Trombe wall
Trombe walls use a combination of thermal mass and glazing to collect and store solar radiation so that it can be used to heat buildings. The broad idea was patented by Edward Morse in 1881, but it was named after French engineer Felix Trombe, who along with architect Jacques Michel used trombe walls as an architectural component in the 1960’s.
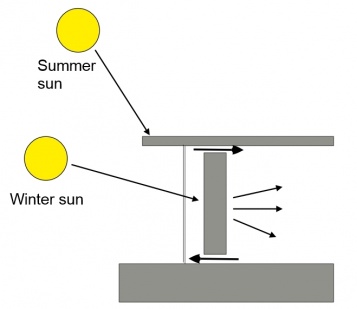
A thermally massive wall with good solar absorption characteristics (perhaps with a matt, dark-coloured surface) is orientated facing towards the direction of the sun. The wall is constructed behind a glazed façade that protects it from external conditions. There is generally a space between the glazing and the wall. This space can be very narrow, just sufficient to allow air movement between the glazing and the wall and to provide access for cleaning, or it can be large enough to be habitable.
Solar radiation that penetrates through the glazing will heat up the wall, but the resulting emission of long-wave infrared radiation from the wall will not re-transmit back through the glazing which is opaque to long-wave infrared radiation. This creates an effect similar to that which allows greenhouses to trap solar radiation.
Heat built up in the wall is slowly released into adjacent spaces by radiation and convection. Depending on the thermal mass of the wall, this heat can be released over long periods of time, moderating fluctuations in conditions. This is a form of ‘passive’ solar heating, as opposed to an ‘active’ building services heating system.
The design of trombe walls needs to enable them to provide solar heating during colder periods, but not to generate overheating during warmer periods. This might require the use of external vents, shading or overhanging eaves to limit peak gains and to enable night time cooling.
The design may also include vents at the top and bottom of the wall (which may be controllable or even include mechanical assistance) to allow more rapid heat transfer between the wall and the adjacent space, or it may rely entirely on conduction through the wall. Where vents are included, cooler air from the adjacent space will enter through the lower vent, will be heated by the wall and so will rise, and will then return to the adjacent space through the upper vent. Closing the vents at night will prevent reverse flows occurring and removing heat from the space.
Typically the wall will be 20-40 cm thick, made out of high heat capacity materials such as masonry or concrete (or even containers filled with water), with the absorbed heat taking up to 10 hours to conduct to the interior.
Installations can also include solar thermal systems to generate hot water.
The efficiency of trombe walls can be improved by the use of double glazing with a low-e coating to reduce heat losses to the outside. Low-e coatings reduce the effective emissivity of the surface of glass so that it reflects, rather than absorbs, a higher proportion of long-wave infra-red radiation. Ideally, the glazing should have exterior insulation, shutters or blinds to prevent heat loss during the night.
[edit] Find out more
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- Cross ventilation.
- Decrement delay.
- Diaphragm wall.
- Dynamic façade.
- Ground energy options.
- Insulation.
- Low-e glass.
- Natural ventilation.
- Passive building design.
- Passive ventilation.
- Solar chimney.
- Solar thermal systems.
- Stack effect.
- Thermal admittance.
- Thermal labyrinth.
- Thermal mass.
- Types of ventilation.
- Ventilation.
- Wall types.
Featured articles and news
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherit assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.
The 2025 draft NPPF in brief with indicative responses
Local verses National and suitable verses sustainable: Consultation open for just over one week.
Increased vigilance on VAT Domestic Reverse Charge
HMRC bearing down with increasing force on construction consultant says.
Call for greater recognition of professional standards
Chartered bodies representing more than 1.5 million individuals have written to the UK Government.
Cutting carbon, cost and risk in estate management
Lessons from Cardiff Met’s “Halve the Half” initiative.
Inspiring the next generation to fulfil an electrified future
Technical Manager at ECA on the importance of engagement between industry and education.
Repairing historic stone and slate roofs
The need for a code of practice and technical advice note.
Environmental compliance; a checklist for 2026
Legislative changes, policy shifts, phased rollouts, and compliance updates to be aware of.