Cash flow in construction
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
In general terms, 'cash flow' is the movement of income into and expenditure out of a business (or other entity) over time. If more money is coming into the business than is going out of it, cash flow is said to be 'positive'. If more money is going out, this is negative cash flow.
In construction, however, the term 'cash flow' typically refers to an analysis of when costs will be incurred and how much they will amount to during the life of a project.
Predicting cash flow is important in order to ensure that an appropriate level of funding is in place and that suitable draw-down facilities are available.
[edit] Client cash flow
Until the main contractor has been appointed, client cash flow projections are likely to be based only on agreed fee payment schedules for consultants and a simple division of the construction cost over the likely construction period (or perhaps an allocation of construction cost over an s-curve distribution). It is only when the main contractor is appointed, a master programme prepared and some form of payment schedule agreed that cash flow projections become reliable.
Cash flow projections may be affected by the need for the early purchase of long-lead time items or by items that the client may wish to purchase that are outside of the main contract (such as furniture or equipment).
[edit] Contractor cash flow
Contractors have to have money coming in to pay suppliers and subcontractors and for the day-to-day running of the business. For example, Carillion's cash flow was very low, leading to their liquidation in January 2018.
At the start of any contract, a payment scheme or table is drawn up and agreed with the client or their quantity surveyor, e.g.: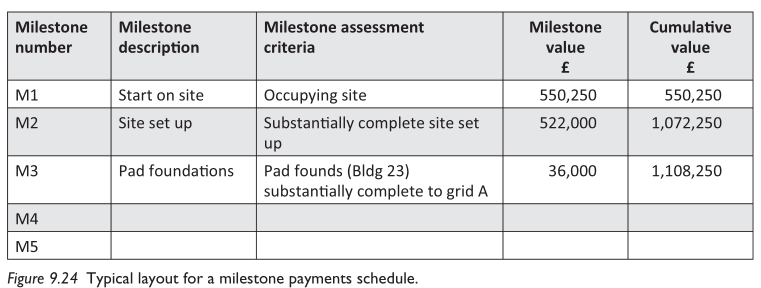
[Brook, M., 2016. Estimating and Tendering for Construction Work. 5th Edition. ed. Taylor & Francis.]
[edit] Supply chain cash flow
Cash flow is also an issue for the construction supply chain, and is a common reason for contractors and sub-contractors becoming insolvent. This can be catastrophic for a project in terms of time and money. It is in the client's interest therefore to ensure that the supply chain is paid promptly.
The government suggest that, 'Historically, it is has not been unusual for lower tier supply chain members to have to wait for up to 100 days to receive payment, which damages their cash flow and can harm their business.' (Ref. Cabinet Office, Project Bank Accounts – Briefing document.)
A number of measures can be adopted to improve payment and so cash flow in the supply chain, including:
In addition, there are a number of remedies for late payment.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Accruals.
- Balance sheet.
- Budget.
- Building society.
- Business administration.
- Cash flow forecast.
- Cash flow statement.
- Commodity.
- Construction supply chain payment charter.
- Credit crunch.
- Demand chain.
- Discounting.
- Discount rate.
- Discounted cash flow.
- Drawdown.
- Earned value.
- Fair payment practices.
- Financial hedging.
- Financial year.
- Microeconomics.
- Net Present Value.
- Payment schedule.
- Profit.
- Project bank accounts.
- Prompt payment.
- Prompt Payment Code boosted to help SMEs.
- Quote.
- Relevant cost.
- Remedies for late payment.
- Retention.
- Solvency.
- Time value of money.
- The Late Payment of Commercial Debts Regulations 2013.
- Trade credit insurance.
- Turnover.
- Whole life costs.
- Working capital.
Featured articles and news
What they are, how they work and why they are popular in many countries.
Plastic, recycling and its symbol
Student competition winning, M.C.Esher inspired Möbius strip design symbolising continuity within a finite entity.
Do you take the lead in a circular construction economy?
Help us develop and expand this wiki as a resource for academia and industry alike.
Warm Homes Plan Workforce Taskforce
Risks of undermining UK’s energy transition due to lack of electrotechnical industry representation, says ECA.
Cost Optimal Domestic Electrification CODE
Modelling retrofits only on costs that directly impact the consumer: upfront cost of equipment, energy costs and maintenance costs.
The Warm Homes Plan details released
What's new and what is not, with industry reactions.
Could AI and VR cause an increase the value of heritage?
The Orange book: 2026 Amendment 4 to BS 7671:2018
ECA welcomes IET and BSI content sign off.
How neural technologies could transform the design future
Enhancing legacy parametric engines, offering novel ways to explore solutions and generate geometry.
Key AI related terms to be aware of
With explanations from the UK government and other bodies.
From QS to further education teacher
Applying real world skills with the next generation.
A guide on how children can use LEGO to mirror real engineering processes.
Data infrastructure for next-generation materials science
Research Data Express to automate data processing and create AI-ready datasets for materials research.
Wired for the Future with ECA; powering skills and progress
ECA South Wales Business Day 2025, a day to remember.
AI for the conservation professional
A level of sophistication previously reserved for science fiction.
Biomass harvested in cycles of less than ten years.
An interview with the new CIAT President
Usman Yaqub BSc (Hons) PCIAT MFPWS.
Cost benefit model report of building safety regime in Wales
Proposed policy option costs for design and construction stage of the new building safety regime in Wales.
Do you receive our free biweekly newsletter?
If not you can sign up to receive it in your mailbox here.























Comments
Cash flow is the movement of income into and expenditure out of a business over time. If there is more money going out than in, this is negative cash flow.
Possible cash flow problems may be:
To minimise the risks of future cash flow problems, the firm could establish a financial system that includes: