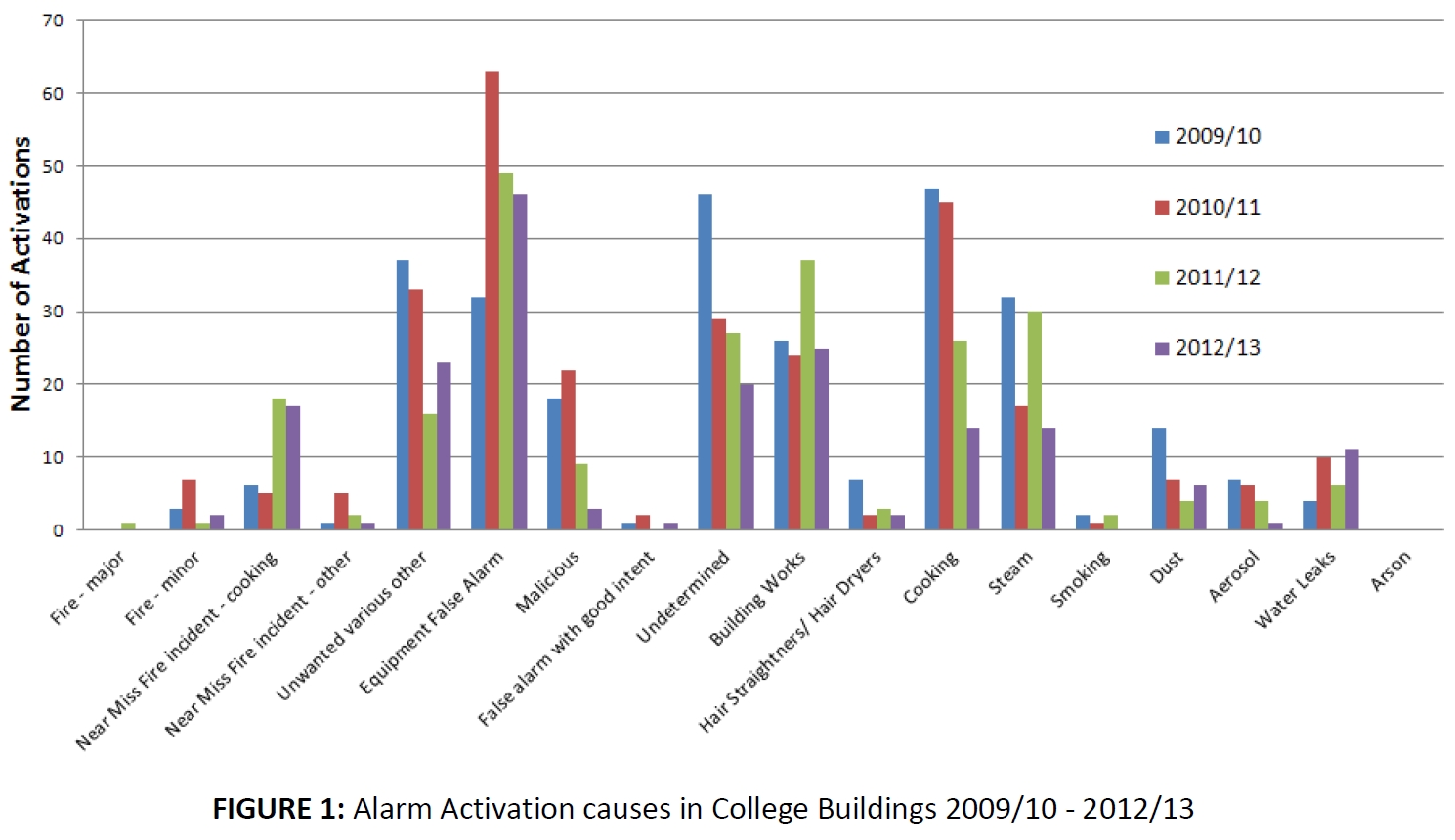
The causes of false fire alarms in buildings
A false alarm is a fire alarm signal resulting from a cause, or causes, other than a fire, in which a fire detection and alarm system has responded, such as:
- A fire-like phenomenon or environmental influence (such as smoke from a nearby bonfire).
- Accidental damage.
- Inappropriate human action (such as malicious manual call point (MCP) activation).
- Equipment false alarms, resulting from a fault in the system.
A false alarm becomes an unwanted fire signal (UWFS) when the Fire and Rescue Service (FRS) is requested to attend.
In the period 2011-2012 there were 584,500 alarms reported in Britain. 53.4% of these were not fires and therefore considered “False alarms”. This is a drain on the FRS authorities and causes business disruptions leading to a loss of productivity and reducing the confidence of the general public.
False alarms generated from remotely monitored fire detection and fire alarm systems cost businesses and FRS authorities an estimated £1 billion a year in the UK. Ref London Fire Brigade 2012.
The causes of false fire alarms in buildings was written by R. Chagger, D. Smith and published by BRE Global in 2014. The briefing paper collates information about the causes of false alarms in buildings and identifies approaches to reduce their occurrence.
It was based on data from Kings College London and Buckinghamshire & Milton Keynes Fire Authority. The data supplied provides a snapshot of the types of false alarms that are observed but is not a comprehensive account of what might be the most common causes in the UK.
Kings College London provided data from 699 false alarm incidents and following a thorough review of the data, 6 physical interventions were identified that would address all of the false alarms reported. Replacement of the existing detectors with intelligent multi-sensor detectors (that detect more than one fire phenomena) was the solution that could reduce false alarms the most (by 69%).
Discussions with the Unwanted Fire Signals Officer of Buckinghamshire and Milton Keynes Fire Authority and analysis of their false alarm trends revealed that the use of a technical and experienced individual dedicated to investigating false alarms and engaging directly with regular offenders is a very effective means for FRS’s to reduce false alarms.
However, reducing the number of false alarms from domestic premises remains a challenge despite the fact that the vast majority are reportedly related to cooking incidents. Educating homeowners on effective installation and use of detectors in and around kitchens is likely to lead to the greatest reduction in false alarms from the domestic environment.
The Incident Recording System, used by Fire Officers to report on all callouts attended, lacks sufficient detail to accurately classify false alarm causes. However educating building owners, responsible persons and the general public could contribute significantly to reducing false alarms as simple measures can often cause notable reductions.
In addition, the increased use of multi-sensor detectors may avert false alarms from common causes such as cooking fumes, steam and so on.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- BRE articles on Designing Buildings Wiki.
- Carbon monoxide detector.
- Fire.
- Fire detection and alarm system.
- Fire performance of external thermal insulation for walls of multistorey buildings, third edition (BR 135).
- Fire protection engineering.
- Heat alarm.
- Ionisation smoke alarm.
- Intruder alarm.
- Live investigations of false fire alarms.
- Multi-sensor alarm.
- New requirements for fire detection and alarm network systems IP 12 13.
- Optical smoke alarm.
- Over £1 billion lost every year due to false alarms.
- Project SHOUT.
- Smoke alarm.
- The role of codes, standards and approvals in delivering fire safety.
- Understanding the factors affecting flashover of a fire in modern buildings.
Featured articles and news
Call for greater recognition of professional standards
Chartered bodies representing more than 1.5 million individuals have written to the UK Government.
Cutting carbon, cost and risk in estate management
Lessons from Cardiff Met’s “Halve the Half” initiative.
Inspiring the next generation to fulfil an electrified future
Technical Manager at ECA on the importance of engagement between industry and education.
Repairing historic stone and slate roofs
The need for a code of practice and technical advice note.
Environmental compliance; a checklist for 2026
Legislative changes, policy shifts, phased rollouts, and compliance updates to be aware of.
UKCW London to tackle sector’s most pressing issues
AI and skills development, ecology and the environment, policy and planning and more.
Managing building safety risks
Across an existing residential portfolio; a client's perspective.
ECA support for Gate Safe’s Safe School Gates Campaign.
Core construction skills explained
Preparing for a career in construction.
Retrofitting for resilience with the Leicester Resilience Hub
Community-serving facilities, enhanced as support and essential services for climate-related disruptions.
Some of the articles relating to water, here to browse. Any missing?
Recognisable Gothic characters, designed to dramatically spout water away from buildings.
A case study and a warning to would-be developers
Creating four dwellings... after half a century of doing this job, why, oh why, is it so difficult?
Reform of the fire engineering profession
Fire Engineers Advisory Panel: Authoritative Statement, reactions and next steps.
Restoration and renewal of the Palace of Westminster
A complex project of cultural significance from full decant to EMI, opportunities and a potential a way forward.
Apprenticeships and the responsibility we share
Perspectives from the CIOB President as National Apprentice Week comes to a close.