Segal Method

|
| All images © Taran Wilkhu. |
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
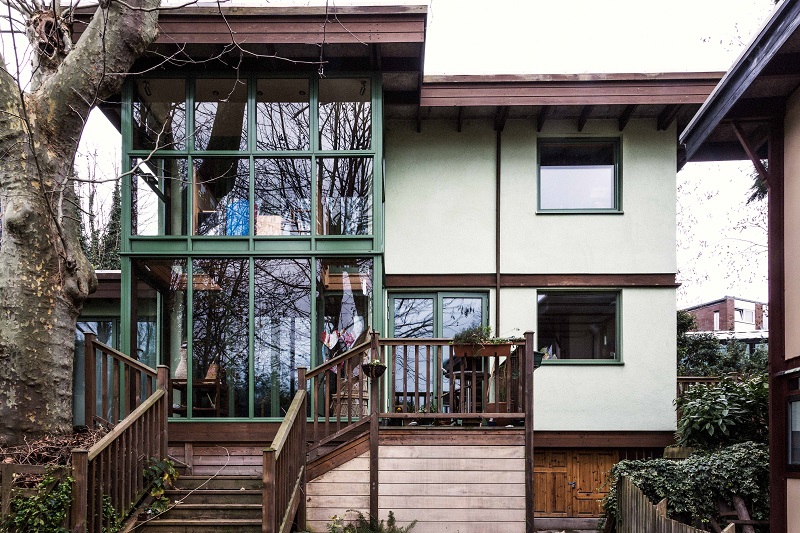
Walter Segal (1907-1985) was a Berlin-born architect who emigrated to England in the 1930s and, in the 1960s, devised the Segal Method of self-building using timber-frame construction. Designed to be simple enough for ordinary people to build their own homes – even without building experience – it is also a minimalist and rational approach to architecture.
[edit] Background
In 1962, Segal needed temporary accommodation for his family in North London and used his system to build a house with paving-slab foundations in just two weeks at a materials’ cost of £800 (around £12,000 at today’s prices). His aim was to ensure that after use, the house could be easily dismantled and the materials recycled or sold. Two of Segal’s major projects in London include houses at Segal Close and Walter’s Way.
These projects were followed by a succession of private clients impressed by the speed and economy of the system, not to mention numerous architects who have used Segal’s method for themselves or their clients. The system was also adopted by Lewisham Council in the 1970s and many examples exist in that borough. More exposure has been given by recent TV shows such as Grand Designs and the general growing popularity of self-build in the UK.
[edit] Principles of the Segal Method
Segal’s method involves simply-constructed timber frames with bolted connections which eliminate wet trades such as bricklaying and plastering. The system has been designed to ensure that potentially problematic construction issues such as tolerances and thermal movement are accommodated without complex construction details.
In summary, the principles of the Segal System are:
- A pervasive attitude of rigorous simplification.
- Timber, bolt-together, post-and-beam-based construction.
- The majority of the work can be undertaken by a single person with basic carpentry skills (although assistance may be required for roofing and services).
- The use of only basic tools e.g hammer, saw, plane, spade, drill/driver, tape measure etc.
- Use of readily-available materials in standard sizes, so there is minimal cutting and waste.
- Typically, 600mm x 600mm concrete pad foundations under posts, so strip foundations are not required, and concrete usage is reduced by around 20%.
- No oversite concrete is used – the ground floor stands above the ground.
- No wet trades are required.
- Can accommodate higher insulation levels.
- Easy to extend.
- Proven to work up to three storeys.
- Can achieve Passivhaus or zero-carbon levels.
As a result, large savings in build costs can be achieved.
In devising the system, Segal rethought the build process from first principles to incorporate ways of dealing with fundamental problems such as thermal expansion and tolerances. Working to standard material sizes, organisation and construction are facilitated by the use of a grid layout.
Because the system is predicated towards self-build and those with few construction skills, component assembly is based on dry joints using simple bolts and screws. The process is further simplified by the drawings required – they can typically be hand-drawn diagrams of the layout and structure. However, as with ordinary houses, planning approval and building regulations approval will generally be required.
Various configurations can be constructed, including one or two-storeys, flat- or pitched-roofs, double-height spaces, split levels and courtyards.
[edit] Appendix
[edit] Photographs taken during construction

|

|
• Photographs showing the Segal Method in action.
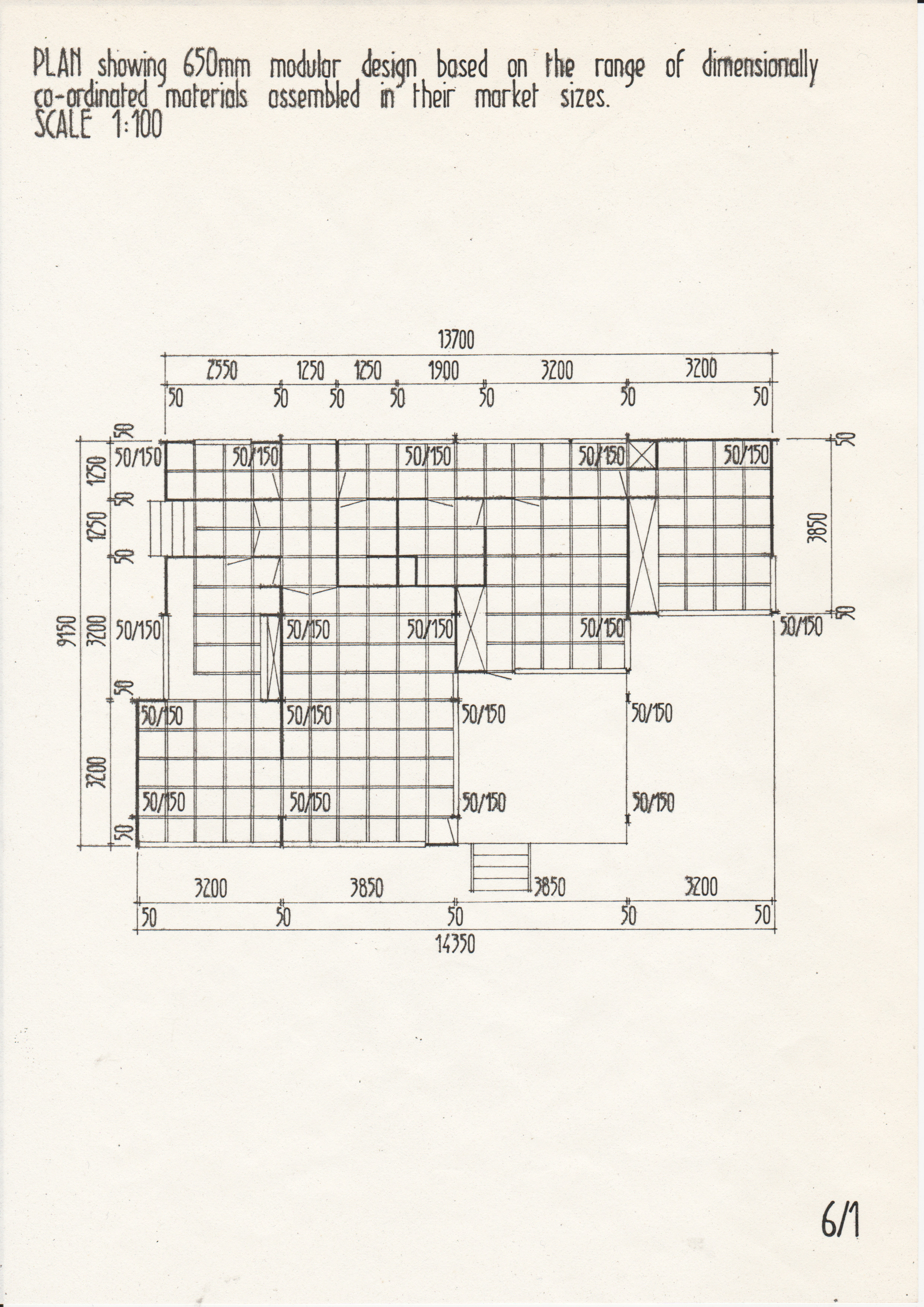
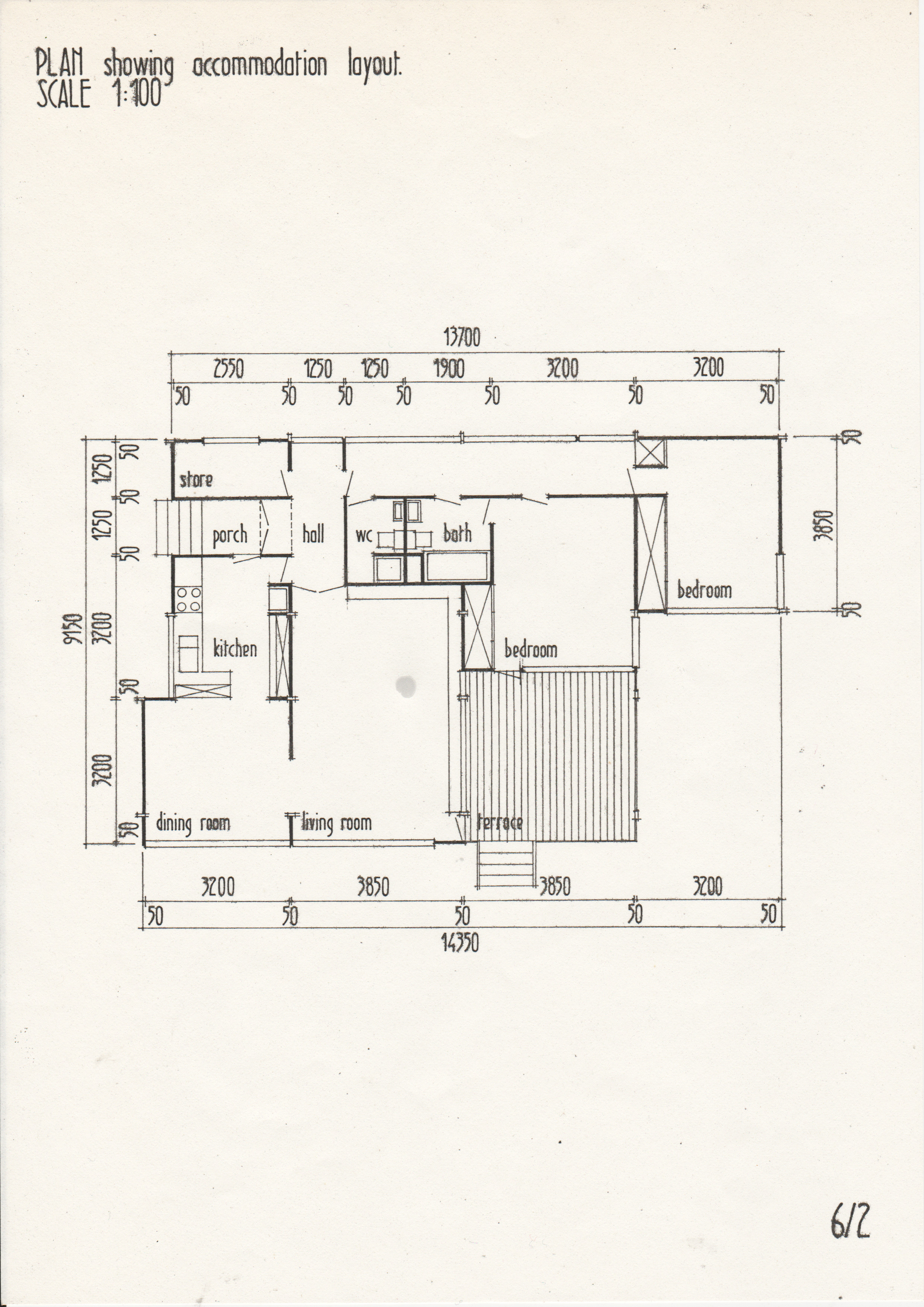
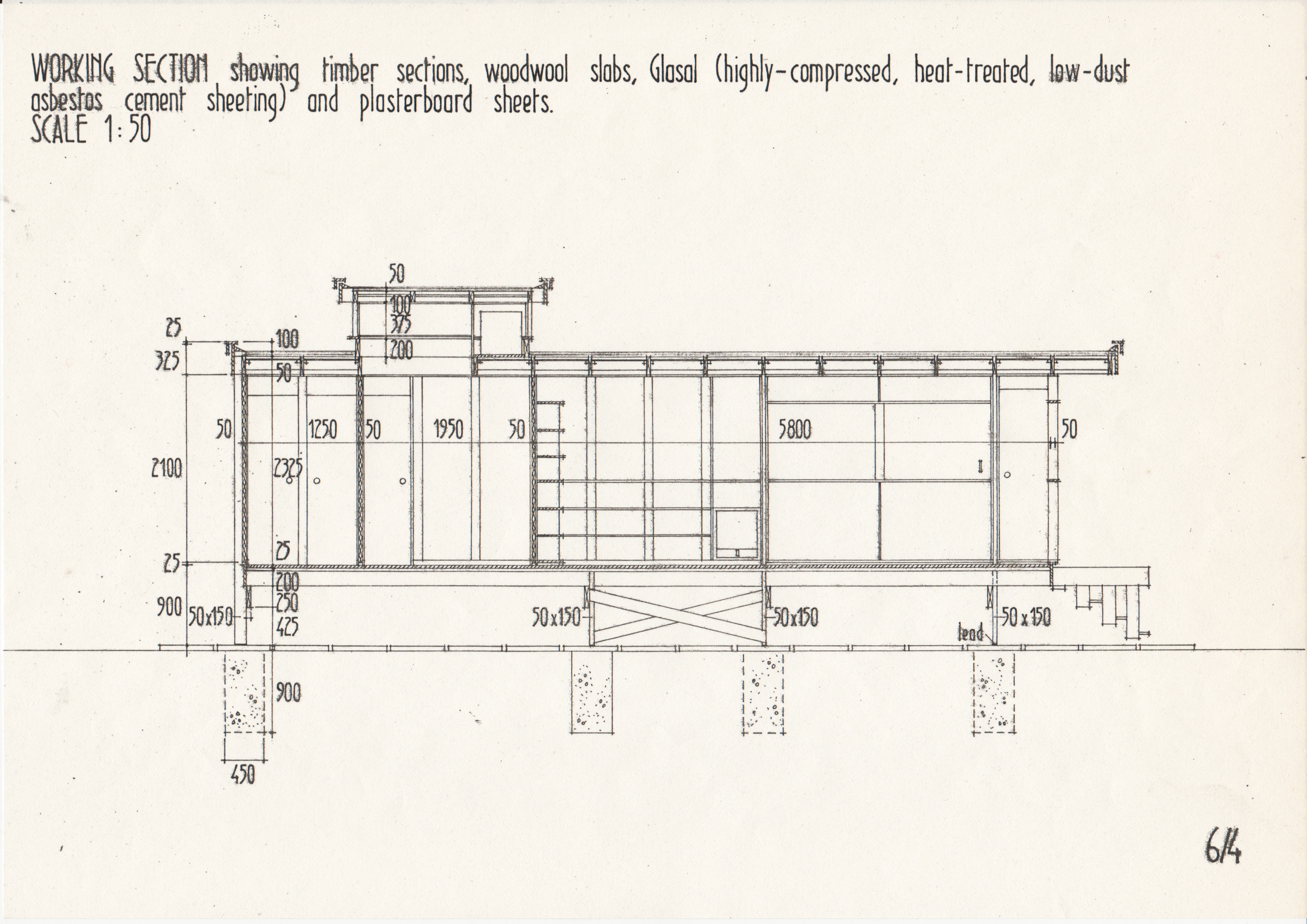
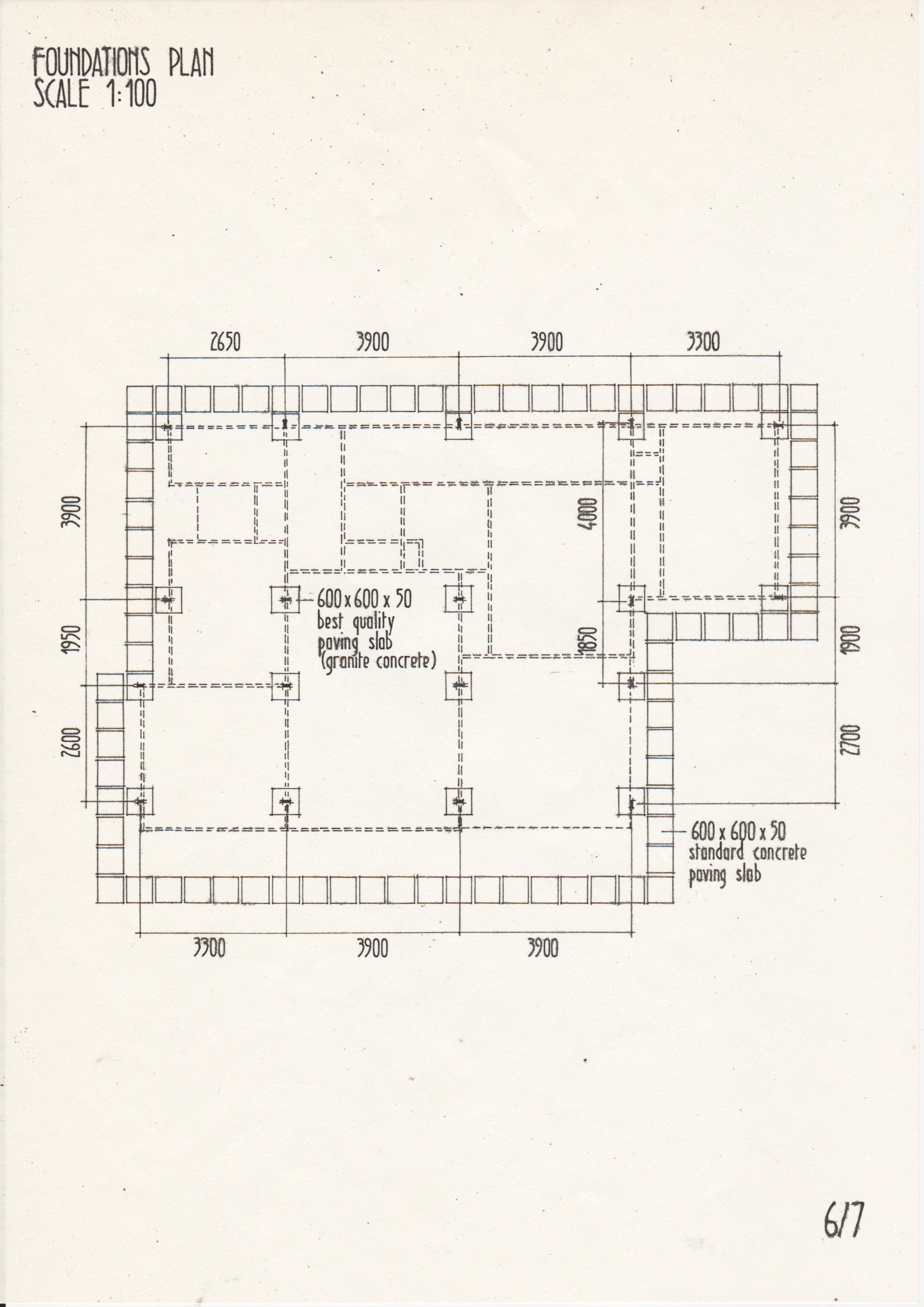
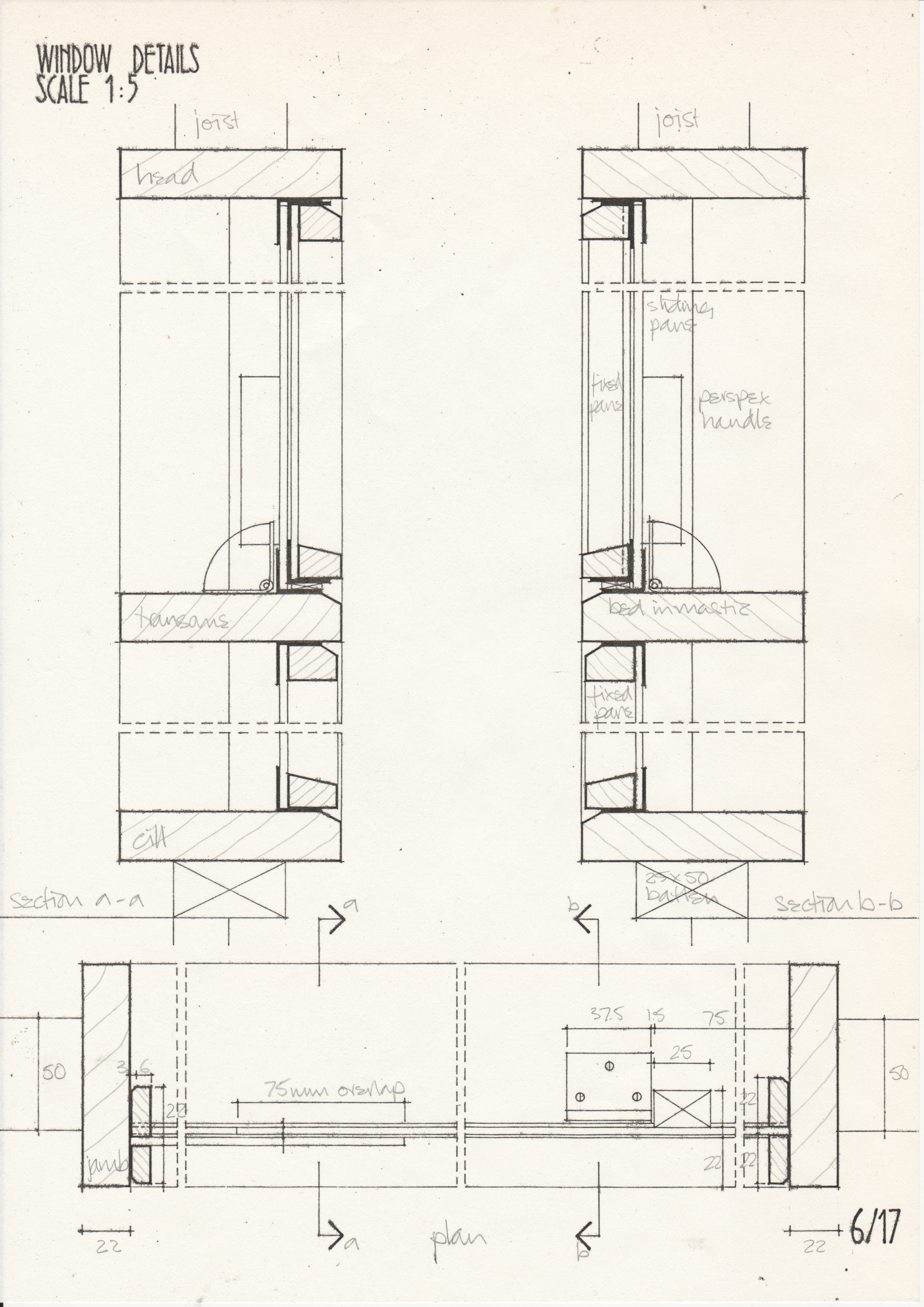
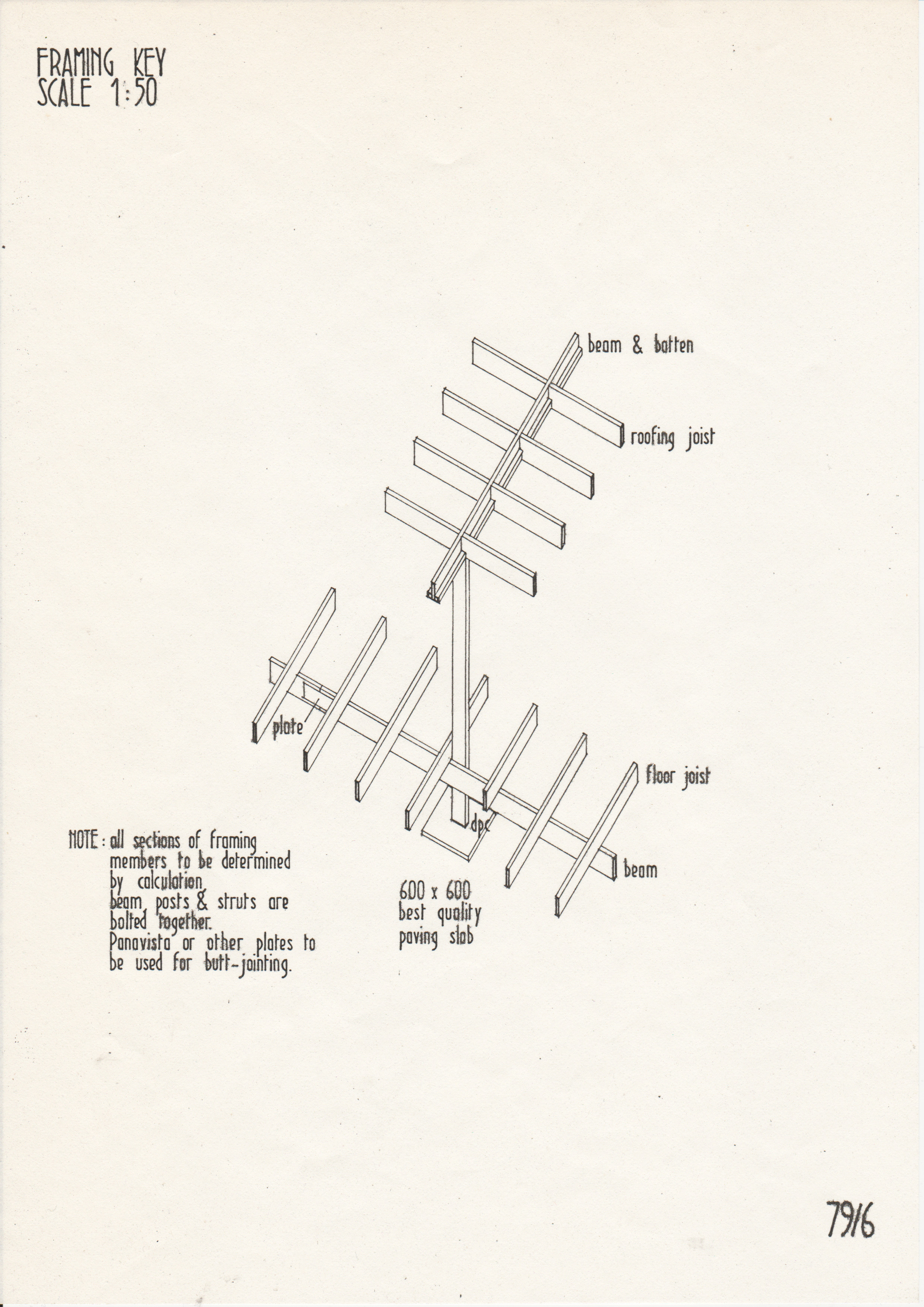
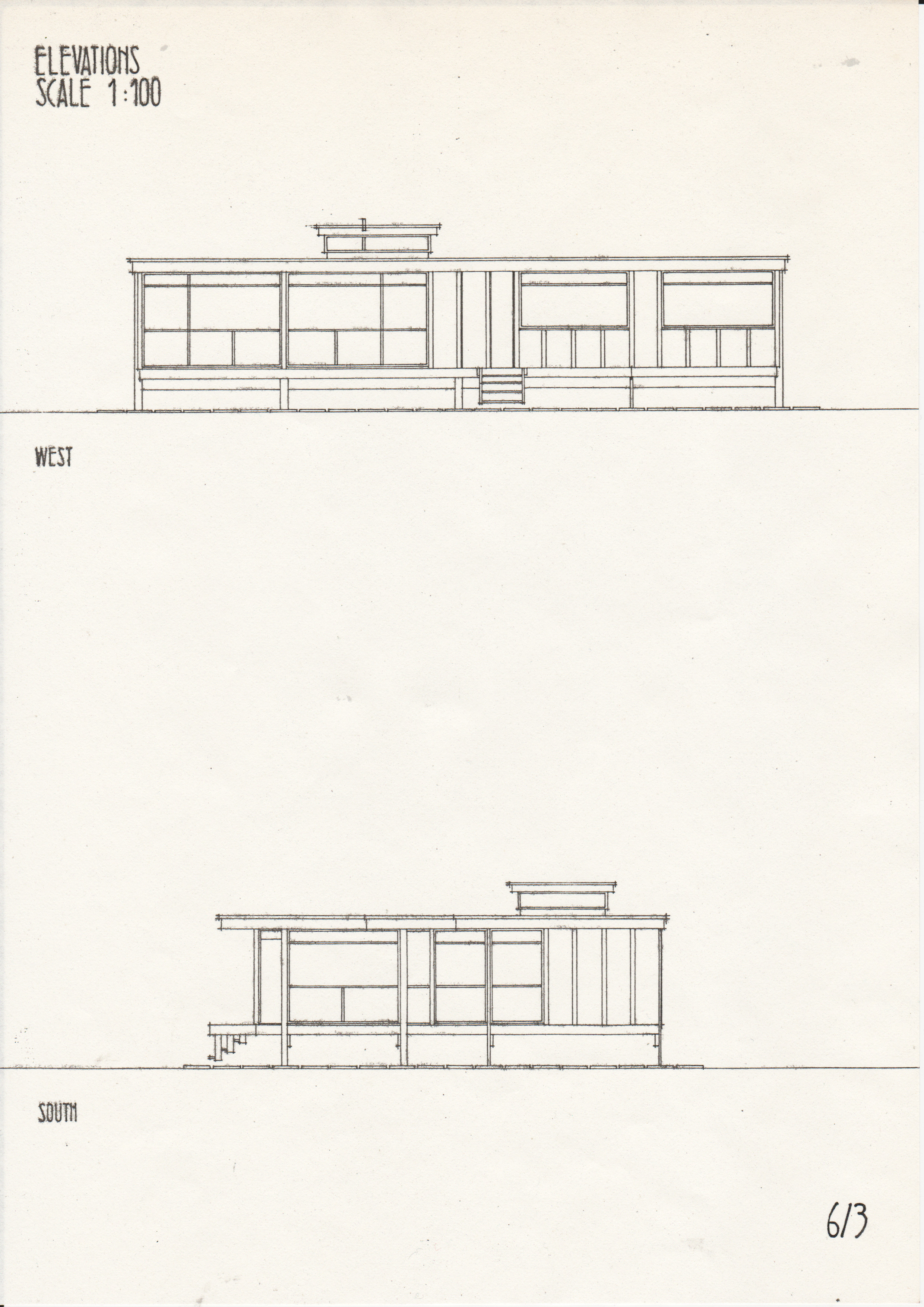
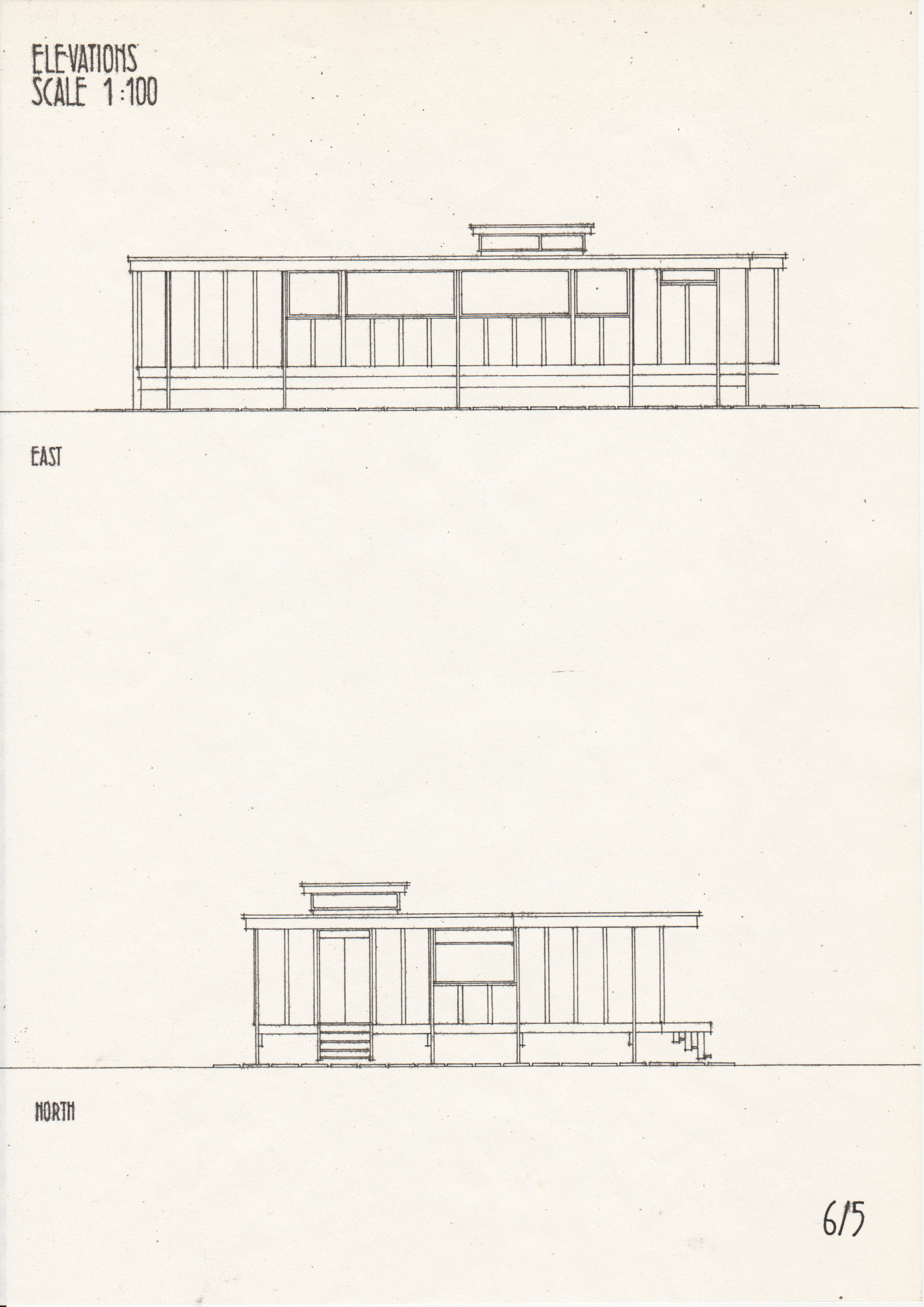
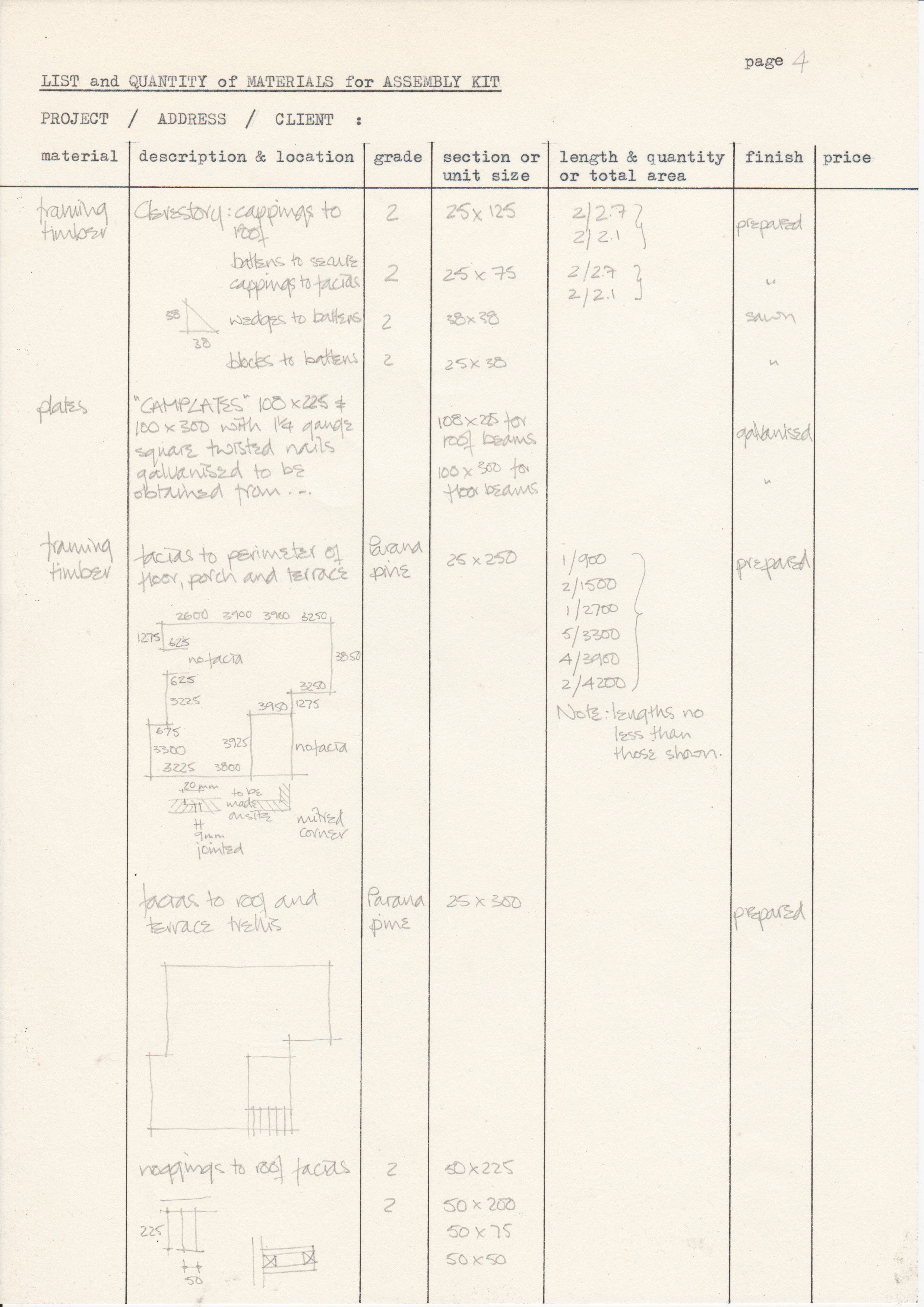
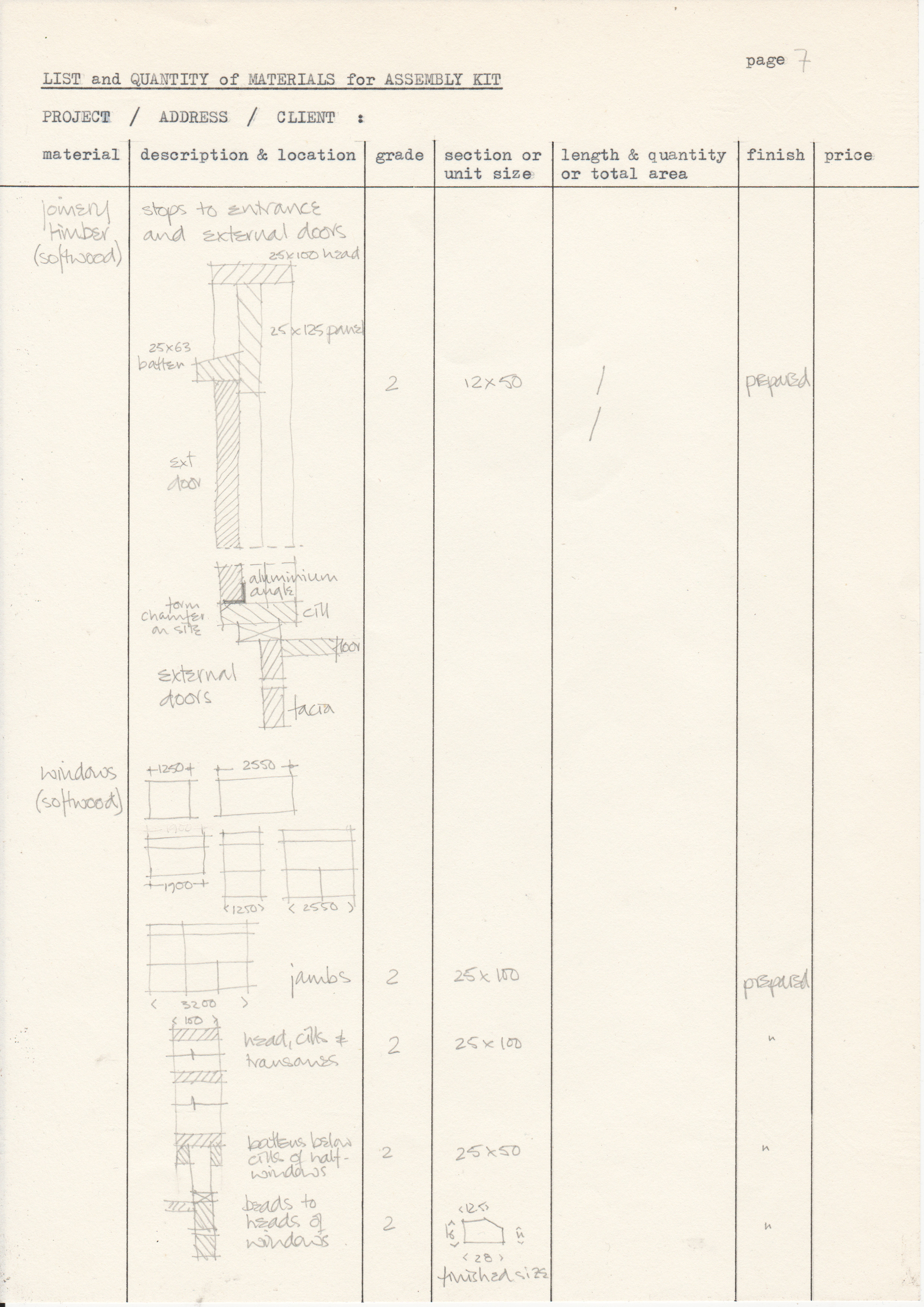
[edit] Typical drawings
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
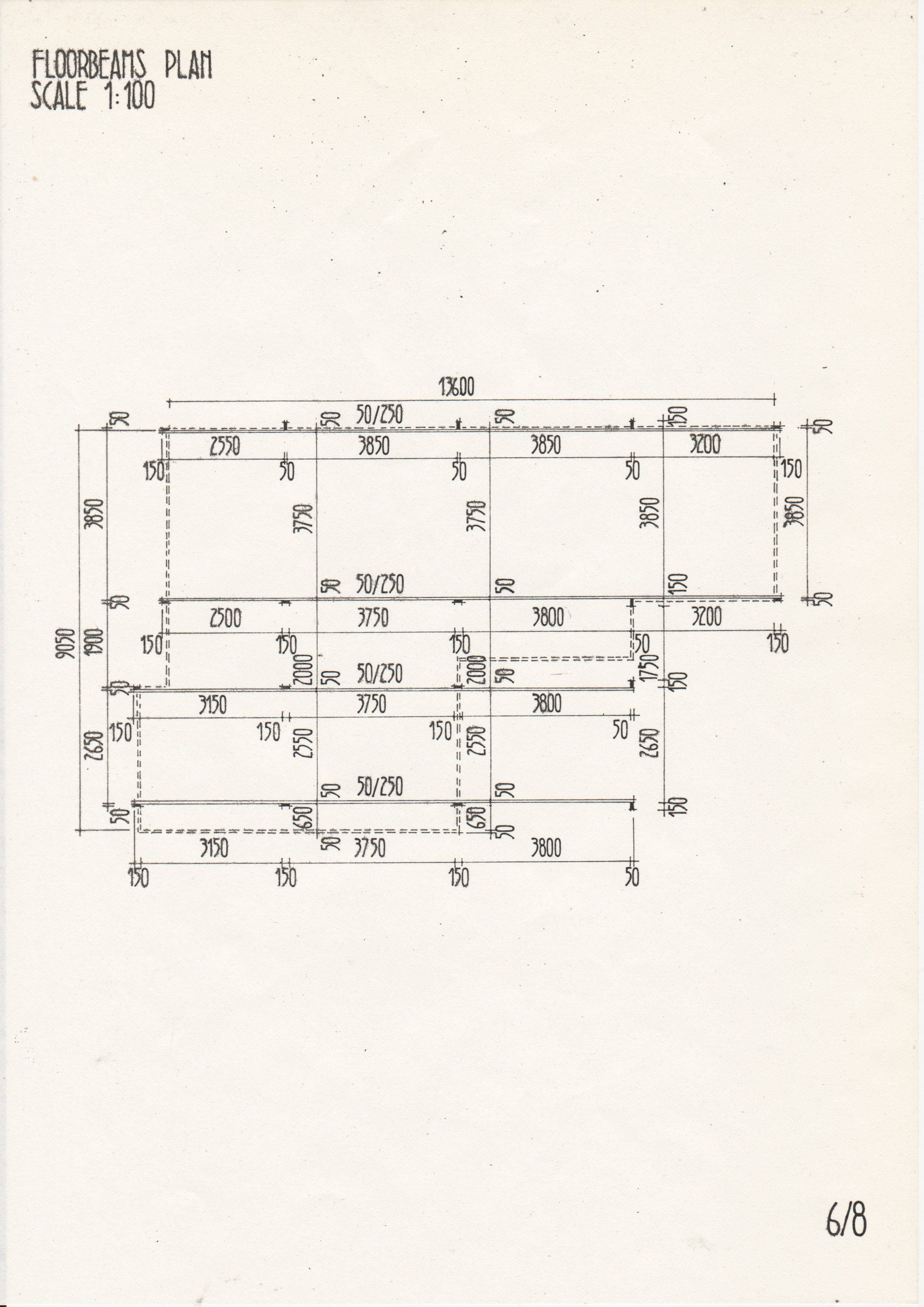
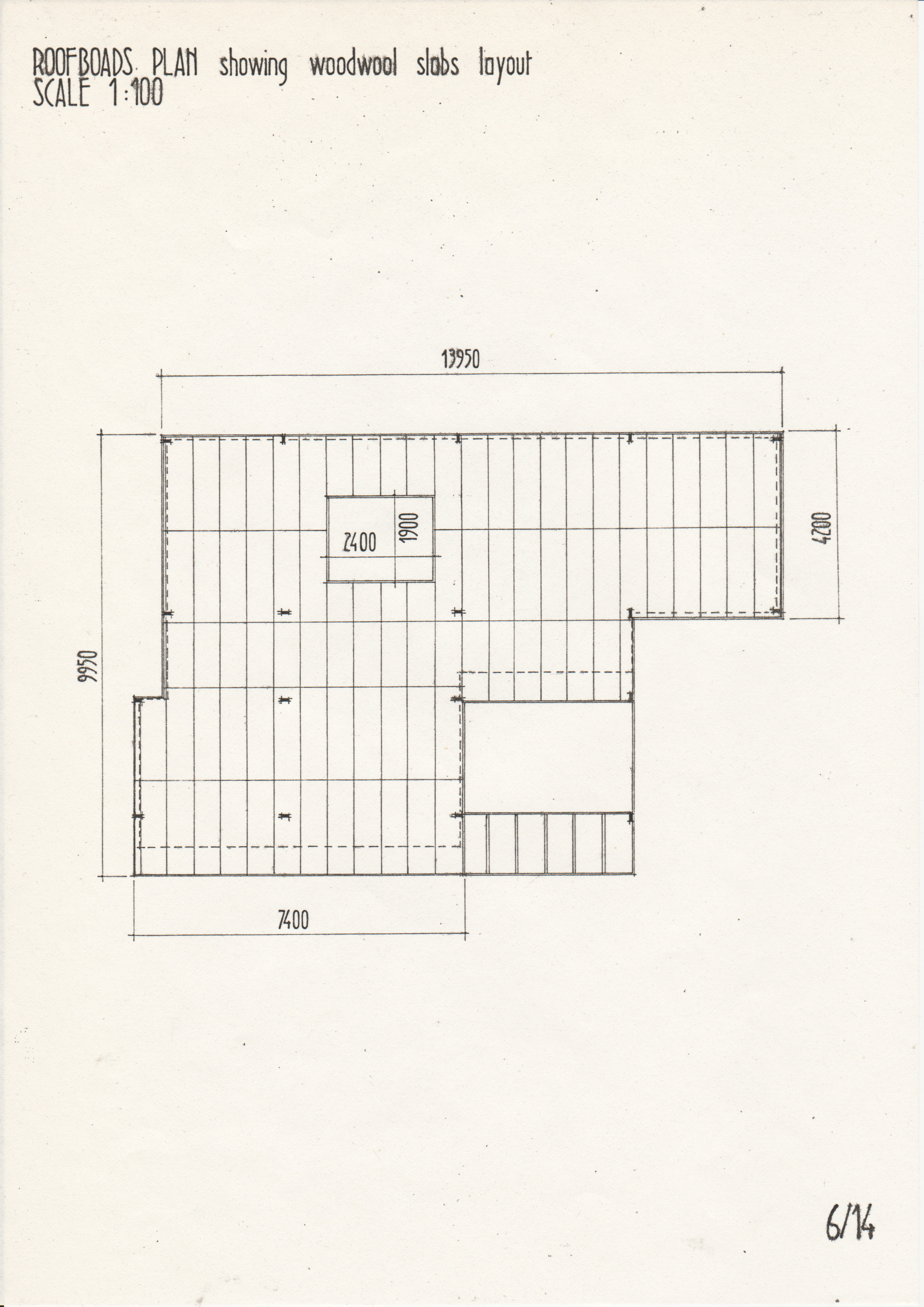
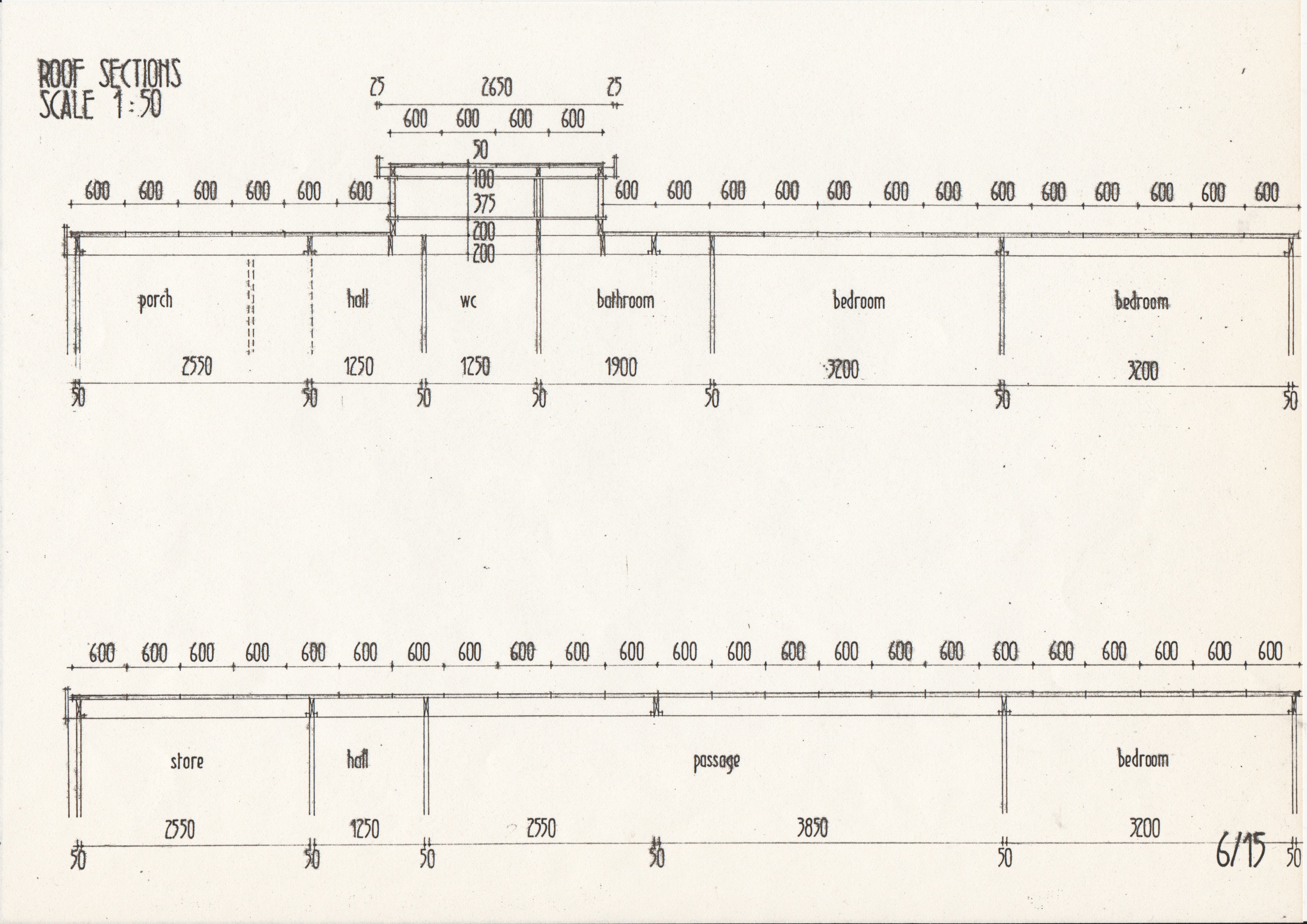
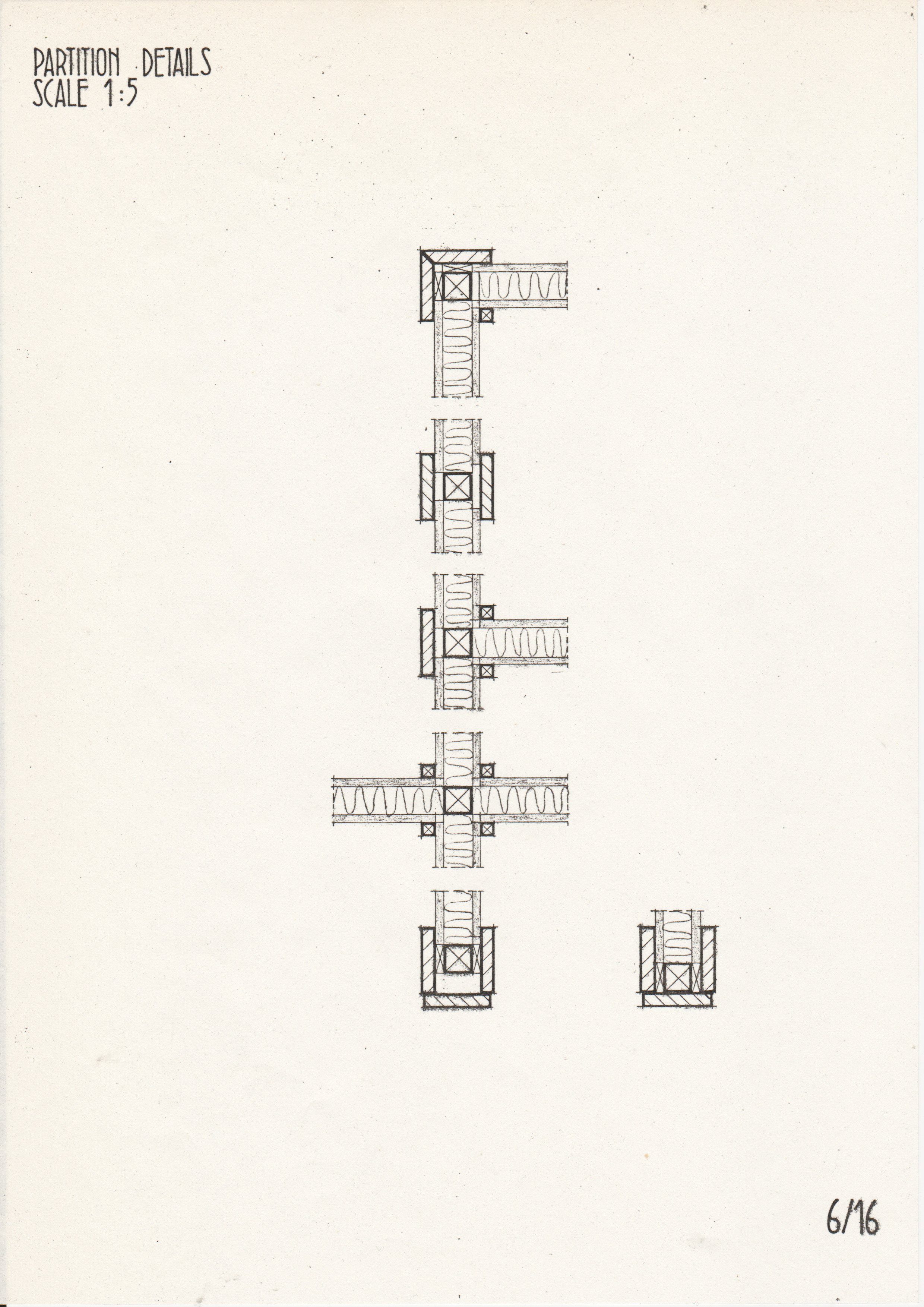
• Drawings from a case study of the Segal Method by Norman Fellows.
[edit] Videos - 'How to build a Walter Segal house'
• Two step-by-step videos showing how to build a Walter Segal house - VID_0082: Steps 1 to 4 and VID_0085: Steps 5 to 8 - both courtesy of Norman Fellows.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Britain's greatest maverick building.
- Building an extension.
- Building of the week series.
- Community right to build.
- Cul-de-sac.
- Custom-build homes.
- Dennis Severs house.
- Interview with Kevin McCloud.
- Open House London 2017.
- Self-build homes.
- Self-build home project plan.
- Walter Segal: self-built architect.
- Walter Way and Segal Close.
Featured articles and news
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help the homebuilding sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.




























Comments
The info is great and most welcome. I'm also delighted to find people here endorsing the open web type culture that used to be more common online. So much of Segal's writing seems to be hidden behind paywalls or foreign libraries. But for us nerds, this stuff is actually going away, for good.
Dominic Stevens did a version of a Segal House in Ireland, with a great website (IrishVernacular) showing how in detail. The website has been down for years but I have collected the contents of the website into a PDF for anybody reading who is interested in a hardcopy. Dominic won't mind for what it's worth, he setup the website in the first place to spread the word and even wrote a book explaining he understood himself as having a debt to the community which was why he documented the build and webbed it.
Internaut Email: [email protected]
I'm looking at the Segal method to produce a really low-impact, inexpensive, environmentally advanced (e.g. solar panels on sloping roofs) series of buildings around a proposed lido. Do you know if anyone else has used the method for anything other than housing? We need changing rooms, a cafe, probably some sort of plant room. I'm pretty confident I could design it but it would help persuade the local authority if there are existing examples. Any help/advice would be gratefully received. Thank you.
Judith Martin
Hi Judith
I suggest you contact the others (eg Lewisham, Brighton) who have built using Segal. I am sure the method can be adapted to suit your needs. I'm curious why you need to persuade the local authority - are they funding?