Buildings that help rebuild lives and communities
With the increasing impact of climate change the number of natural disasters is growing rapidly. How do we ensure that affected communities can quickly and sustainably recover and rebuild their lives and communities?
Providing shelter for displaced people and families is one of the first critical components of disaster relief. Shelters need to be designed for resilience, rapid construction and deployment, but also crucially able to make use of local skills, labour and materials.
It is with this in mind that CRS (Catholic Relief Services) and BRE (Building Research Establishment) have been collaborating to create a demonstration of the techniques and materials that can be used to create an effective humanitarian shelter. How a shelter contributes to the wider humanitarian effort and rebuilding process will also be considered.
CRS has long experience as agency that alleviates suffering and provides assistance to people in need in more than 100 countries. CRS’ relief and development work is accomplished through programmes of emergency response, HIV, health, agriculture, education, microfinance and peacebuilding.
Working with the IFRC, BRE has pioneered the development of QSAND, the self-assessment sustainability tool focused on shelter and settlement reconstruction in the aftermath of natural disasters.
“Our collaboration with BRE is designed to create a focal point for demonstration and research in the provision of humanitarian shelters”, says Jamie Richardson, Shelter and Settlements Technical Advisor for CRS.
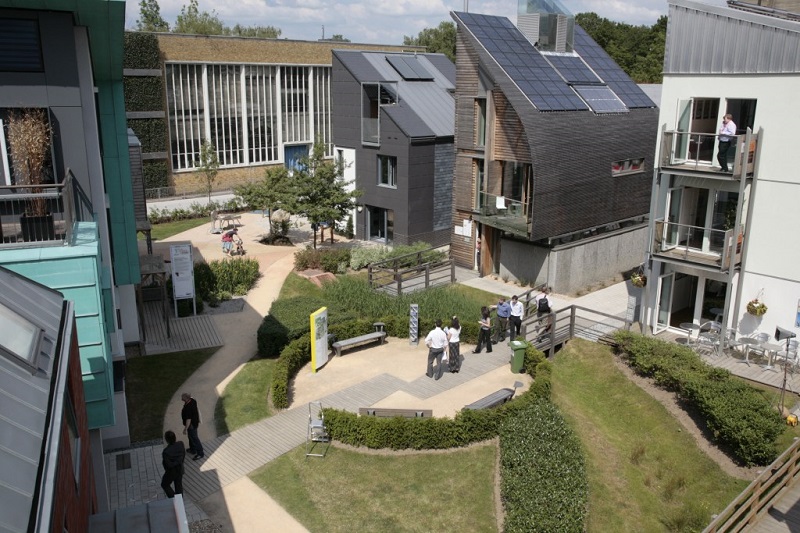
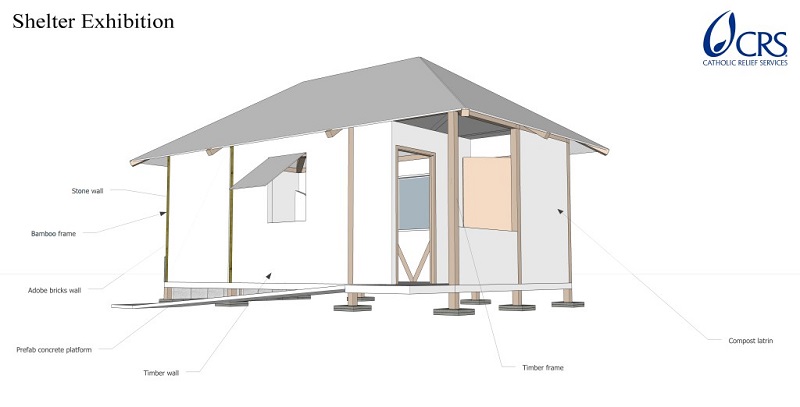
“The exhibition unit we are creating for the BRE Innovation Park in Watford [see top image] is a based on the Sphere Standards for shelter building. Sphere is a voluntary initiative from wide range of humanitarian agencies to improve the quality of humanitarian assistance. The unit will, in fact, be an amalgam of various techniques and materials, showing how various vernacular materials such as bamboo, adobe bricks and mud construction can be used in different parts of the world.”
The shelter will cover an area of 17.5 sq. m and be designed to be occupied by a family of five. This size unit is typical of the usual minimum space allocation of shelters around the world. It will aim to demonstrate materials and construction techniques, and also be the focal point for a research and demonstration programme on process and non-technical issues.
For example, a composting toilet is to be integrated into the shelter structure, to show the linkage with health and sanitation programmes. It will also incorporate features such as the inclusion of inner partitions for privacy and to address the needs of women and children.
“Our aims are to share information with stakeholders and the wider public and media on these issues” says Richardson. “It will be part of our outreach to building professionals and materials experts, and act as a stimulus for wider research and understanding on issues such as climate change resilience and sustainability”.
The home of the demonstration unit is the BRE Innovation Park at Watford, which features full-scale demonstration buildings that have been developed by industry partners across the built environment. These buildings display innovative design, materials and technologies which combine to address the development challenges facing regions across the world.
This article was originally published here by BRE Buzz on 29 June 2017. It was written by Simon Guy.
--BRE Buzz
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- BRE Buzz articles on Designing Buildings Wiki.
- Designing resilient cities: a guide to good practice (EP 103).
- Engineering resilience to human threats.
- Future proofing construction.
- Helping communities recover from disasters and protecting them before they occur.
- Humanitarian shelter exhibition.
- KODA house.
- Managing and responding to disaster.
- QSAND application in Nepal.
- QSAND and the Sustainable Development Goals.
- Resilience.
- Social and sustainable communities.
- Two steps towards a more resilient world.
Featured articles and news
The Home Energy Model and its wrappers
From SAP to HEM, EPC for MEES and FHS assessment wrappers.
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help the homebuilding sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.