The 4 Stages of BIM Process in Construction
Contents |
[edit] Introducing the BIM process
Building Information Modelling (BIM) has revolutionised the construction industry by offering a digital approach to project management and execution. It is a process that involves the generation and management of digital representations of a construction project's physical and functional characteristics. BIM encompasses the entire lifecycle of a construction project, from its conceptualisation to its eventual operation and maintenance.
In this article, we will explore the four stages of the BIM process and delve into its many advantages and challenges.
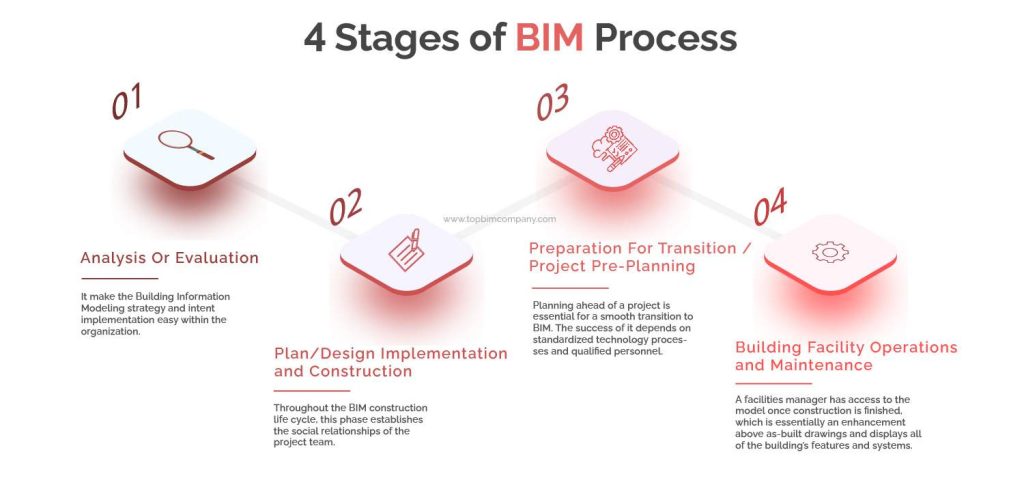
[edit] Stage 1: Initiation and Planning
[edit] Defining Project Goals
The BIM process begins with a clear definition of project goals. This stage involves understanding the client's requirements, project scope, and intended outcomes. These goals act as a compass throughout the project, ensuring that all decisions and activities align with the project's objectives.
[edit] Assembling the Project Team
A crucial step in BIM implementation is forming a multidisciplinary project team. Architects, engineers, contractors, and other stakeholders collaborate from the outset, promoting effective communication and problem-solving.
[edit] Setting the BIM Standards
In this stage, project-specific BIM standards are established. These standards govern how data is created, shared, and managed. Having consistent standards ensures that all project members work seamlessly together.
[edit] Stage 2: Design and Development
[edit] Conceptual Design
The second stage involves conceptualising the project through preliminary design. BIM aids in visualising and analysing design options, promoting creativity while adhering to project goals.
[edit] Detailed Design
As the project progresses, BIM models evolve into detailed designs. This stage focuses on refining the project's specifics, ensuring that it meets regulatory requirements and stakeholder expectations.
[edit] Collaboration and Coordination
BIM facilitates collaboration among different project disciplines. Design clashes and conflicts can be detected and resolved before construction begins, saving time and money.
[edit] Stage 3: Construction and Implementation
[edit] Procurement and Material Management
During this stage, BIM is used to optimise procurement and material management. Real-time data helps ensure that the right materials are ordered at the right time, reducing waste and cost overruns.
[edit] On-site Construction and Monitoring
BIM supports on-site construction by providing 3D models and real-time project data. This aids in project monitoring, progress tracking, and issue identification.
[edit] Quality Control and Issue Resolution
BIM enables quality control by offering a comprehensive view of the project. Any issues can be quickly identified and addressed, ensuring the final product meets quality standards.
[edit] Stage 4: Operation and Maintenance
[edit] As-Built Model
After construction, the BIM model transitions into an as-built model, reflecting the actual conditions of the structure. This model is invaluable for facility management.
[edit] Facility Management
BIM continues to provide benefits during the operation phase. It aids in facility management, including maintenance scheduling, asset tracking, and space management.
[edit] BIM for Renovations and Retrofits
BIM is not limited to new construction. It's equally valuable for renovations and retrofits, as it assists in understanding existing structures and planning changes.
[edit] Benefits of BIM in Construction
BIM offers numerous advantages in construction, including cost savings, improved collaboration, enhanced decision-making, and a positive environmental impact.
Here are some of the benefits of using BIM in construction:
- Improved communication and collaboration between stakeholders
- Increased efficiency and productivity
- Reduced errors and omissions
- Improved decision-making
- Reduced costs
- Increased sustainability
BIM is becoming increasingly important in the construction industry, and it is expected to play a major role in the future of construction.
[edit] Challenges in Implementing BIM
While BIM has immense potential, its implementation comes with challenges, such as initial costs, a learning curve for project teams, and concerns about data security and privacy.
The 4 stages of the BIM process in construction revolutionise the way projects are conceived, designed, constructed, and maintained. With benefits like cost savings and improved collaboration, BIM has become an essential tool for modern construction projects. However, it's crucial to acknowledge the challenges and work toward overcoming them to unlock the full potential of BIM in the construction industry.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Asset information requirements AIR..
- BIM 2018-2026 market predictions.
- BIM and facilities management.
- BIM articles.
- BIM execution plan.
- BIM glossary of terms.
- BIM level 2.
- BIM maturity levels.
- BIM resources.
- Building drawing software.
- Building information modelling BIM.
- Construction Operations Building Information Exchange (COBie).
- Collaborative practices.
- Common data environment.
- Digital information.
- Digital model.
- Government Construction Strategy.
- Government Soft Landings.
- Improving health and safety using BIM.
- Industry Foundation Classes.
- Level of detail.
- MEP BIM and the building lifecycle.
- Revit.
- Uniclass.
BIM Directory
[edit] Building Information Modelling (BIM)
[edit] Information Requirements
Employer's Information Requirements (EIR)
Organisational Information Requirements (OIR)
Asset Information Requirements (AIR)
[edit] Information Models
Project Information Model (PIM)
[edit] Collaborative Practices
Industry Foundation Classes (IFC)