City Cluster, Kit of Parts
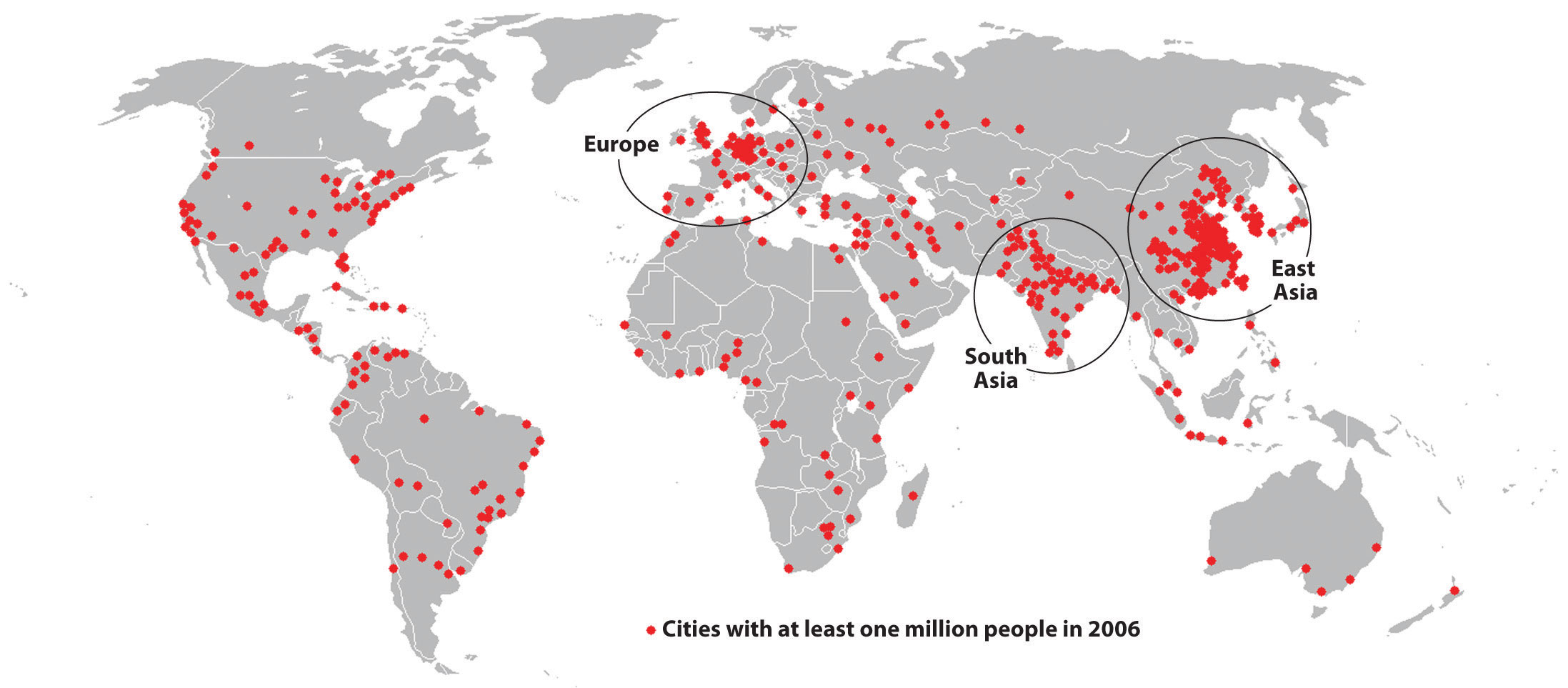
• Robinson projection indicating the major urban areas on the planet in 2006 - CC BY-SA 3.0
- ... [the office building's] increasing dominance in major urban areas throughout the world is accompanied by a disastrous lack of questioning of its medium and long-term usefulness.
- (Price, C. (1969) 'ECHOES', Architectural Design, September.)
Contents |
[edit] CITY CLUSTER: A kit of parts generating a worldwide system
|
1.1 This article is predicated on an ambiguous concept, namely:—
A study of the literature has suggested two possible definitions, namely:—
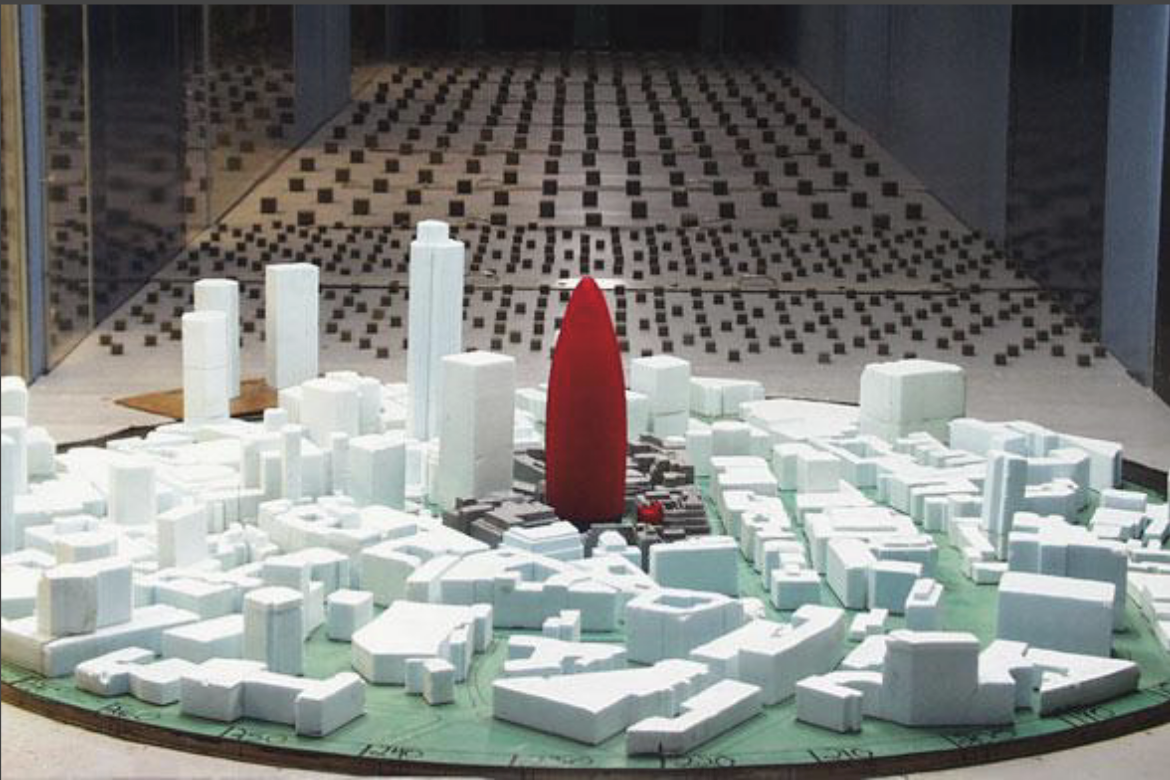
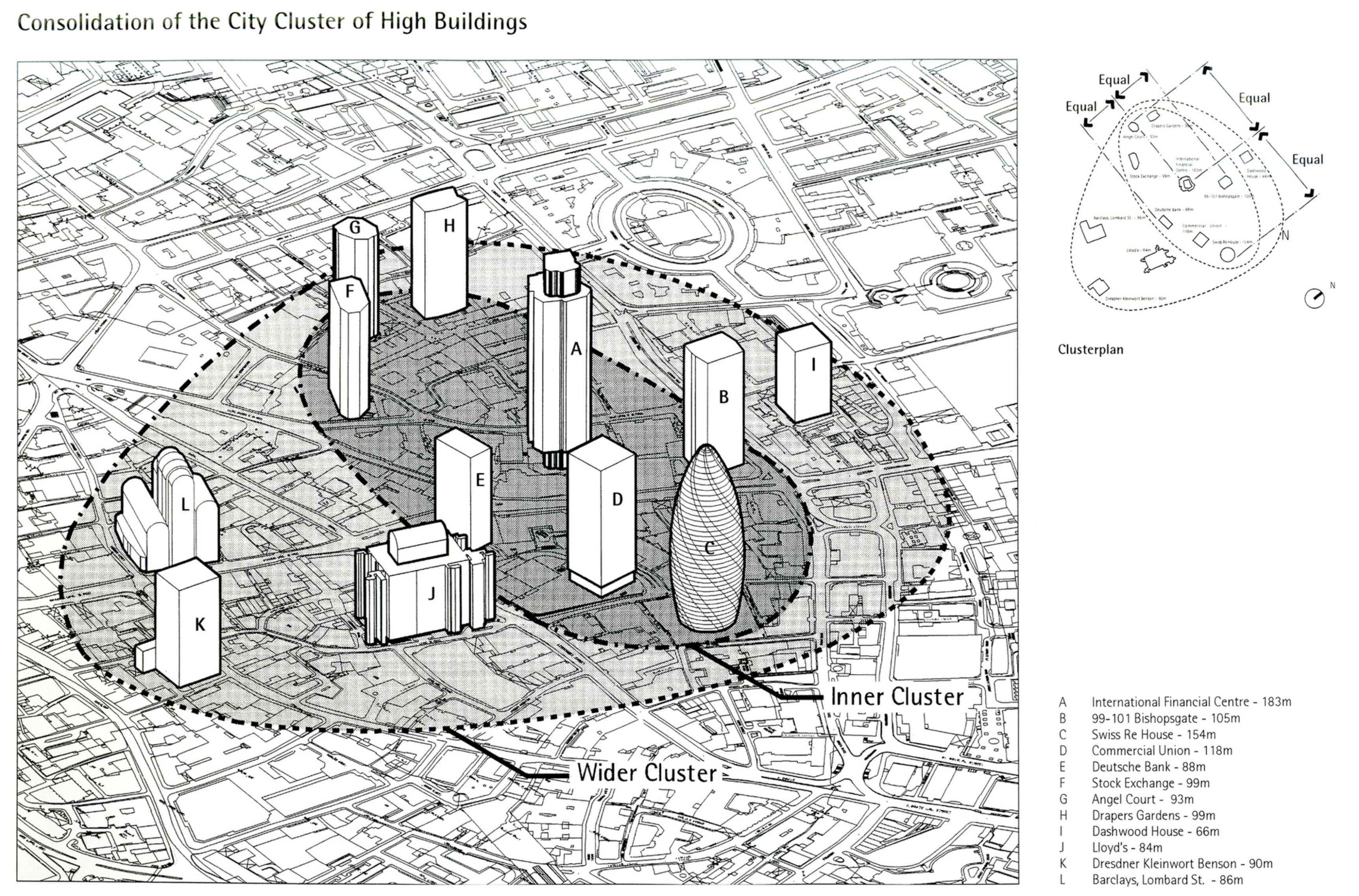
• Drawing 1: "Consolidation of the City Cluster of High Buildings." Courtesy of Foster + Partners, 1998.
Christopher Alexander, however, has introduced the idea of a generating system. For example:—
Thus the first thing is the full title: "City Cluster, Kit of Parts". It means viewing a city cluster not as a single thing but as a kit of parts, or elements, generating a worldwide system of megalopolises, or city clusters - i.e. a megalopolitan system. 1.2 In addition to the subjective need suggested by Foster + Partners in their presentation in 1998, Massey has identified a commercial need, namely:—
In the same year, the Canadian Centre for Architecture (CCA) initiated the Design of Cities competition for a site in western Manhattan, New York City, New York. The five finalists included Cedric Price. [2]
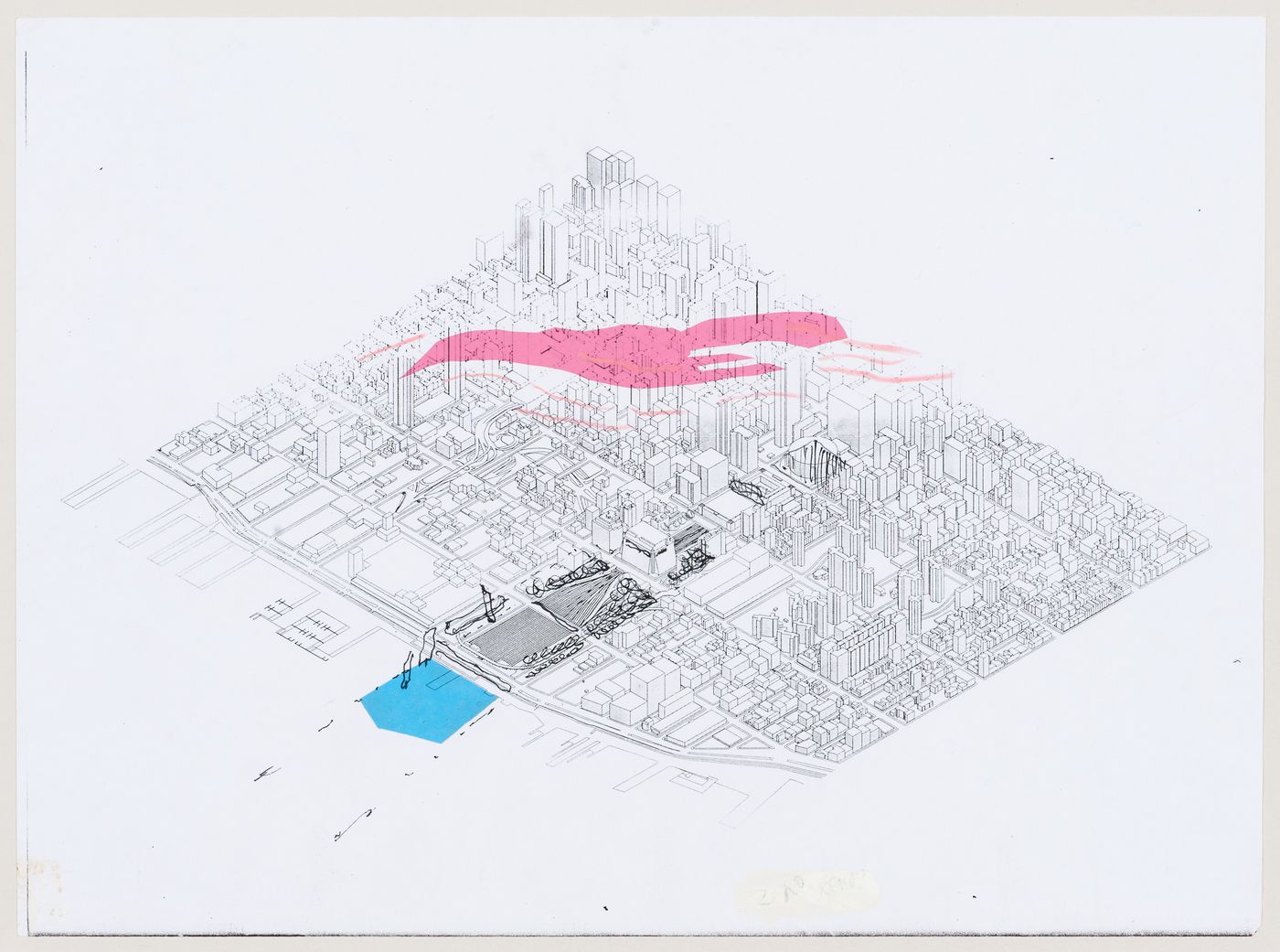
• Drawing 2: "Axonometric for IFPRI site", by Cedric Price, 1999. In the FAX confirming his "nomination and extreme interest in participation in the IFCCA project" Cedric Price identified a need, namely:—
Thus this article focuses on the relation between contemporary aspirations and architecture. 1.3 In response to the commercial need to generate profits Foster + Partners proposed a solution, namely:—
• Model 1: "Site Analysis: Urban Context" - Source: Foster + Partners
In contrast, Cedric Price proposed a radically different solution, namely:— Thus this article also focuses on the link between architecture and design criteria. |
[edit] KIT OF PARTS: A generator of a worldwide system
|
2.1 Points 1.1 to 1.3 above indicate:—
These differences are discussed below in points 2.2 and 2.3. 2.2
However, Norman Fellows has claimed:—
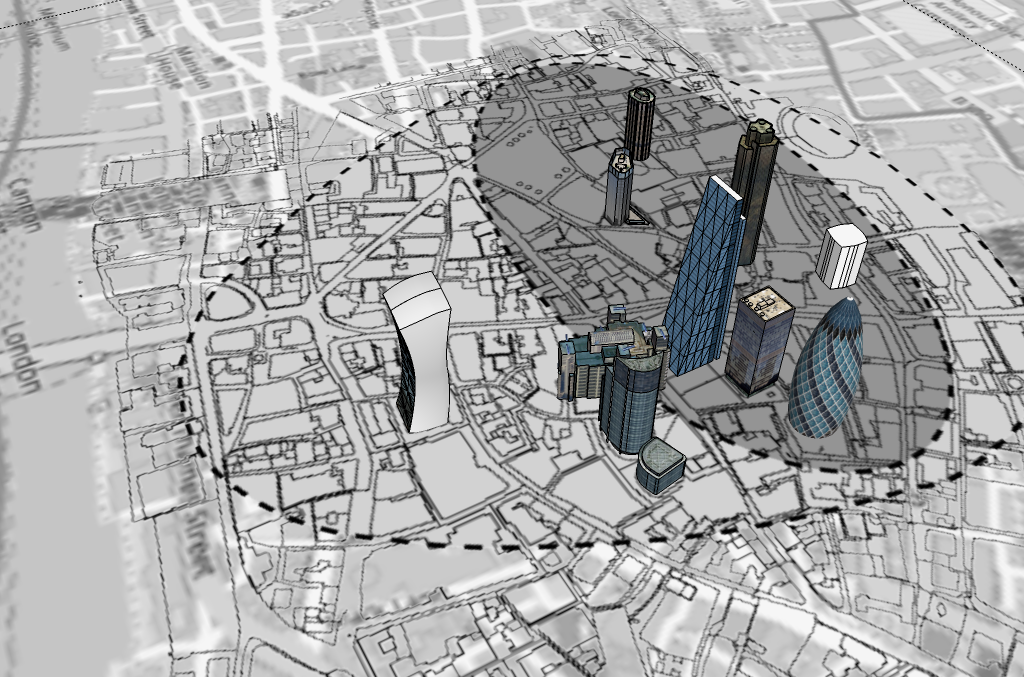
• Model 2: "Plan view with overlay of site Scene 14" - Source: Norman Fellows, 2021.
|
Table 1 below shows models of office buildings A to L from Foster + Partners' original city cluster- see key to Drawing 1.
|
A International Financial Centre |
|
B 99-101 Bishopsgate |
|
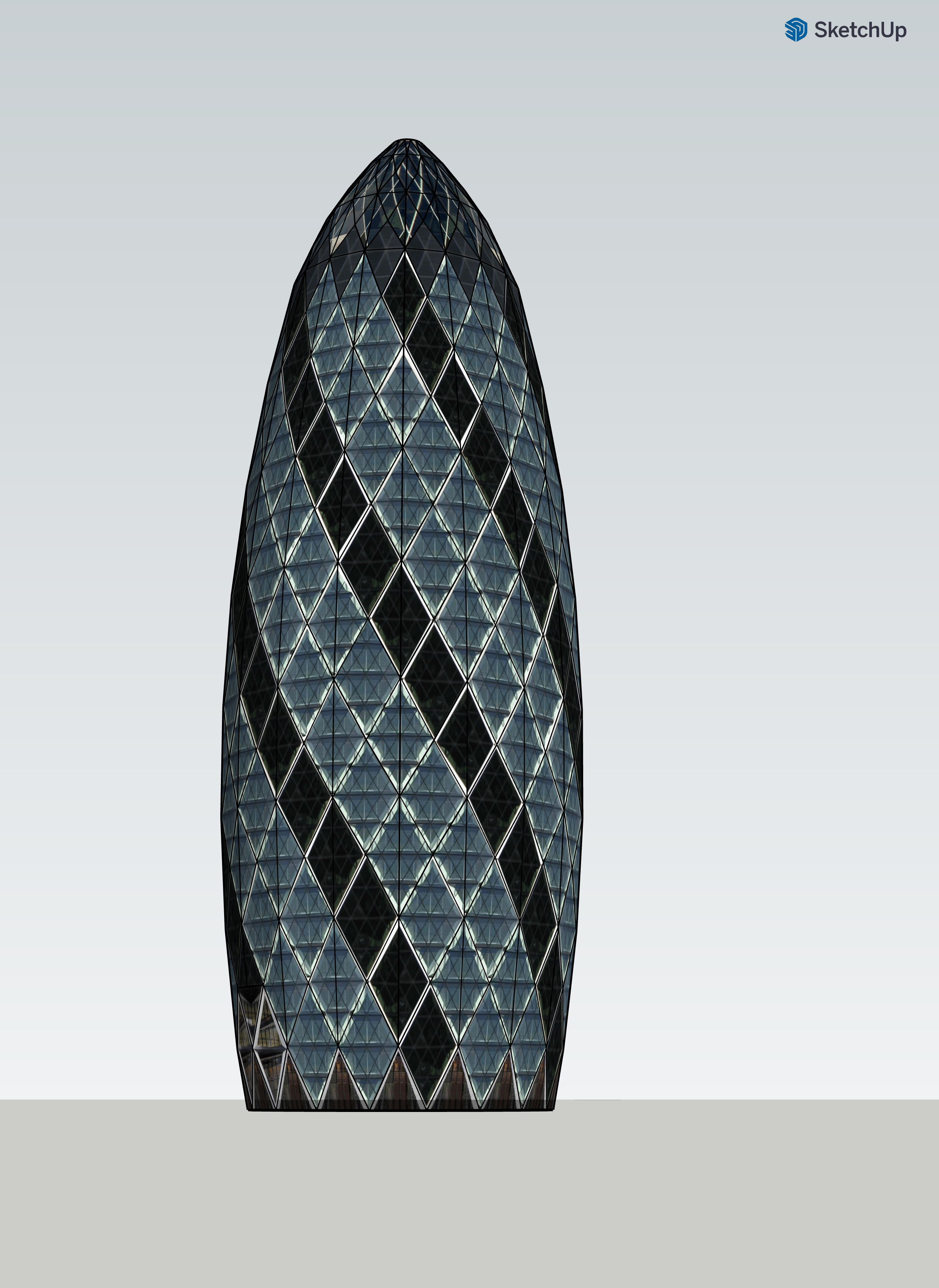
C Swiss Re House |
The invitation to "Learn More" about Swiss Re House links to its description on Wikipedia under 7 headings:— |
|
E Deutsche Bank |
|
F Stock Exchange |
|
G Angel Court |
|
H Drapers' Gardens |
|
I Dashwood House |
|
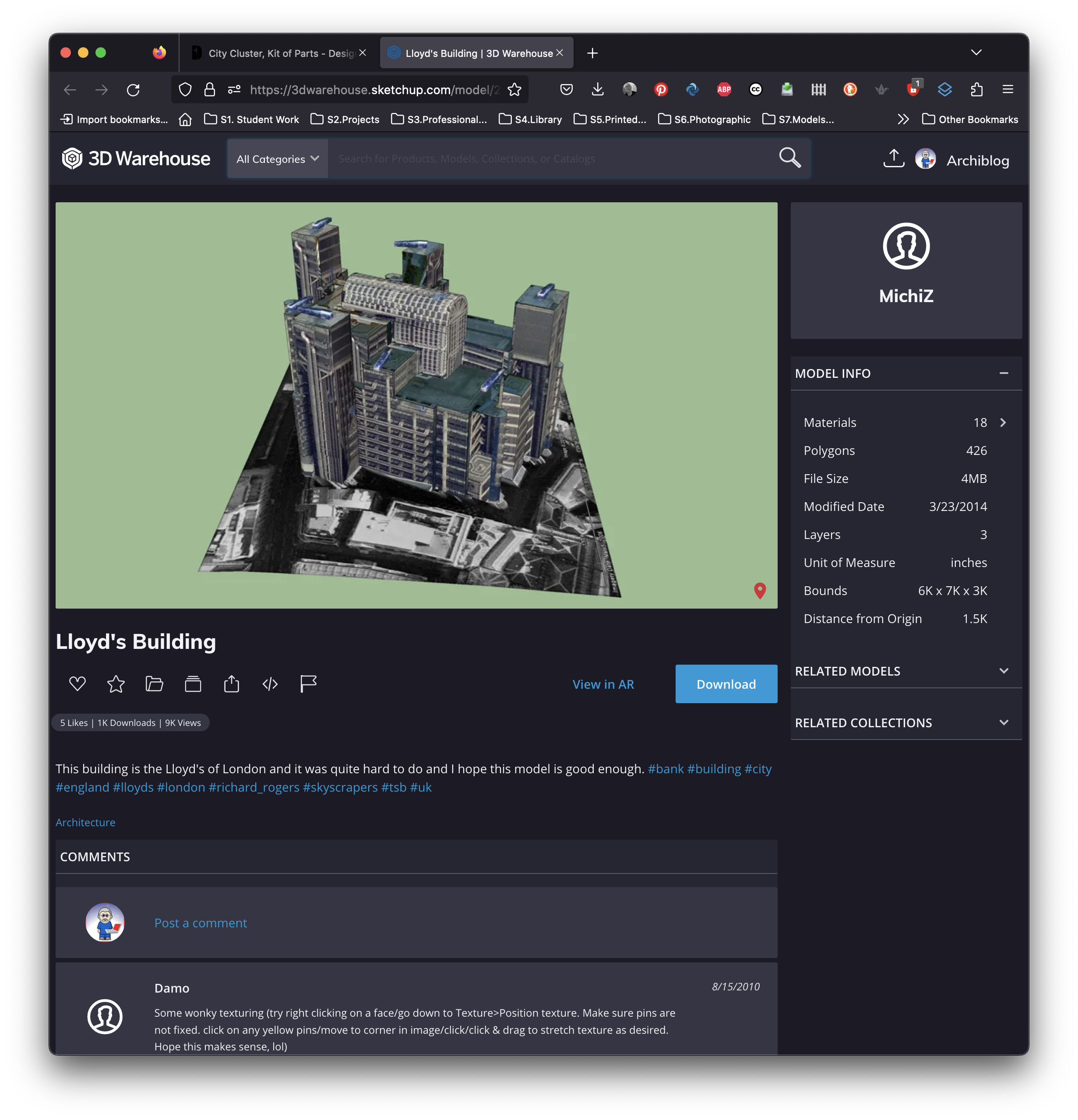
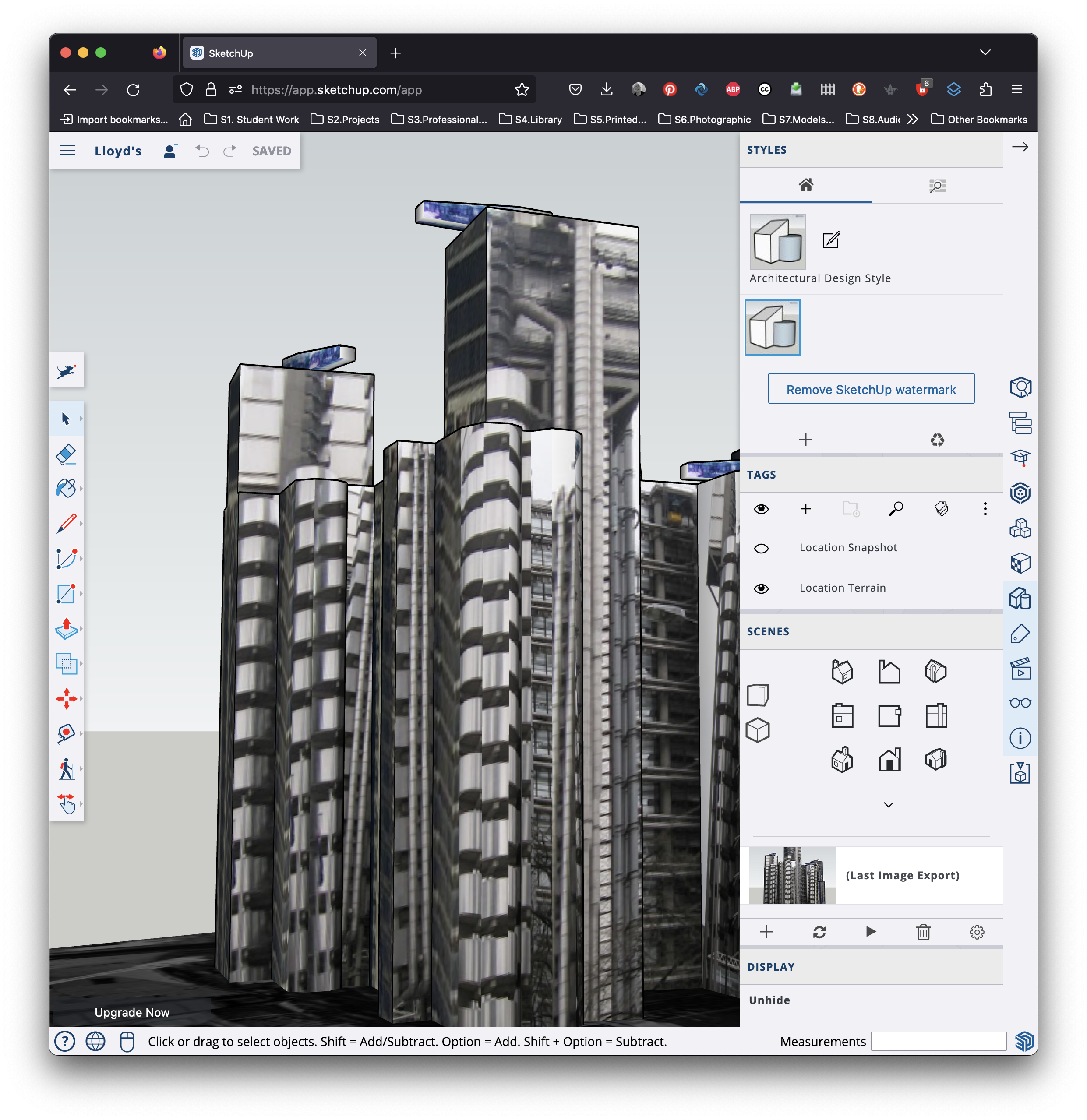
J Lloyd's |
|
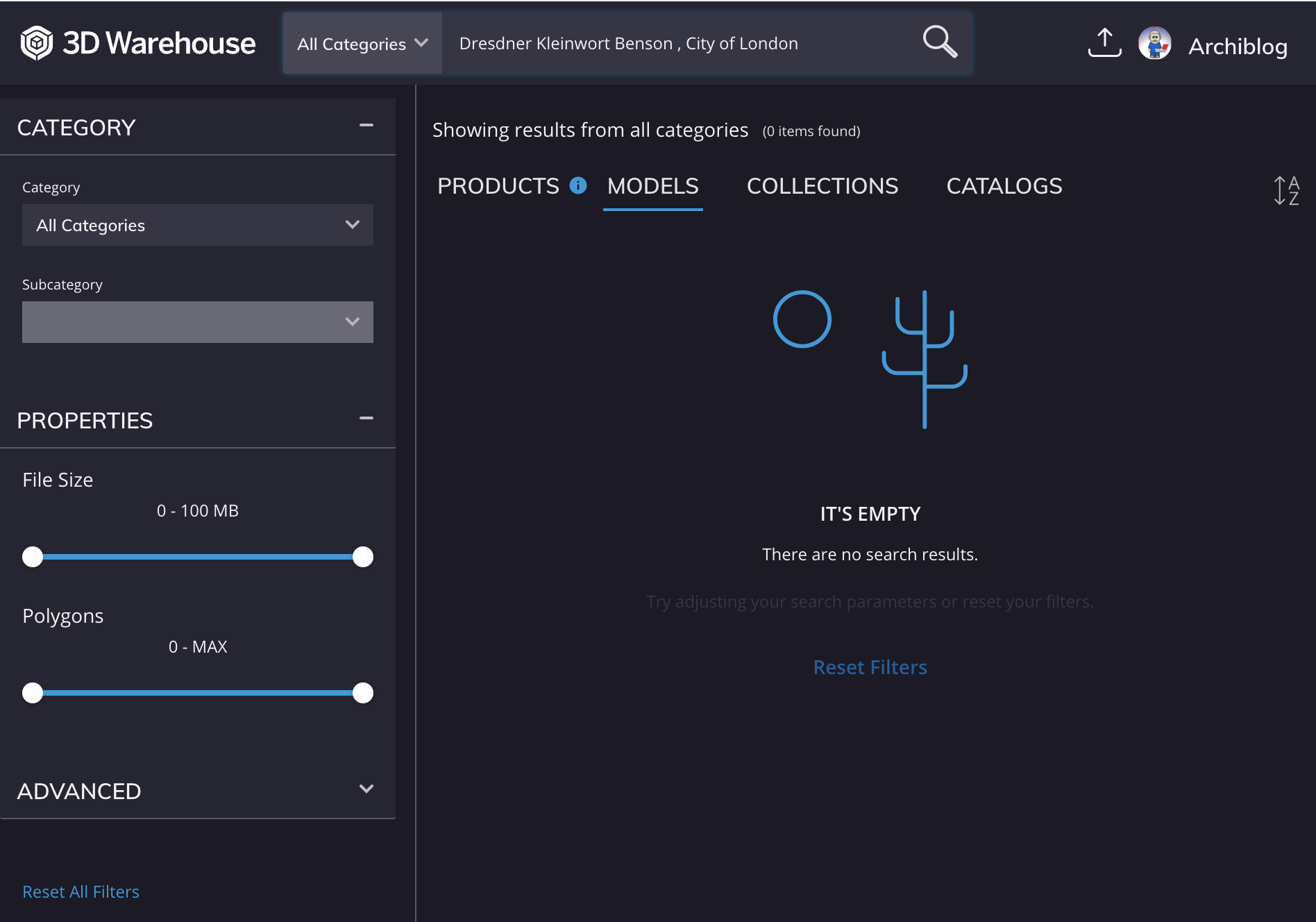
K Dresdner Kleinwort Benson |
|
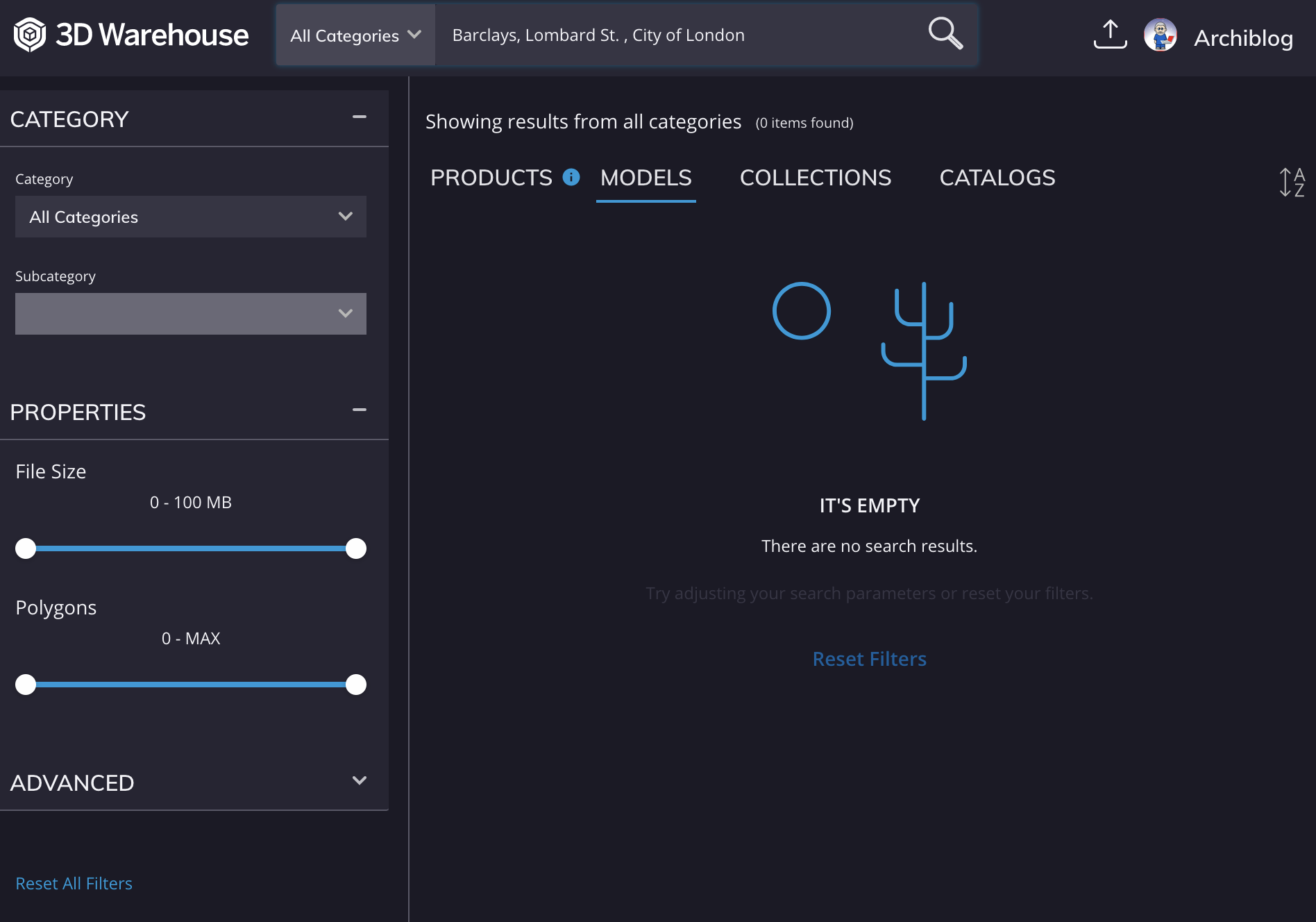
L Barclays, Lombard St. |
Table 1: Models of office buildings A to L from Foster + Partners' original "City Cluster" dated 1998.
|
Other office buildings permitted under the changed planning regime included:—
|
• Table 2 below indicates the continuing generation of a worldwide commercial system
|
2005 - Sydney, Australia |

|
2014 - Dubai, UAE |

|
|
2014 - Paris France |

|
2014 - Washington DC USA |

|
|
2017 - Shanghai, China |

|
2020 - Kuwait |
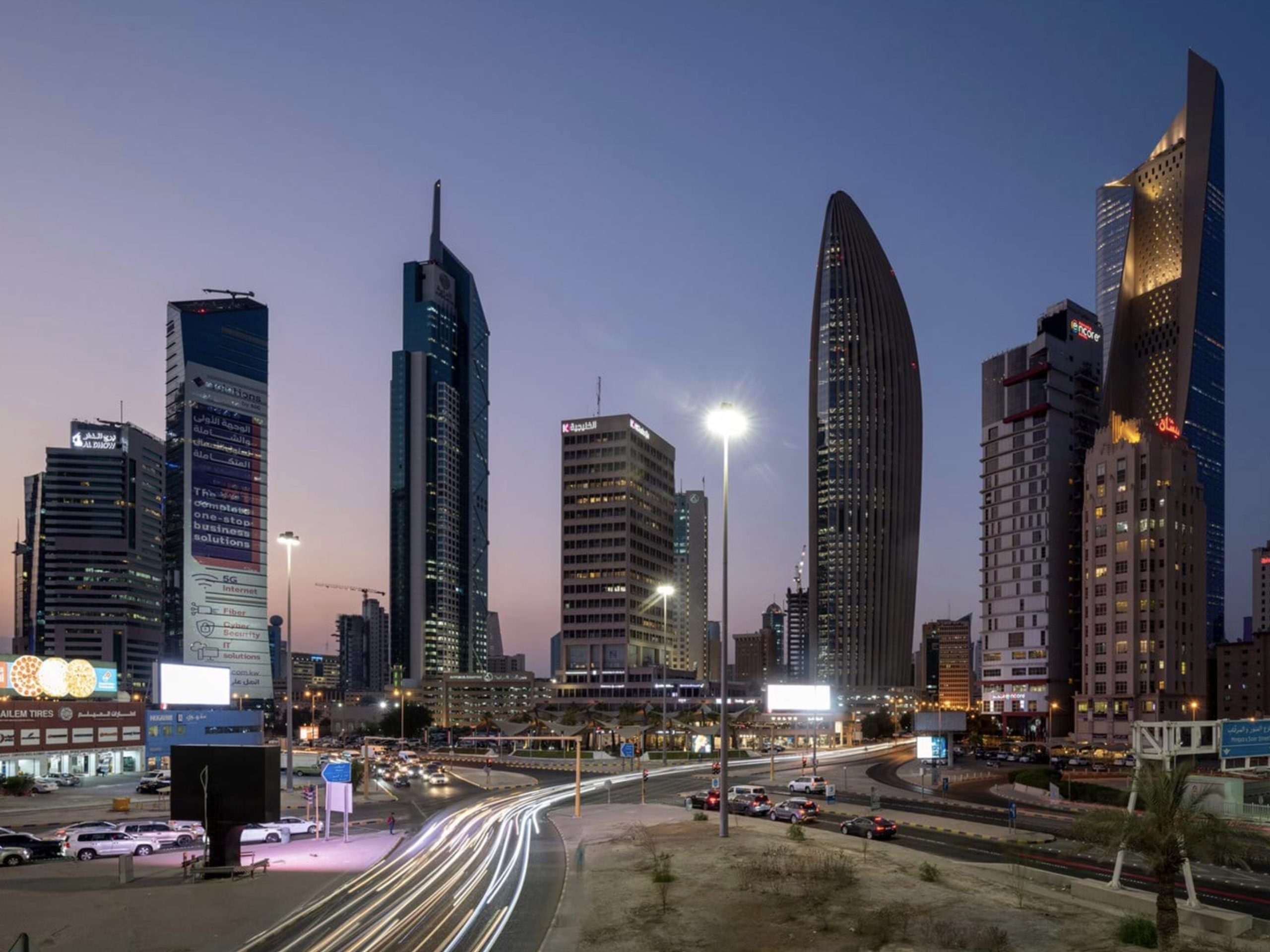

|
|
2020 - Dubai, UAE |
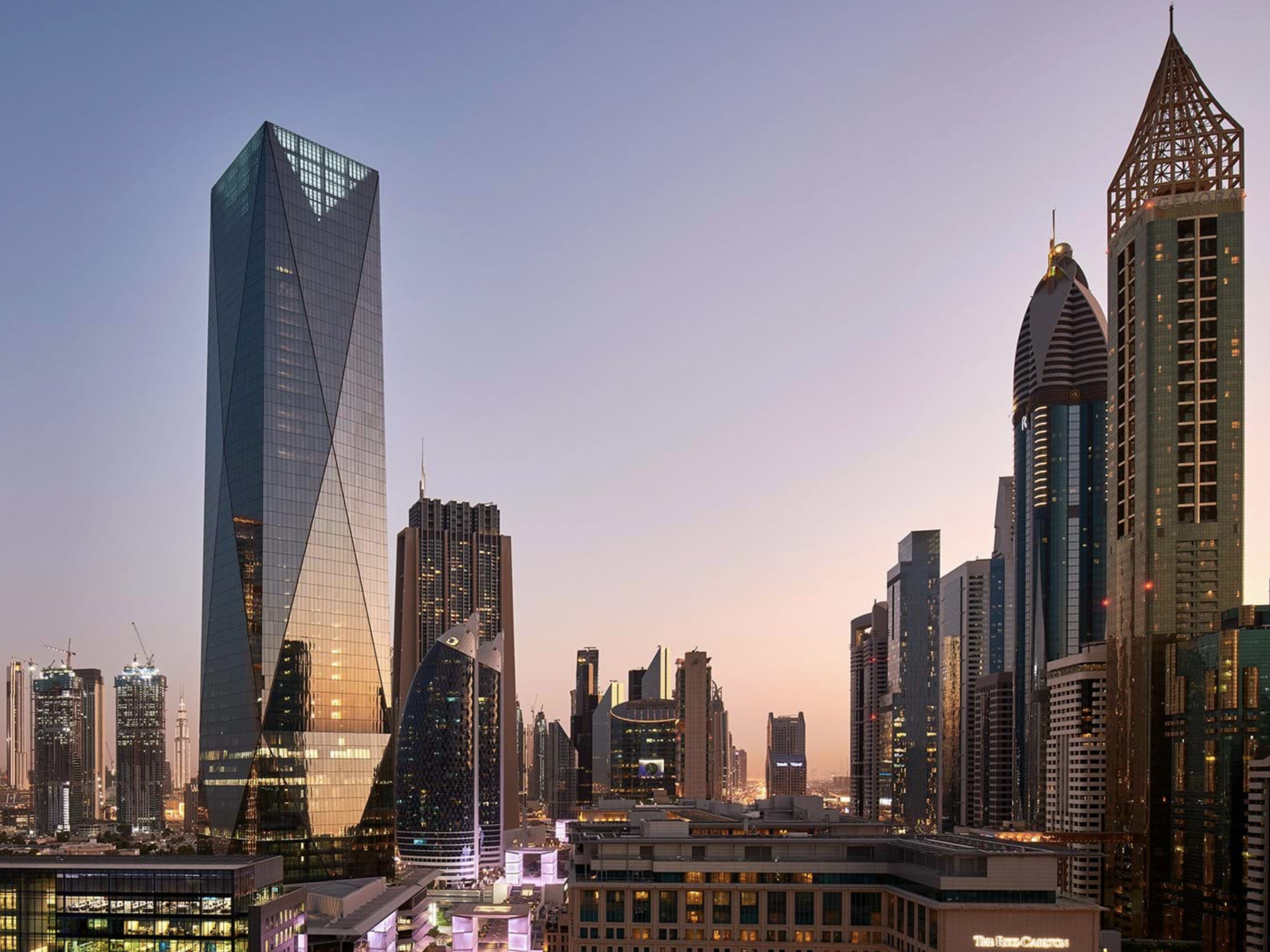

|
2022 - Hangzhou, China |

|
|
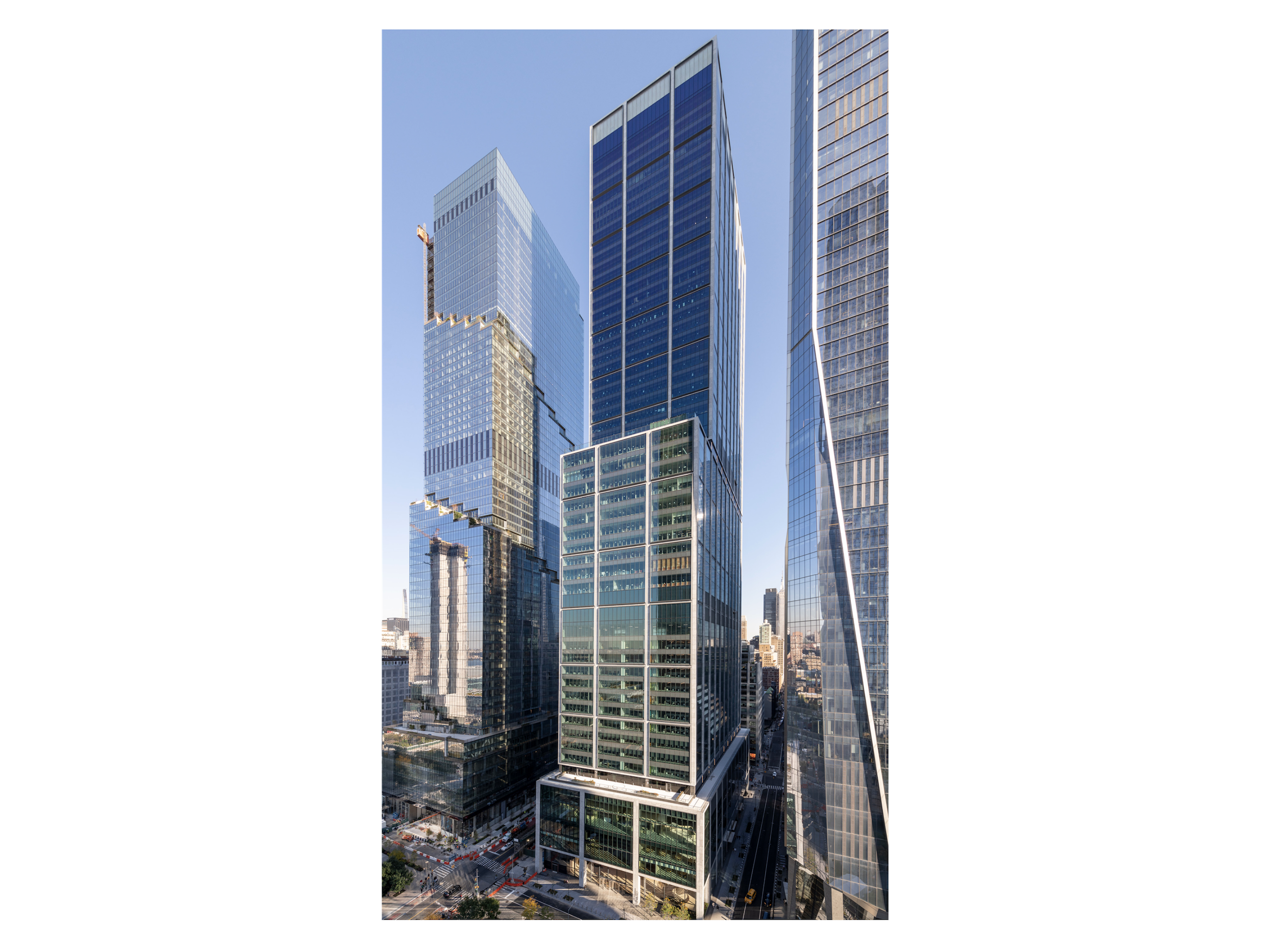
2022 - New York, USA |

|
2022 - Sydney, Australia |

|
|
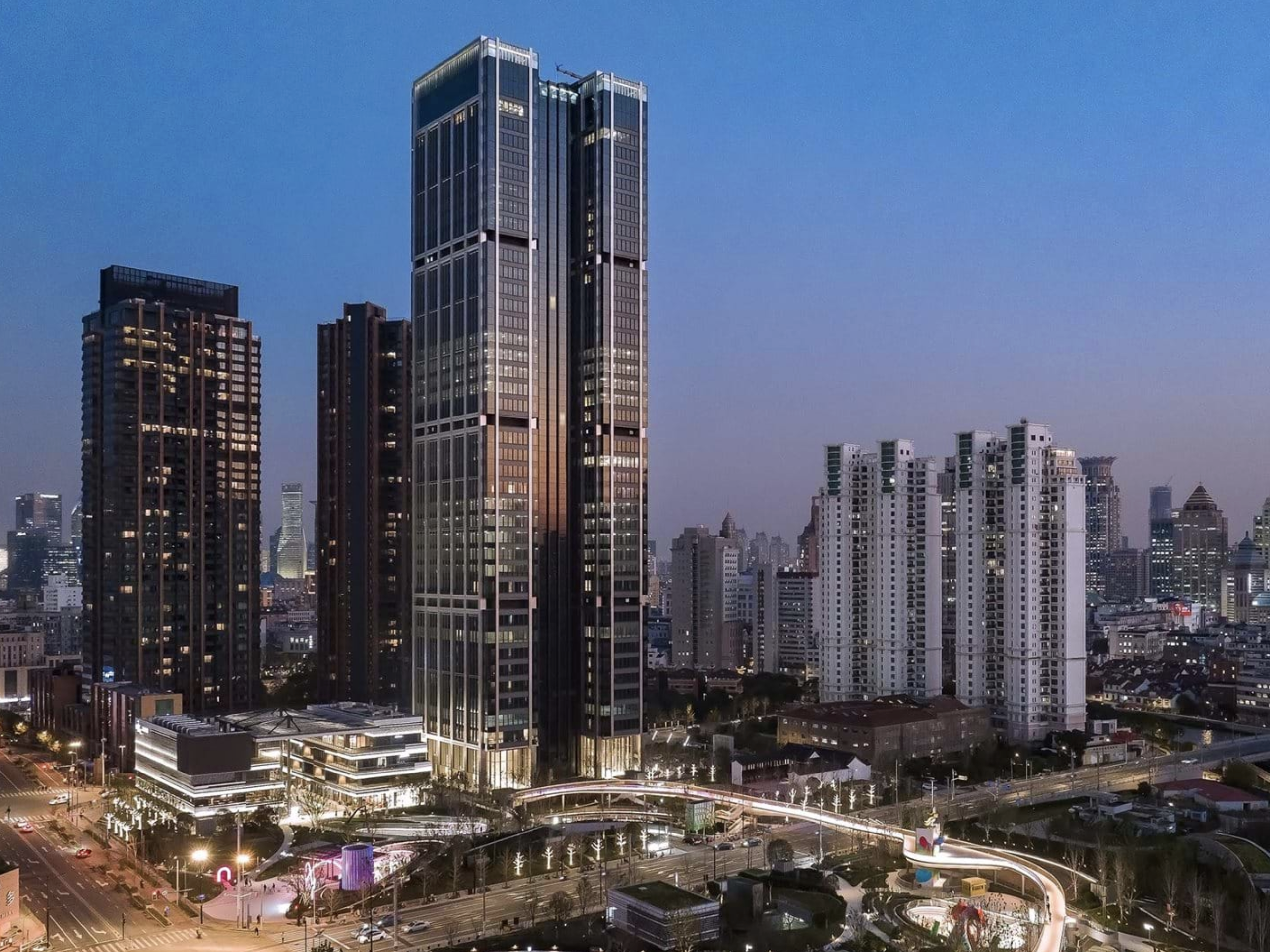
2023 - Shanghai, China |

|
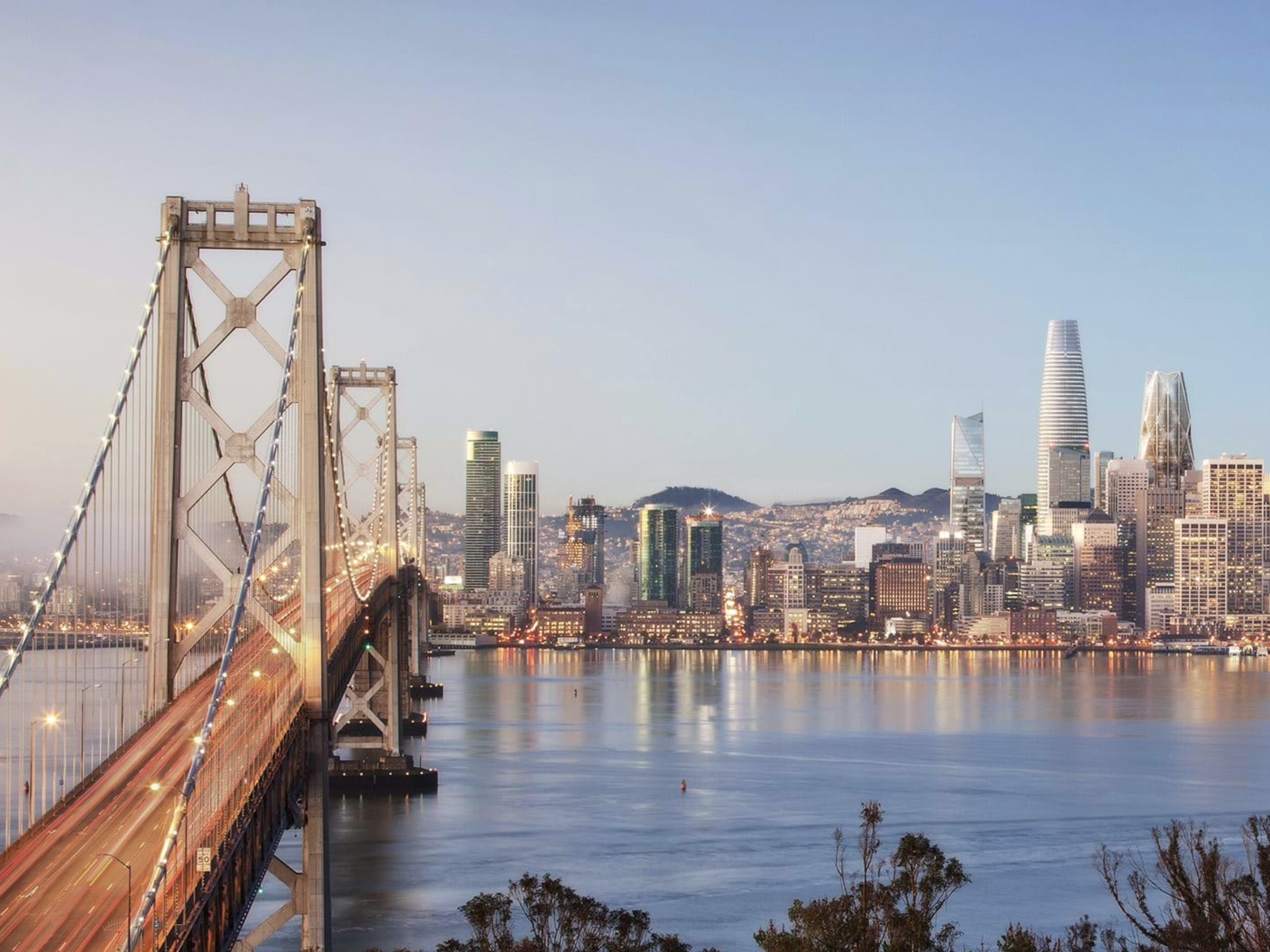
2023 - San Francisco, USA |

|
• Table 2: A selection of office buildings designed by Foster + Partners since the completion of Swiss Re House.
Note:— 50 Hudson Yards is located on the site of the Design of Cities competition in Manhattan.
Thus this article argues, firstly:—
- ... that, in 1998, "City Cluster" was the first in a series of commercial projects by Foster + Partners.
2.3
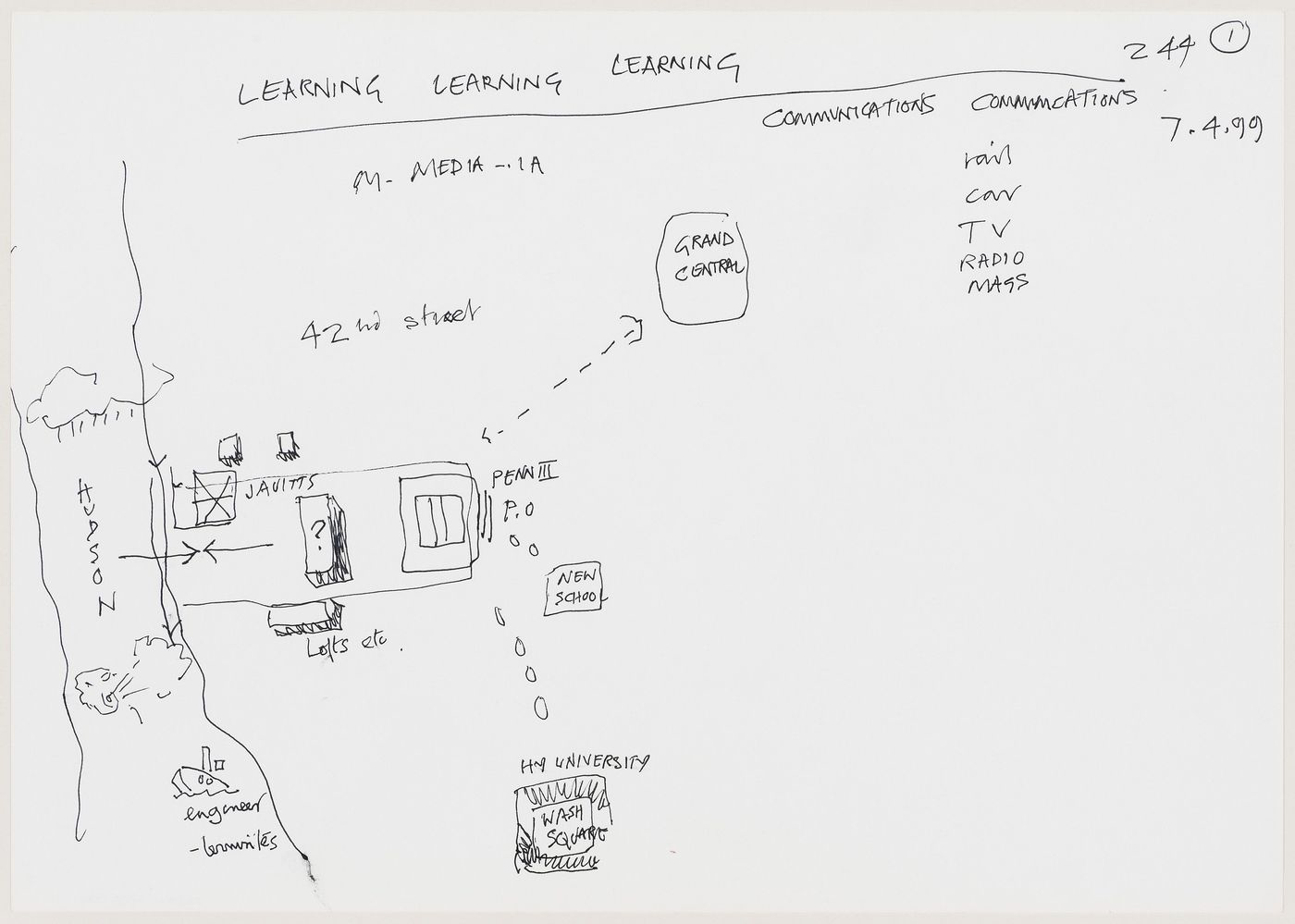
- "Defence, energy and commerce have in the past been sufficient generators of cities. This project assumes that education and the need to exchange information may have a similar generative force: cities can be made by learning."
- (Price, C. (1966) 'Potteries Thinkbelt', Architectural Design, October).
• Drawing 244/001: "LEARNING LEARNING LEARNING", by Cedric Price, 1999.
- "Drawings like this one are evidence of the underlying assumption behind IFPRI."
- (Fellows, N. (2023) 'Swiss Re Think')
Thus this article argues, secondly:—
- ... that, in 1999, "IFPRI" was the last in a series of educational projects by Cedric Price.
[edit] CONCLUSION
This article affirms its major premise as evidenced by the facts:—
- ... that Foster + Partner's commercial aspirations in 1998 related to the architecture of city clusters; and
- ... that Cedric Price's educational aspirations in 1999 related to the architecture of IFPRI.
This article also affirms its minor premise as evidenced by the facts:—
- ... that the architecture of city clusters is linked to desgn criteria such as risk and the transformation of economies and governance but not to the long-term life of office buildings: and
- ... that the architecture of IFPRI is linked to design criteria such as doubt, delight and change.
It therefore concludes:—
- ... that Swiss Re House was the original (commercial) schema of action;
- ... that the "City Cluster" in the City of London was a model for generating a system of city clusters;
- ... that, subsequently, Foster + Partners' other office buildings dotted throughout the world generate an emergent megalopolitan system.
and
- ... that the Potteries Thinkbelt was the original (educational) schema of action;
- ... that ATOM is a model for a kit of educational parts; [5]
- ... that IFPRI anticipates the generation of a worldwide educational system. [6]
- "I think it's only the beginning. I think that a clear and beautiful idea becomes politically stronger and stronger with time."
- (Mike Nichols, Letter to Cedric Price dated October 19, 1999). [7]
[edit] Notes
[1] Wikipedia (2023) 'Megalopolis'.
[2] In addition to Cedric Price, the architects chosen to compete included Ben van Berkel and Caroline Bos of Amsterdam; Peter Eisenman of New York who won the competition and its $100,000 prize with a design developed with David Childs of Skidmore, Owings & Merrill; Thom Mayne of Santa Monica, California.; and Jesse Reiser and Nanako Umemoto of New York.
[3] Foster + Partners, '30 St Mary Axe'.
[4] Comment made in December 1999.
[5] Price, C. (1968) 'Atom', Architectural Design, May.
[6] Fellows, N. (2015 et seq.) 'Edukit'.
[7] Nichols, M. (1999) 'Letter to Cedric Price', October 19 in Hardingham, S. ed. (2003) 'Cedric Price Opera)
[edit] References
Alexander, C. (1968) 'Systems Generating Systems', Architectural Design, December.
Fellows, N. (2023) 'Swiss Re Think', Archimash, February 18.
Foster + Partners (1998) 'Swiss Re House, Record Set of Presentation', 19th and 21st October. [2]
Haber, M. (2023) 'Is living in an empty office the answer to the housing crisis?', The Guardian, 10 February.
Massey, J. (2013) 'Risk Design', Aggregate 1, October.
Massey, J. (2013) 'The Gherkin: How London’s Famous Tower Leveraged Risk and Became an Icon (Part 4)', archdaily, 26 November.
Muschamp, H. (1999) 'Design Fantasies for a Strip of the West Side', New York Times, October 18.
Price, C. (1966) 'Potteries Thinkbelt', Architectural Design, October
Price, C. (1969) 'ECHOES', Architectural Design, September.
Wainwright, O. (2019) 'Welcome to Manc-hattan: how the city sold its soul for luxury skyscrapers', The Guardian, 21 October.
[edit] Further Reading
D'Souza, D. (2022) 'How London Became the World’s Financial Hub', Investopedia.
Fellows, N. (2015) 'The Fuller Challenge: My First Submission', on the 'Beyond Supercrit #1: CP: PTb' website.
Fellows, N. (2019) 'Edukit: A fantasia of the stories behind it'.
Fellows, N. (2020) 'Edukit: World Educational System—Kit of Parts'.
Kaika, M. (2010) 'Architecture and Crisis: Re-inventing the Icon, Re-imag(in)ing London and Re-branding the City', ResearchGate.
Massey, J. (2013) 'The Gherkin: How London's Famous Tower Leveraged Risk and Became an Icon', archdaily, 5 November.
Massey, J. (2013) 'The Gherkin: How London’s Famous Tower Leveraged Risk and Became an Icon (Part 2)', archdaily, 12 November.
Massey, J. (2013) 'The Gherkin: How London’s Famous Tower Leveraged Risk and Became an Icon (Part 3)', archdaily, 19 November.
Massey, J. (2013) 'The Gherkin: How London’s Famous Tower Leveraged Risk and Became an Icon (Part 4).
Muschamp, H. (1999) 'CRITIC’S NOTEBOOK; Design Fantasies for a Strip of the West Side', New York Times, in Extremely Provocative.
Swissinfo.ch (2007) 'Swiss Re sells the "Gherkin"'
--Archiblog 09:28, 23 Mar 2023 (BST)
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
Featured articles and news
The Home Energy Model and its wrappers
From SAP to HEM, EPC for MEES and FHS assessment wrappers.
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help the homebuilding sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.