Eco houses for environment-friendly architecture
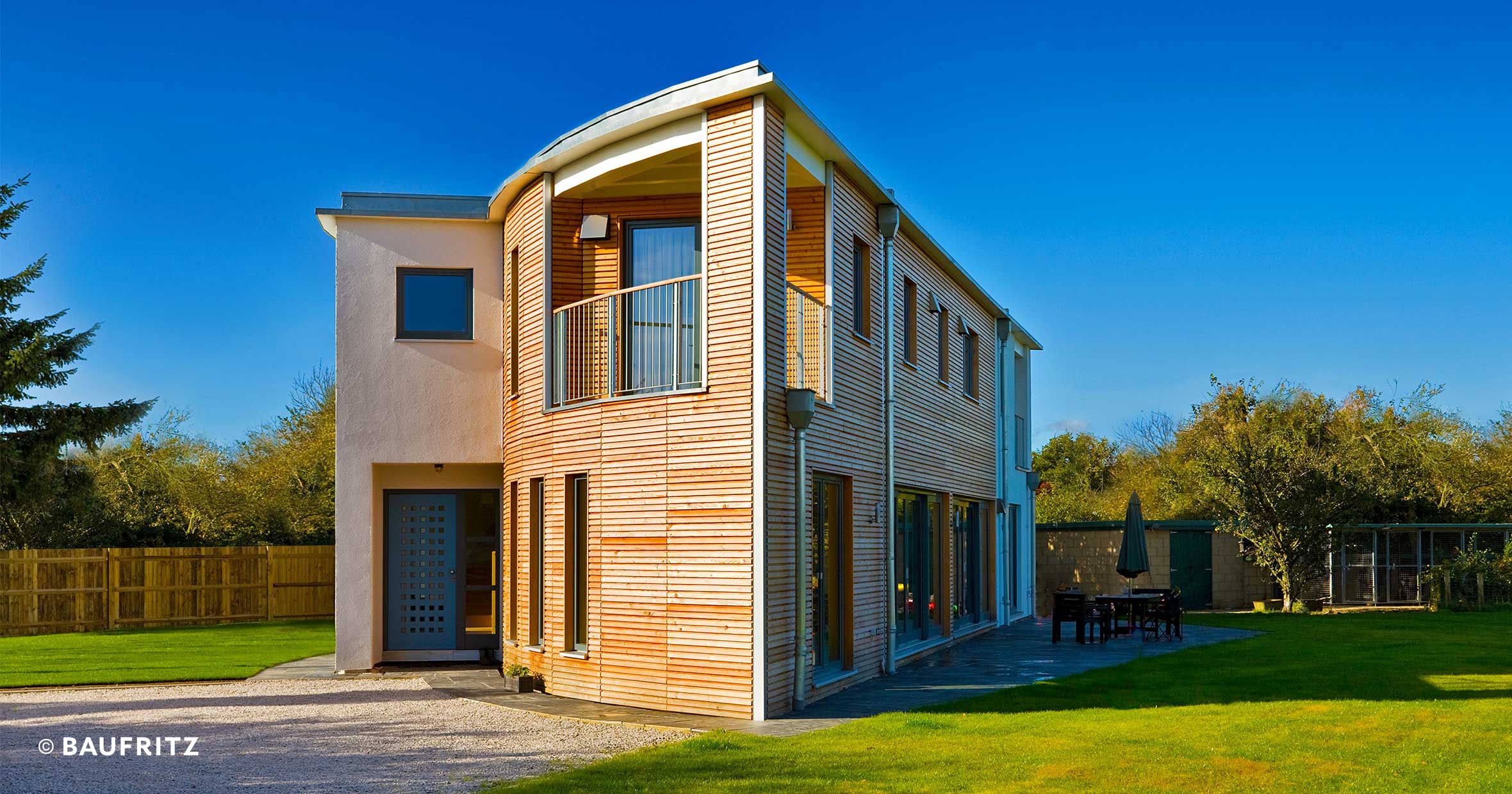

|
| Ainsworth Hales house built by Baufritz. |
Sustainability, renewable energies, environmentally-friendly, carbon footprint ... are terms that have become a part of daily life. But, it is not only vocabulary that is changing, people's awareness of, and their attitude towards, climate change is also shifting. This is why more and more people are becoming interested in green and healthy 'eco-houses' - houses that are built from sustainable materials while at the same time successfully combining contemporary architecture and comfort.
Almost half the respondents to a Statista survey said that they could imagine living in an eco house.
The aim of this 'green architecture' is to minimise the resources that go into construction and the subsequent use of the house, while at the same time, reducing the detrimental effects that emissions, pollution and waste can have on the environment.
The materials used in the intelligent construction of eco houses are pollutant-free, have been produced or grown sustainably and often locally, and have a low impact on the environment. In most cases, a high proportion of the materials used to construct eco homes can be returned to the natural cycle without leaving any trace when the house is deconstructed.
Eco houses are also energy efficient, making them a good investment at a time when energy prices are rising. This can be achieved, for example, by utilising solar or other renewable energies to minimise heating and electricity costs. They are also well insulated and many of them have an energy storage facility. This enables them to be partially or completely independent of external energy suppliers.
There are many different types of eco house using a whole range of methods for generating and storing energy. These include:
- Solar house: This is supplied with thermal energy generated using solar power and usually entails solar technology attached to the roof of the house. The solar heat is then stored in a stratified hot water tank. About 2/3 of the demand for hot water and about 5 % of the energy required for heating can be provided with this method.
- Passive house: The walls of a passive house are insulated so well that heating costs are kept to a minimum. Any heat emitted by appliances or which comes from the sun is retained for a long period; this helps reduce the amount of additional heat required. The positive effect is that the eco house is kept warm in winter and pleasantly cool in the summer.
- Plus energy house: This type of eco-house is equipped with photovoltaic systems and solar thermal systems which enable it to generate more energy than is consumed by the occupants. The plus energy house's surplus energy can be fed into the grid, which brings in extra money for the occupants.
- Energy self-sufficient house: This allows residents to be (almost) independent of any external energy suppliers. It can produce and store sufficient energy to enable the residents to become self-sufficient. The electricity that they use is generated on site and stored.
There are a range of other energy-saving concepts which can be adopted - for example, gas condensing technology, in which gas is converted to heat, which together with the use of the condensation heat from the developing gases, leads to a reduction in energy consumption of up to 20%. Another energy concept is geothermal, where geothermal heat from the ground is delivered via a pump into the property and used for heating and hot water.
Eco houses enable their owners to meet their housing needs effectively. They prevent adverse impacts on the environment, and use energy, water and other resources responsibly and efficiently without compromising health or comfort.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- Approved documents.
- Building Regulations.
- BREEAM.
- Consequential improvements.
- Dwelling Emission Rates.
- Earthship.
- Eco town.
- Energy certificates.
- Green deal.
- Home Quality Mark.
- Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design.
- Lifetime homes.
- Lifetime neighbourhoods.
- Nationally described space standard.
- NHBC technical standards.
- Passivhaus.
- Roof insulation.
- Ska rating.
- Sustainability.
- Sustainable Urban Drainage Systems.
- U-values.
- Zero carbon homes.
--BaufritzUK 11:04, 02 Jan 2020 (BST)
Featured articles and news
Government consultations for the summer of 2025
A year of Labour, past and present consultations on the environment, the built environment, training and tax.
CMA competitiveness probe of major housing developers
100 million affordable housing contributions committed with further consultation published.
Homes England supports Greencore Homes
42 new build affordable sustainable homes in Oxfordshire.
Zero carbon social housing: unlocking brownfield potential
Seven ZEDpod strategies for brownfield housing success.
CIOB report; a blueprint for SDGs and the built environment
Pairing the Sustainable Development Goals with projects.
Types, tests, standards and fires relating to external cladding
Brief descriptions with an extensive list of fires for review.
Latest Build UK Building Safety Regime explainer published
Key elements in one short, now updated document.
UKGBC launch the UK Climate Resilience Roadmap
First guidance of its kind on direct climate impacts for the built environment and how it can adapt.
CLC Health, Safety and Wellbeing Strategy 2025
Launched by the Minister for Industry to look at fatalities on site, improving mental health and other issues.
One of the most impressive Victorian architects. Book review.
Common Assessment Standard now with building safety
New CAS update now includes mandatory building safety questions.
RTPI leader to become new CIOB Chief Executive Officer
Dr Victoria Hills MRTPI, FICE to take over after Caroline Gumble’s departure.
Social and affordable housing, a long term plan for delivery
The “Delivering a Decade of Renewal for Social and Affordable Housing” strategy sets out future path.
A change to adoptive architecture
Effects of global weather warming on architectural detailing, material choice and human interaction.
The proposed publicly owned and backed subsidiary of Homes England, to facilitate new homes.
How big is the problem and what can we do to mitigate the effects?
Overheating guidance and tools for building designers
A number of cool guides to help with the heat.
The UK's Modern Industrial Strategy: A 10 year plan
Previous consultation criticism, current key elements and general support with some persisting reservations.
Building Safety Regulator reforms
New roles, new staff and a new fast track service pave the way for a single construction regulator.