Raft foundation
Contents |
[edit] What are foundations?
Foundations provide support for structures, transferring their load to layers of soil or rock that have sufficient bearing capacity and suitable settlement characteristics.
Very broadly, foundations can be categorised as shallow foundations or deep foundations. Shallow foundations are typically used where the loads imposed by a structure are low relative to the bearing capacity of the surface soils.
Deep foundations are necessary where the bearing capacity of the surface soils is not adequate to support the loads imposed by a structure and so those loads need to be transferred to deeper layers with higher bearing capacity.
Shallow foundations include:
- Strip foundations (or footings).
- Pad foundations.
- Raft foundation.
[edit] What are raft foundations?
Raft foundations (sometimes referred to as raft footings or mat foundations) are formed by reinforced concrete slabs of a uniform thickness (typically 150 mm to 300 mm) that cover a wide area, often the entire footprint of a building. They spread the load imposed by a number of columns or walls over the area of foundation, and can be considered to ‘float’ on the ground as a raft floats on water.
[edit] Where are raft foundations appropriate?
They are suitable where:
- Floor areas are small and structural loadings are low, such as in one or two-storey domestic buildings.
- A basement is required.
- Ground conditions are poor and strip or pad foundations would require significant excavation, for example on soft clay, alluvial deposits, compressible fill, and so on.
- Settlement, or differential settlement is likely.
- Where it may be impractical to create separate strip or pad foundations for a large number of individual loads. In very general terms, if strip or pad foundations would cover 50% or more of the floor area, then a raft may be more appropriate.
Raft foundations can be fast and inexpensive to construct, as they tend not to require deep excavations compared to strip or pad foundations and they may use less material as they combine the foundation with the ground slab. However, they tend to be less effective where structural loads are focussed on a few concentrated areas, and they can be prone to erosion at their edges.
[edit] How are raft foundations constructed?
The design of raft foundations involves a number of disciplines, as consideration must be given not only to the structure itself, but also to; integration of other constructions (such as external walls), insulation, damp proofing and complex ground conditions such as the presence of groundwater, trees or contamination.
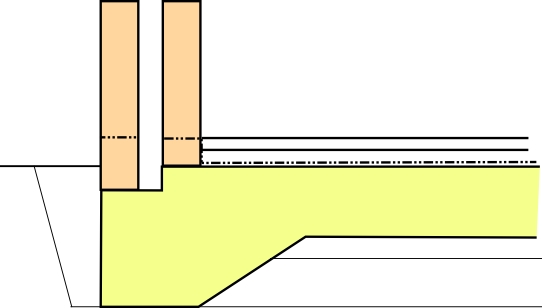
Raft foundations are generally constructed on a compacted hardcore base (perhaps 100 mm thick). A layer of blinding concrete (typically 50 mm) may then be laid with a waterproof membrane above to create an even, dry surface to allow formation of the raft .
The concrete raft tends to include steel reinforcement to prevent cracking, and may incorporate stiffening beams or thickened areas to provide additional support for specific loads, for example, below internal walls or columns (which may require punching shear reinforcement). Beams may stand proud of the raft, either above or below it, or may be 'hidden' beams, formed by reinforced areas within the depth of the raft itself. These thickened areas are particularly useful where there are poor ground conditions, as the required thickness of the raft itself might otherwise be uneconomic.
Typically, a thickened reinforced area is created at the perimeter of the raft to form an edge beam supporting the external walls of the building. A concrete toe often supports the external leaf of the wall.
Insulation will generally be laid on top of the raft, with a concrete floor, or raised floor above.
Drainage may be required under raft foundations in some circumstances, and geotextile barriers may be required to prevent free-draining materials from becoming clogged up by the surrounding soil.
[edit] What are the different types of raft foundation?
Types of raft foundation include:
- Solid slab raft, sometimes referred to as a plain raft, and including; flat rafts, mats, wide toe rafts, slip plane rafts, blanket rafts, and so on.
- Slab beam raft.
- Cellular raft.
- Piled raft.
For more information, see Types of raft foundation.
Where soil is compressible, a raft foundation may be formed as a compensated foundation. In this case, the raft slab is provided to a depth that the weight of the excavated soil is equal to the raft slab weight plus that of the structure to be supported. This can be appropriate when constructing buildings on soft clay or loose sand, as settlement can be significantly reduced.
For more information see: Compensated foundation.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
Featured articles and news
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.
The 2025 draft NPPF in brief with indicative responses
Local verses National and suitable verses sustainable: Consultation open for just over one week.
Increased vigilance on VAT Domestic Reverse Charge
HMRC bearing down with increasing force on construction consultant says.
Call for greater recognition of professional standards
Chartered bodies representing more than 1.5 million individuals have written to the UK Government.






















Comments
[edit] To make a comment about this article, click 'Add a comment' above. Separate your comments from any existing comments by inserting a horizontal line.