Truss
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
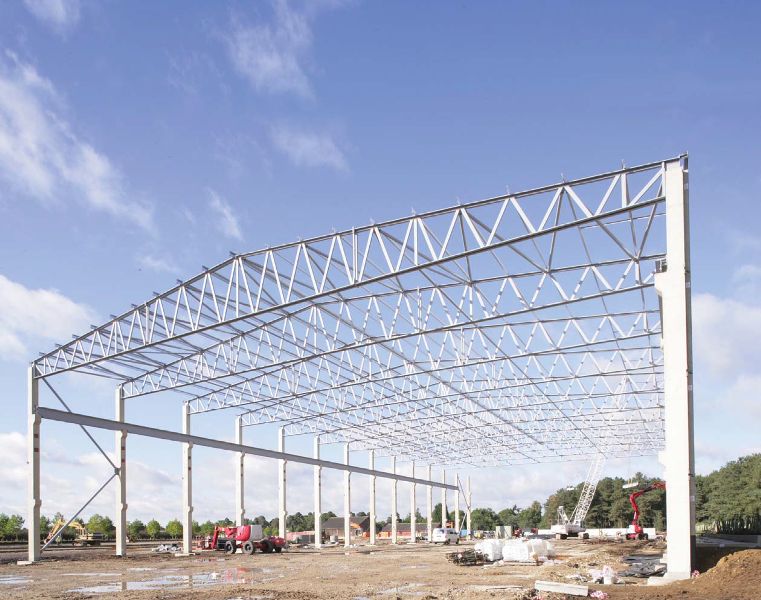
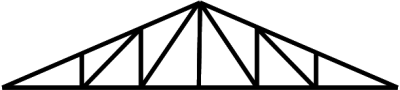
A truss is a structure that consists of members organised into connected triangles so that the overall assembly behaves as a single object. Trusses are most commonly used in bridges, roofs and towers.
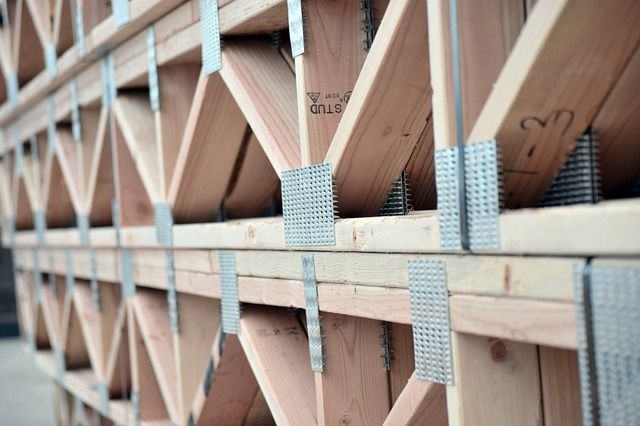
A truss is made up of a web of triangles joined together to enable the even distribution of weight and the handling of changing tension and compression without bending or shearing. The triangle is geometrically stable when compared to a four (or more) -sided shape which requires that the corner joints are fixed to prevent shearing.
Trusses consist of triangular units constructed with straight members. The ends of these members are connected at joints, known as nodes. They are able to carry significant loads, transferring them to supporting structures such as load-bearing beams, walls or the ground.
In general, trusses are used to:
- Achieve long spans.
- Minimise the weight of a structure.
- Reduced deflection.
- Support heavy loads.
Trusses are typically made up of three basic elements:
- A top chord which is usually in compression.
- A bottom chord which is usually in tension.
- Bracing between the top and bottom chords.
The top and bottom chords of the truss provide resistance to compression and tension and so resistance to overall bending, whilst the bracing resists shear forces.
The efficiency of trusses means that they require less material to support loads compared with solid beams. Generally, the overall efficiency of a truss is optimised by using less material in the chords and more in the bracing elements.
[edit] Types of truss
[edit] Simple truss
This is a single triangle such as might be found in a framed roof consisting of rafters and a ceiling joist.
[edit] Planar truss
A planar truss is a truss in which all the members lie in a two-dimensional plane. This type of truss is typically used in series, with the trusses laid out in a parallel arrangement to form roofs, bridges, and so on.
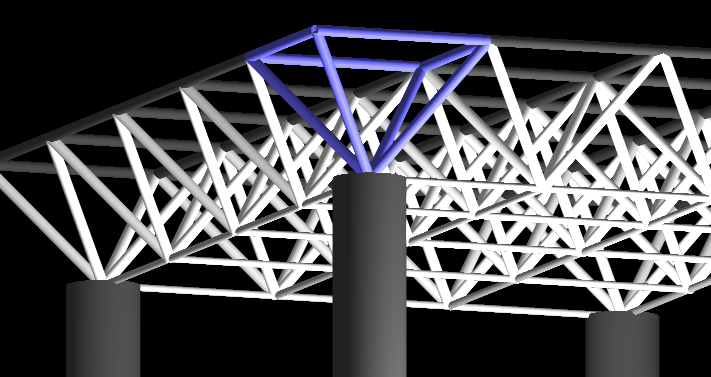
[edit] Space frame truss
In contrast to a planar truss which lies in a two-dimensional plane, a space frame truss is a three-dimensional framework of connected triangles.
[edit] Truss forms
There are a wide range of truss forms that can be created, varying in materials, overall geometry and span. Some of the most common forms are described below.
[edit] Pratt truss
Also known as an ‘N’ truss, this form is often used in long-span buildings, with spans ranging from 20-100 m, where uplift loads may be predominant, such as in aircraft hangers. A Pratt truss uses vertical members for compression and horizontal members for tension. The configuration of the members means that longer diagonal members are only in tension for gravity load effects which allows them to be used more efficiently.
[edit] Warren truss
A Warren truss has fewer members than a Pratt truss and has diagonal members which are alternatively in tension and compression. The truss members form a series of equilateral triangles, alternating up and down.
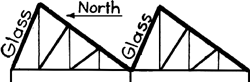
[edit] North light truss
This form of truss is usually used for short spans in industrial buildings, and is so called because it allows maximum benefit to be gained from natural lighting by the use of glazing on the steeper north-facing pitch (sometimes referred to as a sawtooth roof). It is common, on the steeper sloping portion of the truss, to have a second truss running perpendicular to the plane of the north light truss, providing large column-free space.
[edit] King post truss
Typically made from timber, and spanning up to 8m, king post trusses are commonly used in the construction of domestic roofs. They take the form of a simple triangle, with a vertical member between the apex and the bottom chord.
[edit] Queen post truss
Similar to the king post truss, but with diagonal members between the centre of the bottom chord and each of the inclined top chords, queen post trusses can span 10m.
[edit] Flat truss
The top and bottom chords are parallel, allowing the construction of floors or flat roofs.
[edit] Belfast Truss
The Belfast Truss is truss consisting of a lower horizontal member or tie-beam and a curved upper member or bow which has smaller intersecting members at various points, in a fan grid or lattice-like pattern. The upper curved member has a radius which is half that of the setting out point for the fanning lines.
[edit] Other types of truss:
Other variations include:
- Howe truss.
- Scissor roof truss.
- Hip truss.
- Bowstring truss.
- Fan truss.
- Fink Truss.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
Featured articles and news
The Home Energy Model and its wrappers
From SAP to HEM, EPC for MEES and FHS assessment wrappers.
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help the homebuilding sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.




























Comments
So the definition of truss is that it is a structure made by triangles? What about the Vierendeel truss ?
It is arguable whether a Vierendeel truss is a true truss in the strictest definition of the term - and it is certainly not typical of the form of conventional trusses or the forces they resist.