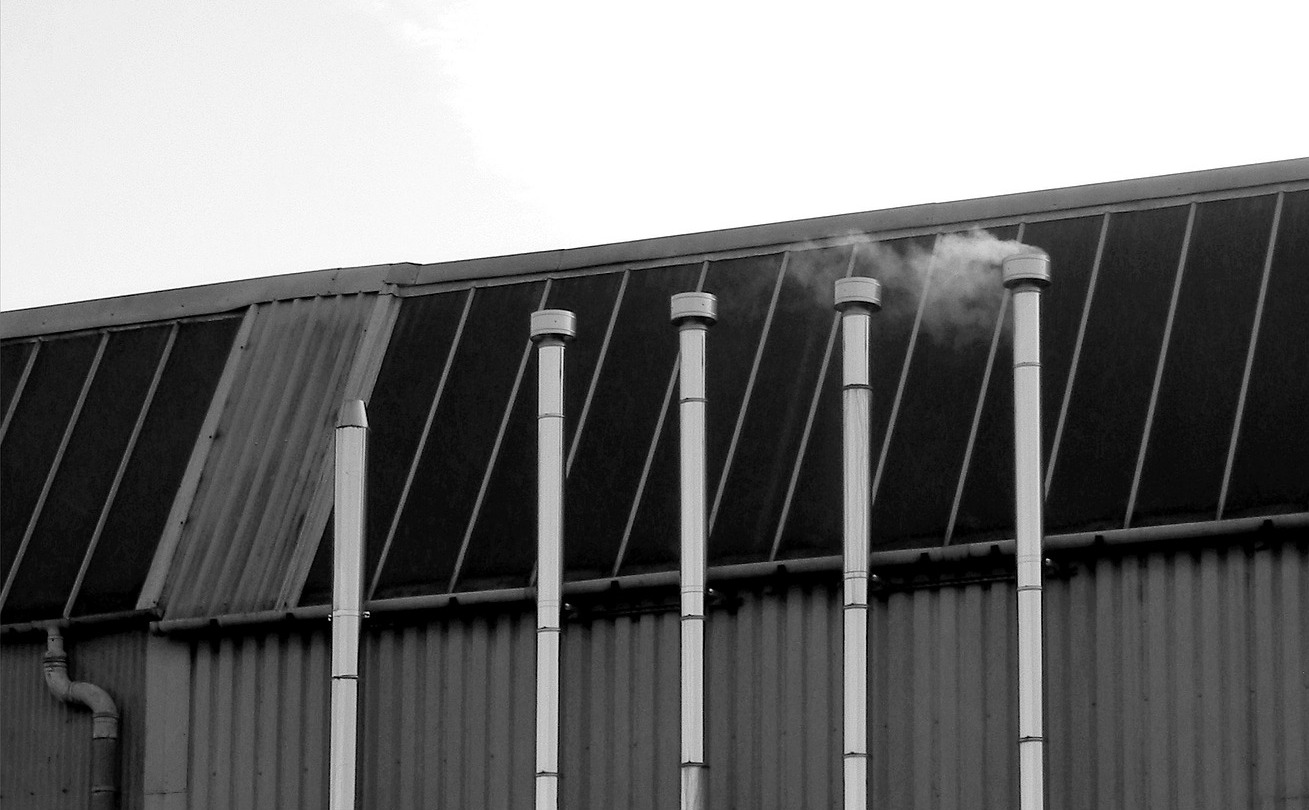
Patent glazing
The term ‘patent glazing’ refers to a non-load bearing, two-edge support cladding system. Its name relates to the number of patents that were taken out in the 19th and 20th centuries for different versions of the system.
Patent glazing bars provide continuous support along two edges of glazing infill panels, and are fixed back to the main structure of the building. This system supports its own weight, and provides resistance to wind and snow loading, but does not contribute to the stability of the primary structure of the building.
Patent glazing is a dry glazing system in which the patent glazing bars are drained and ventilated.
The earliest systems were typically manufactured from a steel section, covered with lead. However, the development of aluminium manufacturing during the second world war, and the clear advantage of the material in terms of weight and cost resulted in aluminium becoming the main manufacturing material in the 1950’s and 60’s.
Modern patent glazing systems are typically formed by aluminium T or box section patent glazing bars which provide continuous support along two edges of infill panels such as single or double glazing or composite panels. The glazing bars are fixed back to the main structure of the building.
Channels within the patent glazing bars collect rainwater that penetrates through the outer bead, or condensation that accumulates within the bar, and drain this to the outside.
Typically, aluminium patent glazing bars are available in lengths up to 7 or 8m, but beyond 3 to 6m, they generally need intermediate support, depending on their section size, anticipated loads and the weight of the infill panels.
Patent glazing can offer a more economical alternative to four-edge support curtain walling, particularly in situations where glazing needs to be installed at an angle, such as in a glass roofs.
Guidance for the design and installation of patent glazing is provided in BS 5516-1:2004 Patent glazing and sloping glazing for buildings. Code of practice for design and installation of sloping and vertical patent glazing.
Design and installation considerations might include:
- Maximum required span.
- Supporting structure.
- Access for maintenance.
- Requirement for opening roof lights to allow natural ventilation and smoke ventilation.
- Use of laminated glass to prevent glass falling in the event of breakage.
- Movement.
- Drainage (typically, a pitch of at least 15° is required to ensure rainwater run-off).
- Acoustic performance.
- Security.
- Heat accumulation and shading.
- Wind, snow and maintenance loads.
- The pressure difference across the patent glazing.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
Featured articles and news
International Electrician Day, 10 June 2025
Celebrating the role of electrical engineers from André-Marie Amperè, today and for the future.
New guide for clients launched at Houses of Parliament
'There has never been a more important time for clients to step up and ...ask the right questions'
The impact of recycled slate tiles
Innovation across the decades.
EPC changes for existing buildings
Changes and their context as the new RdSAP methodology comes into use from 15 June.
Skills England publishes Sector skills needs assessments
Priority areas relating to the built environment highlighted and described in brief.
BSRIA HVAC Market Watch - May 2025 Edition
Heat Pump Market Outlook: Policy, Performance & Refrigerant Trends for 2025–2028.
Committing to EDI in construction with CIOB
Built Environment professional bodies deepen commitment to EDI with two new signatories: CIAT and CICES.
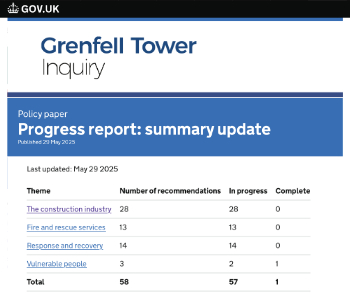
Government Grenfell progress report at a glance
Line by line recomendation overview, with links to more details.
An engaging and lively review of his professional life.
Sustainable heating for listed buildings
A problem that needs to be approached intelligently.
50th Golden anniversary ECA Edmundson apprentice award
Deadline for entries has been extended to Friday 27 June, so don't miss out!
CIAT at the London Festival of Architecture
Designing for Everyone: Breaking Barriers in Inclusive Architecture.
Mixed reactions to apprenticeship and skills reform 2025
A 'welcome shift' for some and a 'backwards step' for others.
Licensing construction in the UK
As the latest report and proposal to licence builders reaches Parliament.
Building Safety Alliance golden thread guidance
Extensive excel checklist of information with guidance document freely accessible.
Fair Payment Code and other payment initiatives
For fair and late payments, need to work together to add value.
Pre-planning delivery programmes and delay penalties
Proposed for housebuilders in government reform: Speeding Up Build Out.
High street health: converting a building for healthcare uses
The benefits of health centres acting as new anchor sites in the high street.