation.
- Cold bridge
- Condensation.
- Damp.
- Damp-proof course.
- Defects in brickwork
- Defects in stonework.
- Flashing.
- Insulation.
- Interstitial condensation.
- Lintel.
- Parapet.
- Penetrating damp.
- Rising damp.
- The cavity wall real performance question.
- Types of brick bonding.
- Vapour barrier.
- Wall ties.
- Wall tie failure.
- Weep hole.
Featured articles and news
The Association of Consultant Architects recap
A reintroduction and recap of ACA President; Patrick Inglis' Autumn update.
The Home Energy Model and its wrappers
From SAP to HEM, EPC for MEES and FHS assessment wrappers.
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.



























