Modern train stations
The modern rail transport hub of today is much more than platforms, track and somewhere to buy a ticket.
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
Train stations were places of wonder in the 19th century. The buildings, like the trains within, symbolised technological progress and economic power. These ‘palaces’ of the industrial age were awe-inspiring in their sheer size, dramatic in architecture and feats of engineering.
St Pancras Station in London was one such example and on its completion in 1868 was the largest enclosed space in the world. This has allowed it to be remodelled into today’s spectacular transport hub.
By the second half of the 20th century, with car travel on the rise, train stations in many parts of the world lost prominence as cities planned for greater road use – undermining the prestige of rail travel. Now as passenger numbers increase rail is playing a central role in urban life and the economic and cultural importance of stations is increasing.
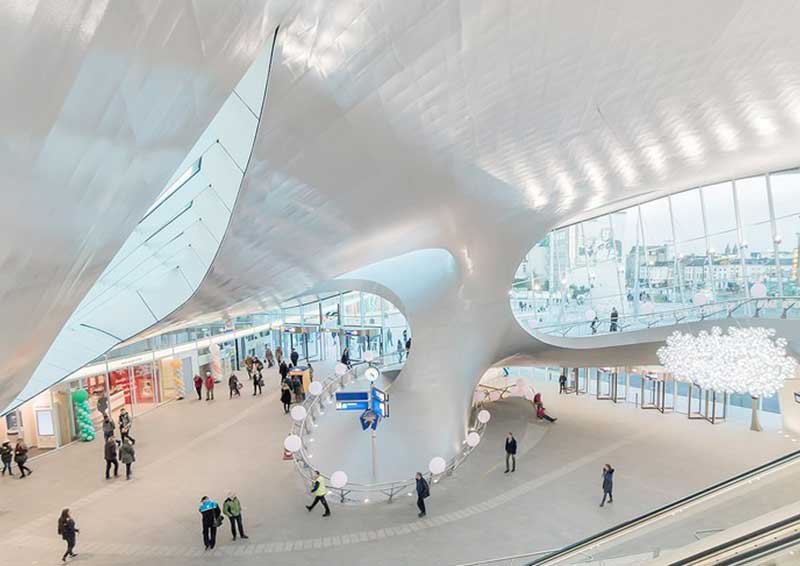
A need for high quality, beautiful, yet flexible stations, integrated into their place in the city has emerged. Investment programmes have modernised and expanded many stations across Europe and North America. Arnhem Central Station is one example (see top image).
Dating back to 1845, the station has been completely redeveloped to better meet today’s travel needs. It was opened late 2015. In other regions, the focus is more often on the construction of new public transport systems, like Shenzhen Metro’s new Line 4 in China – 15 stations built with provision for development above.
“Driving this need for integration is the fundamental question of what a station contributes, economically and socially, to a city,” says Malcolm Smith, Global Masterplanning and Urban Design Leader, Arup
[edit] Rail renaissance brings new expectations
Some rail and metro stations, such as Cityringen in Copenhagen, are designed to be places of transit, prioritising citizens’ desire for simple journeys without distraction.
In other stations designers are called on to create dynamic, multifunctional spaces where people can do much more than set out or arrive on a journey. They are destinations in their own right, providing space for everything from libraries, medical centres and cinemas, to shopping and eating.
This requires greater flexibility – as seen in Canary Wharf’s new Crossrail station. There the commercial space can be completely redesigned to meet tenant needs but this in turn needs careful planning and design.
What’s known as the ‘red line’ that separates travel spaces from public spaces is more blurred. To get this right station designers must become more open to involving the community in defining what their station is, what it will contain and how it contributes to the surrounding area.
“People sit at the very heart of our cities, and their stations, which is why we need to engage local communities in the renewal of these spaces, to encourage collaborative and tailored urban regeneration,” says Arup Director of Architecture Nille Juul-Sorensen.
[edit] Flexible rail stations not just about transport
Passenger needs are paramount and considered at every stage of the planning process. The aim is to create stations that allow people to move through them and pause within and around them with ease, rather than simply in the way the transport planners think is best.
At London’s King’s Cross Station we modelled the expected flow of people in and around the station in minute detail to get the design right. We must ‘design in’ flexibility so that as people’s needs evolve stations can be adapted easily and quickly.
As stations become more flexible they can also become more fun. Ikea certainly surprised passengers of the Parisian metro system when it placed a selection of its sofas on station platforms for people to test – and buy. Stations will always need to be places of safety and security, but there is no reason why they can’t delight and entertain.
Rail and metro stations are powerful catalysts for regeneration. Distrito Castellana Norte Madrid acknowledges this: the regeneration scheme is being planned with new high speed rail at its heart.
More than ever, stations are symbols of a place and need to be seamlessly integrated into the personalities of the cities in which they are located.
This article was originally published here by ICE on 13 Nov 2017. It was written by Malcolm Smith, Global Masterplanning and Urban Design Leader, Arup.
--The Institution of Civil Engineers
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- Articles by ICE on Designing Buildings Wiki.
- Beeching cuts.
- Crossrail 2.
- ECA backs joint rail electrification statement.
- From Gotthard to Guadarrama – these are the world’s longest railway tunnels.
- High Speed 2 (HS2).
- King's Cross Station Redevelopment.
- Nineteenth century building types.
- Railway engineering.
Featured articles and news
70+ experts appointed to public sector fire safety framework
The Fire Safety (FS2) Framework from LHC Procurement.
Project and programme management codes of practice
CIOB publications for built environment professionals.
Sustainable development concepts decade by decade.
The regenerative structural engineer
A call for design that will repair the natural world.
Buildings that mimic the restorative aspects found in nature.
CIAT publishes Principal Designer Competency Framework
For those considering applying for registration as a PD.
BSRIA Building Reg's guidance: The second staircase
An overview focusing on aspects which most affect the building services industry.
Design codes and pattern books
Harmonious proportions and golden sections.
Introducing or next Guest Editor Arun Baybars
Practising architect and design panel review member.
Quick summary by size, shape, test, material, use or bonding.
Types of rapidly renewable content
From forestry to agricultural crops and their by-products.
Terraced houses and the public realm
The discernible difference between the public realm of detached housing and of terraced housing.
Looking back at the influence of climate events
From a designer and writer: 'There are limits to growth but no limits to development'.
Terms, histories, theories and practice.
Biophilic design and natural light
Letting in the light and natural elements into spaces.