JTI Headquarters, Geneva
(Image: Adrien Barakat)
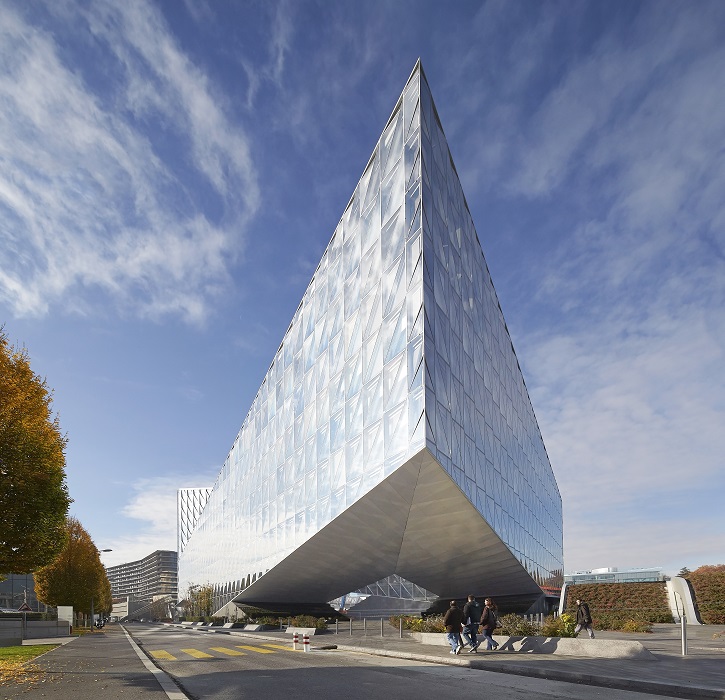
In March 2016, a major new headquarters for Japan Tobacco International (JTI) was completed in Geneva, Switzerland. The nine-storey building, designed by Skidmore, Owings & Merrill, Inc. (SOM), features an innovative façade of glass triangles as well as a huge central courtyard, and has been praised as one of the most sustainable development projects in Europe.
The design was initially a collaboration between SOM’s architecture, structural engineering and interior teams, and was intended to draw reference ‘not only from its immediate context, but also Lake Geneva and the Alps, establishing a strong identity amongst its illustrious neighbours while responding sensitively to its low-rise context.’
(Image: Hufton + Crow)
Dictated by the challenging triangular site, the angular form is the result of two raised corners, providing the structure with its tilted profiles. The cantilevered space of the courtyard, with clear-spans of up to 75 m, create permeability through the site and facilitate direct pedestrian flow to a local transport hub.
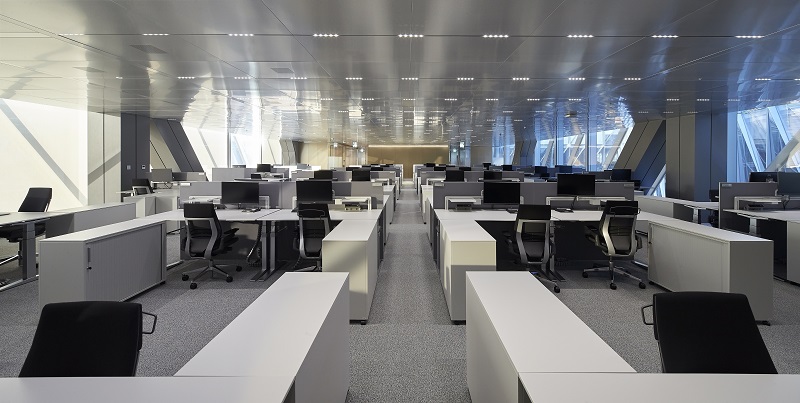
The interior design concept maximises both vertical and horizontal interconnectivity, fulfilling JTI’s request for a social and collaborative environment for the 1,000-plus people employed.
(Image: Hufton + Crow)
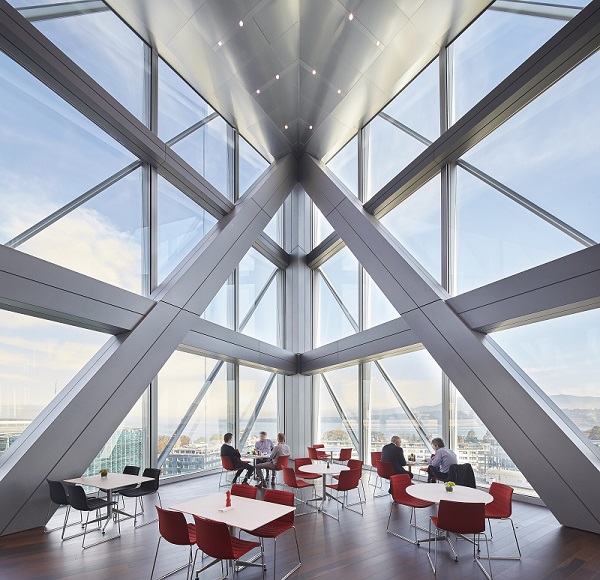
The open-plan office space is intended to ‘break down corporate silos and contribute to the creation of a seamless workplace network, providing long-term flexibility to accommodate JTI’s evolving needs’. This was achieved using an peripheral torsional tube structural steel system allowing floor plates to span 18 m without columns.
(Image: Hufton + Crow)
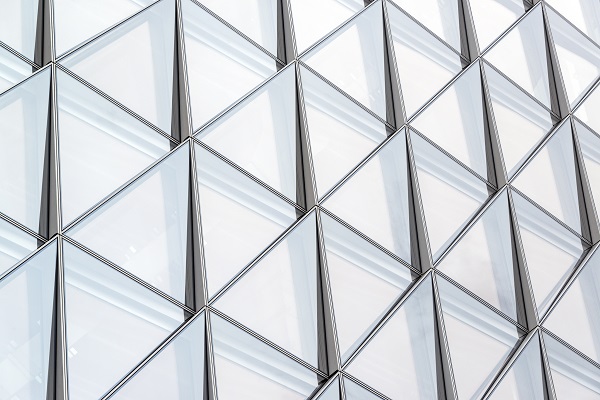
The building incorporates an innovative Closed Cavity Façade (CFF), a curtain wall system that is responsive to external climatic conditions while maximising daylight penetration and providing exceptional views. The floor-to-ceiling glazed panels consist of an inner layer of triple glazing and an outer layer of single glazing, with a fabric roller blind in the cavity between. The panels are sealed and equipped with a pressurised supply of filtered and dehumidified air that prevents condensation and heat build-up inside.
(Image: Johannes Marburg)
The CCF system prioritises occupant comfort and reduces the building’s overall energy demand and carbon emissions, helping it to meet the requirements of European Energy Directives and the Swisse Minergie sustainability rating.
SOM claim that the system represents ‘one of the best-performing all-glass façade systems’ in their history.
Content and images courtesy of SOM.
For more information, see SOM.
[edit] Find out more
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- Building of the week series.
- Curtain wall systems.
- Design for deconstruction, office building.
- Emissivity.
- Glazing.
- Kaplan North Masterplan Complex.
- New York Horizon.
- Nexus.
- Office space planning.
- Skyfarm.
- Structural systems for offices.
- The Mile.
- Unusual building design of the week.
- Wellbeing and creativity in workplace design - case studies.
- Wire mesh church installation.
Featured articles and news
Retired firefighter cycles world to raise Grenfell funds
Leaving on 14 June 2025 Stephen will raise money for youth and schools through the Grenfell Foundation.
Key points for construction at a glance with industry reactions.
Functionality, visibility and sustainability
The simpler approach to specification.
Architects, architecture, buildings, and inspiration in film
The close ties between makers and the movies, with our long list of suggested viewing.
SELECT three-point plan for action issued to MSPs
Call for Scottish regulation, green skills and recognition of electrotechnical industry as part of a manifesto for Scottish Parliamentary elections.
UCEM becomes the University of the Built Environment
Major milestone in its 106-year history, follows recent merger with London School of Architecture (LSE).
Professional practical experience for Architects in training
The long process to transform the nature of education and professional practical experience in the Architecture profession following recent reports.
A people-first approach to retrofit
Moving away from the destructive paradigm of fabric-first.
International Electrician Day, 10 June 2025
Celebrating the role of electrical engineers from André-Marie Amperè, today and for the future.
New guide for clients launched at Houses of Parliament
'There has never been a more important time for clients to step up and ...ask the right questions'
The impact of recycled slate tiles
Innovation across the decades.
EPC changes for existing buildings
Changes and their context as the new RdSAP methodology comes into use from 15 June.
Skills England publishes Sector skills needs assessments
Priority areas relating to the built environment highlighted and described in brief.
BSRIA HVAC Market Watch - May 2025 Edition
Heat Pump Market Outlook: Policy, Performance & Refrigerant Trends for 2025–2028.
Committing to EDI in construction with CIOB
Built Environment professional bodies deepen commitment to EDI with two new signatories: CIAT and CICES.
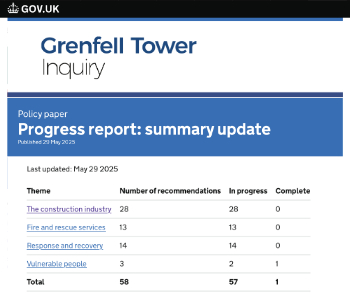
Government Grenfell progress report at a glance
Line by line recomendation overview, with links to more details.
An engaging and lively review of his professional life.
Sustainable heating for listed buildings
A problem that needs to be approached intelligently.
50th Golden anniversary ECA Edmundson apprentice award
Deadline for entries has been extended to Friday 27 June, so don't miss out!
CIAT at the London Festival of Architecture
Designing for Everyone: Breaking Barriers in Inclusive Architecture.
Mixed reactions to apprenticeship and skills reform 2025
A 'welcome shift' for some and a 'backwards step' for others.