Piled raft foundation
Foundations provide support for structures, transferring their load to layers of soil or rock that have sufficient bearing capacity and suitable settlement characteristics.
Very broadly, foundations can be categorised as shallow foundations or deep foundations:
- Shallow foundations are typically used where the loads imposed by a structure are low relative to the bearing capacity of the surface soils.
- Deep foundations are necessary where the bearing capacity of the surface soils is not adequate to support the loads imposed by a structure and so those loads need to be transferred to deeper layers with higher bearing capacity.
When ground conditions rule out the use of ground bearing rafts or shallow strip foundations (less than 1.8m deep), a piled raft foundation often presents a more cost-effective and practical alternative.
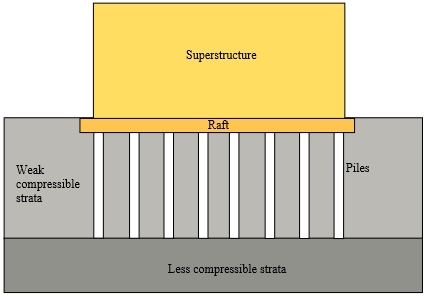
In their normal form, raft foundations (sometimes referred to as mat foundations) are shallow foundations formed by a reinforced concrete slab of uniform thickness (typically 150-300 mm) covering a wide area, often the entire footprint of a building. This 'raft' spreads the load imposed by a number of columns or walls over the area of foundation, and can be considered to ‘float’ on the ground as a raft floats on water.
However, where a conventional raft foundation does not provide adequate support, it can be enhanced by the addition of piles, creating what is known as a piled raft foundation.
Piles are deep foundations. They are formed by long, slender, columnar elements typically made from steel or reinforced concrete. A foundation is described as 'piled' when its depth is more than three times its breadth (Atkinson, 2007). Pile foundations can help transfer loads through weak, compressible strata or water onto stronger, more compact, less compressible and stiffer soil or rock at depth.
The addition of piles to a raft increases the effective size of a foundation and can help resist horizontal loads. This can improve the performance of the foundation in reducing the amount of settlement and differential settlement, as well as improving the ultimate load capacity.
Piled raft foundations are typically used for large structures, and in situations where soil is not suitable to prevent excessive settlement. They are an increasingly popular choice for high-rise buildings.
The reinforced concrete (RC) raft acts as an effective ground gas barrier, achieving 2.0 points in accordance with the scoring system set out in BS 8485. This provides adequate protection for CS2 and CS3 gas regimes, when used in combination with a correctly designed, detailed, and installed membrane system above the raft and/or a ventilation layer beneath (required for CS3 conditions only).
During the design process, the optimum number and position of piles, as well as their diameter, reinforcement and length, is determined to ensure the stability of the structure while providing an economical solution, with the raft and piles acting together to ensure the required settlement is not exceeded. Typically, the piles provide most of the stiffness while the raft provides additional capacity at the ultimate loading.
If there are one or more ineffective piles, the raft can allow some degree of load redistribution to other piles, reducing the influence of the pile’s weakness on the overall performance of the foundation.
In an Unconnected Piled Raft Foundation (UCPRF), the piles are not directly connected to the raft, but are separated from it be a structural fill 'cushion' (such as a compacted a sand-gravel mixture or compacted soil) which redistributes load between the raft and piles. This can be a more efficient, and so economic solution.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Driven piles.
- Foundations.
- Geothermal pile foundations.
- Micropiles.
- Pad foundation.
- Pile cap.
- Pile foundations.
- Raft foundation.
- Screw pile foundations.
- Secant pile wall.
- Types of raft foundation.
- Types of pile foundation.
[edit] External references
- Numerical analysis of unconnected piled raft with cushion. Alaa Ata, Essam Badrawi, Marwa Nabil. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2014.11.002
- Strip foundation depth and ground gas barrier reference. https://speedeck.uk/our-solutions/construction/piled-raft-foundations/
Featured articles and news
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help the homebuilding sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.

























Comments
Thanks for the comments. Did you know you can write and publish your own article, associate it to your profile, so that your details, website and logo will appear at the top. For free ! Just make it relevant and informative and without backlinks.