Dowel laminated timber DLT
Dowel Laminated Timber (DLT) is also know as brettstapel, literally meaning board stack in German. it is a technique of constructing large-scale solid timber panels for use as structural or non-structural elements, utilising smaller untreated sawn timber sections, which are mechanically fixed together with timber dowels.
In a similar way to traditional green oak frame the dowels are seasoned or dried, whilst the main body of timbers are not, so the have a higher moisture content, the dowels soak the moisture from their wetter surroundings and expand ensuring the dowels connection is strong and tight. In oak framing structure the dowels tend to also be made from oak, in DLT they may be made from beech or any other suitably dried hardwood, in both cases the structure and dowels dry over time creating stable established connections.
DLT is said to have been originally conceived by the German engineer Julius Natterer in around the 1970s (hence the reason it is still often referred to as brettstaple). At this time the technique consisted of low grade posts of sawn timber laid side by side, continuously nailed together to create solid structural elements, which then evolved to include glues for increased strength and wider spans. Apart from issues around end of life scenarios, the randomly placed nails also caused problems for modifying or cutting any elements.
In 1999 a German company developed a dowelled wood system (Dübelholz) replacing the nails, this overcame the issues of modification and end-of life because the system became a single material solution. However contraction and expansion from variations in temperature or moisture over time, could potentially cause separation along the dowel axi, compromising strength leading to reintroduction of glue or nails.
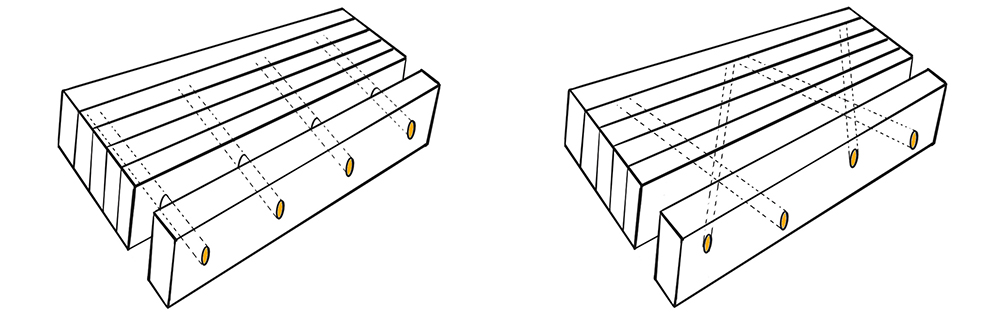
2001 An Austrian company developed a system of inserting timber dowels at angles through the posts in ‘V’ and ‘W’ formations to solve the issue, it virtually eliminated the potential for movement gaps retaining a 100% timber product. Other manufacturers have different means of dealing with the issue, including driving dowels through rotating layers of boards, though this is perhaps the most innovative.
Today many different companies manufacture Brettstapel in Austria, Germany, Switzerland and Norway. The most common form of Brettstapel is the perpendicular dowel with the majority of systems not utilising any glue. DLT utilizes locally sourced material and does not include adhesives it can be considered a natural low carbon value engineered product.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Carpentry.
- Compressive strength of timber lattice columns for low-rise construction.
- Cross laminated timber.
- Nail Laminated timber.
- Engineered bamboo.
- Engineered wood products.
- Facts about forestry.
- Glulam.
- Janka hardness rating scale.
- Laminated veneer lumber LVL.
- Modified wood.
- Nails - a brief history.
- Plywood.
- Predicting service life of timber structures.
- Sustainable timber.
- Testing timber.
- The differences between hardwood and softwood.
- The use of timber in construction.
- Timber frame.
- Timber vs wood.
- Types of timber.
- Types of timber species.
- Whole life carbon assessment of timber.
- Wood around the world.
[edit] External Links
Featured articles and news
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help the homebuilding sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.

























Comments
[edit] To make a comment about this article, or to suggest changes, click 'Add a comment' above. Separate your comments from any existing comments by inserting a horizontal line.