Damp proofing buildings
The term ‘damp proofing’ refers to types of moisture control that are applied to walls and floors to prevent damp from setting in or spreading in a building.
Damp problems are among the most frequent problems encountered in buildings, particularly older buildings which may have been constructed without a damp-proof membrane.
Damp may be apparent from:
- Damp patches.
- Mould growth.
- Mildew, salts, staining and 'tide marks'.
- Damage to surface finishes, such as blistering paint and bulging plaster.
- Corrosion and decay of the building fabric.
- Slip hazards.
- Frost damage.
- Poor performance of insulation.
- Damage to equipment, or electrical failure.
The most common causes of persistent damp in buildings are:
- Condensation (surface or interstitial).
- Rising damp.
- Penetrating damp.
The two most common damp proofing techniques are:
Installation of a damp-proof course. A damp-proof course is a barrier, usually formed by a membrane built into the walls of a property, typically 150 mm above ground level, to prevent damp rising through the walls. Damp-proof courses are now required in the construction of new buildings to prevent rising damp and in some situations to prevent penetrating damp.
Damp proof courses can also be retrofitted to existing buildings by the injection of water-repellent chemicals. Treatment generally also involves remedial work to any corroded or decayed elements of the building fabric, as well as hacking off and replacing existing plaster to a height of 1 m.
For more information, see Damp proof course.
Installation of a damp-proof membrane (DPM). Typically, a DPM is a polyethylene sheet laid under a concrete slab to prevent the concrete from transmitting moisture through capillary action.
For more information, see Damp proof membrane.
Other damp proofing techniques include:
- Integral damp proofing: Concrete production can involve the addition of materials to make it more impermeable.
- Surface coating: Waterproof surface materials can be used internally or externally, such as render or waterproof plaster.
- Cavity wall systems: A cavity separates the interior walls from the exterior walls.
- Pressure grouting: This can fill in cracks and joints in masonry.
- Colourless water-repellent treatments.
However, it is important to note that damp is often just a symptom of another problem in a building, such as a lack of ventilation, drainage problems, cracks in walls, missing tiles or leaking pipework. It is important therefore that the underlying problem is rectified before other treatments are applied.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- An interview with Matthew Mallows - Surveyor at British Damp Proofing.
- Basement waterproofing.
- Bitumen.
- Building damp-free cavity walls.
- Condensation.
- Damp.
- Damp-proof course.
- Damp-proof membrane.
- Draught proofing.
- Electrical resistance meters.
- Humidity.
- Moisture.
- Moisture content.
- Mould growth.
- Penetrating damp.
- Rising damp.
- Spalling.
- Stain.
- Structural waterproofing consultant.
- Tanking.
- Types of damp-proof courses.
- Understanding dampness.
- Wall insulation and moisture risk.
- Water.
- Waterproofing.
Featured articles and news
Professional practical experience for Architects in training
The long process to transform the nature of education and professional practical experience in the Architecture profession following recent reports.
A people-first approach to retrofit
Moving away from the destructive paradigm of fabric-first.
International Electrician Day, 10 June 2025
Celebrating the role of electrical engineers from André-Marie Amperè, today and for the future.
New guide for clients launched at Houses of Parliament
'There has never been a more important time for clients to step up and ...ask the right questions'
The impact of recycled slate tiles
Innovation across the decades.
EPC changes for existing buildings
Changes and their context as the new RdSAP methodology comes into use from 15 June.
Skills England publishes Sector skills needs assessments
Priority areas relating to the built environment highlighted and described in brief.
BSRIA HVAC Market Watch - May 2025 Edition
Heat Pump Market Outlook: Policy, Performance & Refrigerant Trends for 2025–2028.
Committing to EDI in construction with CIOB
Built Environment professional bodies deepen commitment to EDI with two new signatories: CIAT and CICES.
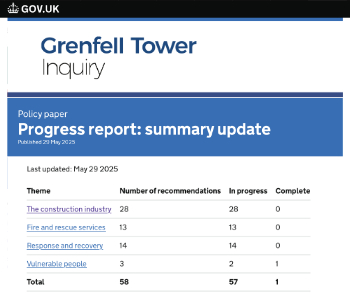
Government Grenfell progress report at a glance
Line by line recomendation overview, with links to more details.
An engaging and lively review of his professional life.
Sustainable heating for listed buildings
A problem that needs to be approached intelligently.
50th Golden anniversary ECA Edmundson apprentice award
Deadline for entries has been extended to Friday 27 June, so don't miss out!
CIAT at the London Festival of Architecture
Designing for Everyone: Breaking Barriers in Inclusive Architecture.
Mixed reactions to apprenticeship and skills reform 2025
A 'welcome shift' for some and a 'backwards step' for others.




















Comments