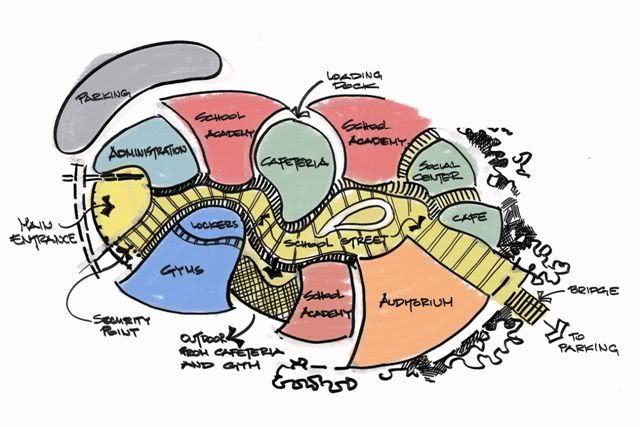
Spatial diagram
A spatial diagram, or spatial plan, can be used to investigate or illustrate the future spatial development of an area. It communicates a development concept as physical spatial elements and demonstrates how extending and developing spatial uses and infrastructure can shape a location, district or region.
The development of spatial diagrams requires imaginative and innovative ideas. Inspiration for developing a spatial diagram is often drawn from the results of other district or regional analysis methods.
A spatial diagram may give indications as to the highest priority areas to be developed, as well as decisions on the settlement pattern for development in the future. Approximate scales are used for the diagram in order to avoid committing to detail. More specific land use plans are developed once a decision has been taken to implement certain elements of a diagram.
A spatial diagram is not constrained by time, but is designed to be a flexible model, capable of providing guidance and information to urban planners and decision-makers in optimising investment. Such investment can encourage and enable economic and social development, and may result in the progressive delivery of the spatial diagram over time.
Investment decisions are often taken, particularly effecting urban centres, with consideration of functional specialisation to avoid too much competition and duplication, which can lead to a decline in markets or services. Spatial diagrams can be used to assist in this planning work, with what is termed a 'settlement pattern'. This indicates issues such as whether or not the economies of the main urban centres are to be further developed or consolidated, whether urban specialisation should be either maintained or encouraged, and so on.
As well as the settlement pattern, information that is often provided on a spatial diagram may include:
- Road networks.
- The land use system.
- Conservation areas.
- Areas where development is to be restricted or controlled.
Some of the benefits of using a spatial diagram include:
- It is a useful method for reviewing proposed development policies and how they may interrelate functionally with ‘space’.
- It provides a framework for guiding an area’s development.
- It can coordinate development activities undertaken by different planning institutions, organisations or departments.
- It can provide guidance to decision-makers and planners about strategic investment decisions.
Some of the limitations of using a spatial diagram include:
- Spatial diagrams do not contain a time line for development.
- The costs and resource mobilisation required are not illustrated, and so, unless previous analytical steps, such as demographic projections and locational evaluations, have been undertaken, the diagram can be misleading.
- There is the risk that spatial diagrams can be interpreted as masterplans, rather than just being used to guide development decisions.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
Featured articles and news
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help the homebuilding sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.