Design of Intermodal Passenger Terminal
Contents |
[edit]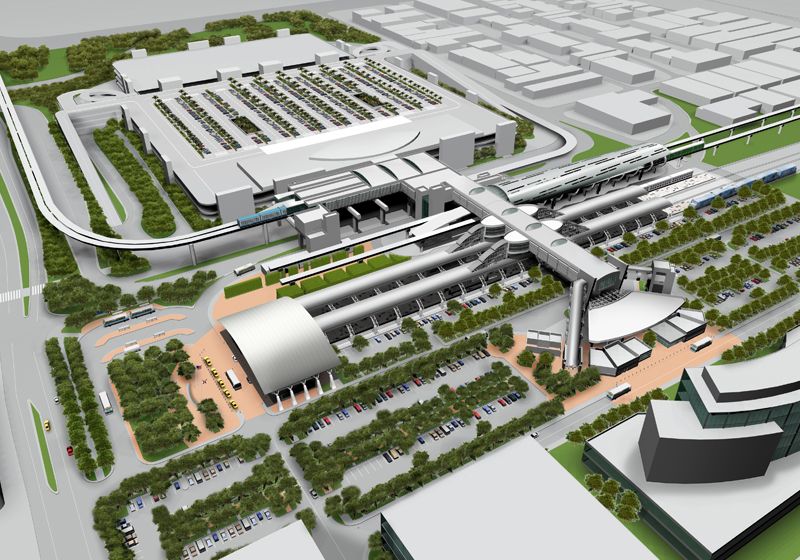  Introduction
Introduction
A multimodal passenger terminal is transportation centre in which several modes of transportation are physically and operationally integrated, usually under one roof.
At one terminal, complex vehicles arrive and depart while passengers interchange between the modes. Interchanges interconnect different transport modes that complement each other to accommodate a person’s journey from its origin to its destination. They are key public transport nodes. The function of the interchange is to reduce the distance between transport modes to facilitate multi-activities patterns.
The benefits of multimodal transport include time-saving, reduced waiting time, urban integration, reduced pollution, carbon emission, noise and congestions, and improvement of business operational models.
Multimodal passenger terminals can accommodate bus, rail, transit, taxi, automobile, ferry and aircraft modes. Mode integration can be achieved by methods such as coordinated schedules, joint use of services, and fare integration.Designing intermodal terminals is a multi-disciplinary task, the aim of which is to obtain maximum efficiency and enhance accessibility to all users.
Travel information and intermodal services are provided in all zones as well as in the facilities and retailing. The main design considerations are safety and security, transfer conditions, emergency planning, information, aesthetics, services and facilities, environmental quality, and comfort of waiting time.
The factors that influence the architecture of an interchange include; users, operators, third part deals with local impacts, governance and business models, mobility patterns, urban density and location of activities, technology, land use planning and social concerns.
The typologies of intermodal terminals depend on functions, logistics and spatial location (local constraints).
Demand – the volume of passengers define the size of the size of the terminal, the need for space and access characteristics. There are three levels of demand:
- Less than 30,000 passengers/day.
- Between 30,000 and 120,000 passengers/day.
- More than 120,000 passengers/ day.
Modes of transport include:
- Intermodal terminal with buses as the dominant mode of transport.
- Intermodal terminal with rail as the dominant mode of transport.
- Two or more public transport modes or different lines of the same mode jointly.
[edit] The physical components of intermodal terminals
The interchange will typically have three spatial zones:
- Access-egress zone - a zone in which links to the local area and access to transport modes are present.
- Facilities zones - a zone that comprises supporting services like retail shops, restaurants, ticketing, hotels etc.
- Arrival-departure - this caters for intermodal transfers.
[edit] The access-egress zone
This zone should provide facilities and services for users arriving and leaving the terminal. Services and facilities in this zone are those that aid safe, efficient movement in and out of the terminal enhancing convenient access, signposting and way finding. Outside waiting areas should be provided with shelters for those waiting for public transport.
[edit] The facilities and retail zone
This is a zone where travellers who have more time available to spend at the terminal such as tourists, can do shopping or eating while waiting for transfer. It also provides space for ticketing services and contains real time information.
[edit] The transport/transfer zone
This a zone that users are waiting for transport modes. This zone should be convenient to all and easy to navigate, and should contain provision of up to date information.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
Featured articles and news
Key points for construction at a glance with industry reactions.
Functionality, visibility and sustainability
The simpler approach to specification.
Architects, architecture, buildings, and inspiration in film
The close ties between makers and the movies, with our long list of suggested viewing.
SELECT three-point plan for action issued to MSPs
Call for Scottish regulation, green skills and recognition of electrotechnical industry as part of a manifesto for Scottish Parliamentary elections.
UCEM becomes the University of the Built Environment
Major milestone in its 106-year history, follows recent merger with London School of Architecture (LSE).
Professional practical experience for Architects in training
The long process to transform the nature of education and professional practical experience in the Architecture profession following recent reports.
A people-first approach to retrofit
Moving away from the destructive paradigm of fabric-first.
International Electrician Day, 10 June 2025
Celebrating the role of electrical engineers from André-Marie Amperè, today and for the future.
New guide for clients launched at Houses of Parliament
'There has never been a more important time for clients to step up and ...ask the right questions'
The impact of recycled slate tiles
Innovation across the decades.
EPC changes for existing buildings
Changes and their context as the new RdSAP methodology comes into use from 15 June.
Skills England publishes Sector skills needs assessments
Priority areas relating to the built environment highlighted and described in brief.
BSRIA HVAC Market Watch - May 2025 Edition
Heat Pump Market Outlook: Policy, Performance & Refrigerant Trends for 2025–2028.
Committing to EDI in construction with CIOB
Built Environment professional bodies deepen commitment to EDI with two new signatories: CIAT and CICES.
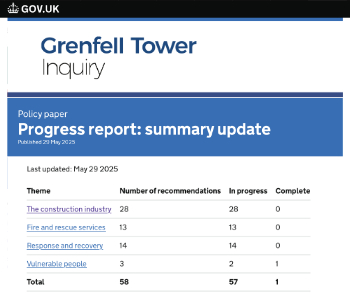
Government Grenfell progress report at a glance
Line by line recomendation overview, with links to more details.
An engaging and lively review of his professional life.
Sustainable heating for listed buildings
A problem that needs to be approached intelligently.
50th Golden anniversary ECA Edmundson apprentice award
Deadline for entries has been extended to Friday 27 June, so don't miss out!
CIAT at the London Festival of Architecture
Designing for Everyone: Breaking Barriers in Inclusive Architecture.
Mixed reactions to apprenticeship and skills reform 2025
A 'welcome shift' for some and a 'backwards step' for others.