Double glazing
The term 'glazing' refers to the glass component of a building's façade or internal surfaces.
Historically, the external windows of buildings were generally single glazed, consisting of just one layer of glass, however, a substantial amount of heat is lost through single glazing, and it also transmits a significant amount of noise, so mulit-layerd glazing systems were developed such as double glazing and triple glazing.
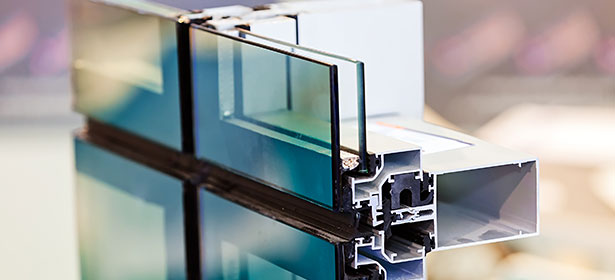
Double glazing comprises two layers of glass separated by a spacer bar (also known as a profile); a continuous hollow frame typically made of aluminium or a low heat-conductive material. The spacer bar is bonded to the panes using a primary and secondary seal which creates an airtight cavity, typically with 6-20 mm between the two layers of glass. This space is filled with air or with a gas such as argon, which improves the thermal properties of the window. Larger cavities may be provided to achieve greater sound reduction.
A desiccant in the spacer bar absorbs any residual moisture within the cavity, preventing internal misting as a result of condensation.
U-values (sometimes referred to as heat transfer coefficients or thermal transmittances) are used to measure how effective elements of a buildings fabric are as insulators. That is, how effective they are at preventing heat from transmitting between the inside and the outside of a building. Typically, the U-value of single glazing is around 4.8 to 5.8 W/m²K, whilst double glazing is around 1.2 to 3.7 W/m²K. NB Triple can achieve a U-value below 1 W/m²K.
Thermal performance is affected by the quality of the installation, the inclusion of thermal breaks in the frame, suitable weather seals, the gas used to fill the units, and the type of glass used. Low-e glass has a coating added to one or more of its surfaces to reduce its emissivity so that it reflects, rather than absorbs, a higher proportion of long-wave infra-red radiation..
The sound reduction achieved by single glazing (6 mm thick) is typically around 27 dB, whilst double glazing (100 mm air space) is around 42 dB.
The sound reduction achieved by double glazing is affected by:
- Good installation to ensure airtightness
- Sound absorbent linings to the reveals within the air space.
- The weight of glass used – the heavier the glass, the better the sound insulation.
- The size of air space between layers - up to 300 mm.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- Air tightness in buildings.
- BFRC window rating scheme.
- Choosing the correct glazed facade heating system.
- Conservation rooflights.
- Domestic windows.
- Double glazing v triple glazing.
- Glass.
- Glazing.
- Low-E glass.
- Sash windows.
- Secondary glazing.
- Thermal conduction in buildings.
- Triple glazing.
- Types of window.
- U-values.
- Window.
Featured articles and news
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.
























Comments