Climate emergency - time for action

|
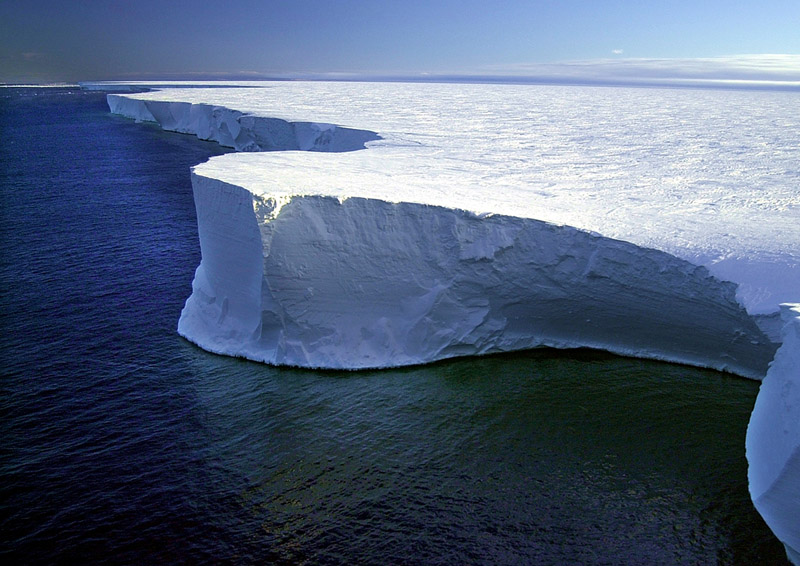
| Civil engineers should be helping society with valid concerns on climate change and helping with coming emergencies. Robert Thorniley-Walker reviews past and future needs. Photo caption: Arctic summer ice volumes have fallen exponentially in the past 40 years and could disappear by 2025, |
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
Younger civil engineers have started to demand action in a profession that once claimed to control the natural environment. As suggested by a former Institution of Civil Engineers (ICE) task force (Kermode, 2017), civil engineers are pleased to help resist the impact of the changing environment, but they also need to admit to their role and responsibility in heating the planet.
[edit] Assessing the environmental fallout
Construction continues to cause around 17% of world greenhouse gas emissions, so it must be time to assess the risks from the industry’s short-term impact, as originally recommended by the UK Engineering Council in 1994. Instead, there has been extraordinary inertia over the past few decades. Many question how and why they should act without firm proof of danger, pointing out that land temperatures almost stopped rising at one point.
Instead the profession’s efforts in recent years have centred on achieving social and economic sustainability, using established high-carbon-dioxide solutions, and delivering the United Nations’ 17 sustainable development goals, even though only one involves the critical issue of climate change. Furthermore targets, codes of practice and even climate-emergency declarations tend to consider whole-life emissions over 60−120 years rather than current emission levels.
[edit] Forensic view of environmental risks
ICE has published many papers, often in its Engineering Sustainability journal, on aspects of engineering in relation to climate change, but remarkably few concentrate on the underlying causes and likely conditions to be met. ICE’s Forensic Engineering journal has published two useful themed issues (Thorniley-Walker, 2015a and 2017) by climate scientists and engineers, giving updates on the exponential temperatures, design needs and risk, Arctic sea-ice melt, flood risks and new hurricane risks.
When pressed, even sceptical civil engineers accept there are real and imminent dangers from climate change. Surveys of opinions by the author (Thorniley-Walker, 2015b) have, for example repeatedly indicated that for 2°C of warming, 10% of the world population will need to move, for 3°C 35% of lives will be at risk and for 5°C only 45% of the population will survive. There will soon be blame and liability for major loss of livelihoods and life among the younger generation and their children, especially in the most vulnerable of countries.
[edit] Engineers are part of the problem
In October 2019, the Institution of Structural Engineers held an emergency climate conference,which revealed some alarming statistics. For example, a typical engineer has a carbon dioxide footprint of 1000 t/year, compared to the hard-won savings of just 2t/year from a vegan diet. Civil engineers must refurbish rather than demolish. Replacing concrete and steel and in new-build with stone and solid timber even offers the potential to store carbon in the short to medium term. However, the planet’s eco-system has already been degraded. Clearly the profession needs to stop being part of the problem and instead drive change and restoration.
The key issue is that civil engineers should be using simple risk assessments to address the hazards to and from projects, and particularly the incremental global impacts from the short-term emissions. They then need to have confidence to help society with the approaching climate emergencies.
Civil Engineering is planning a special issue in 2021 on how civil engineers can rise to the challenge of climate change. Read the call for papers.
[edit] About this article
This article, written by ice.org.uk Robert Thorniley-Walker, ex-ICE Climate Task Force member, is based on his briefing article in the 173 CE1 issue of the ICE Civil Engineering journal. It also appeared on the ICE website in January 2020 and can be accessed HERE.
Other articles by the ICE on Designing Buildings Wiki can be accessed HERE.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- Biomass.
- BREEAM Adaptation to climate change.
- Carbon capture processes.
- Carbon emissions.
- Carbon plan.
- Climate Change Act.
- COP21 Paris 2015.
- Emission rates.
- Energy.
- Energy targets.
- Environmental modelling.
- Environmental policy.
- Everything we thought we knew about civil engineering improving the world is wrong.
- Global warming and the tipping point precipice.
- Globe temperature.
- Green Deal.
- Green plot ratio.
- Greenhouse gases.
- Happold lecture on climate change.
- ICE launches engineering route map to deliver UN SDGs.
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change IPCC.
- Kyoto Protocol.
- Not a choice between renewables and nuclear - we need both.
- Radiation.
- RIBA Stirling Prize winners' open letter declaring climate and biodiversity emergency.
- Sustainability.
- UN Sustainable Development Goals.
Featured articles and news
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.
The 2025 draft NPPF in brief with indicative responses
Local verses National and suitable verses sustainable: Consultation open for just over one week.
Increased vigilance on VAT Domestic Reverse Charge
HMRC bearing down with increasing force on construction consultant says.
Call for greater recognition of professional standards
Chartered bodies representing more than 1.5 million individuals have written to the UK Government.