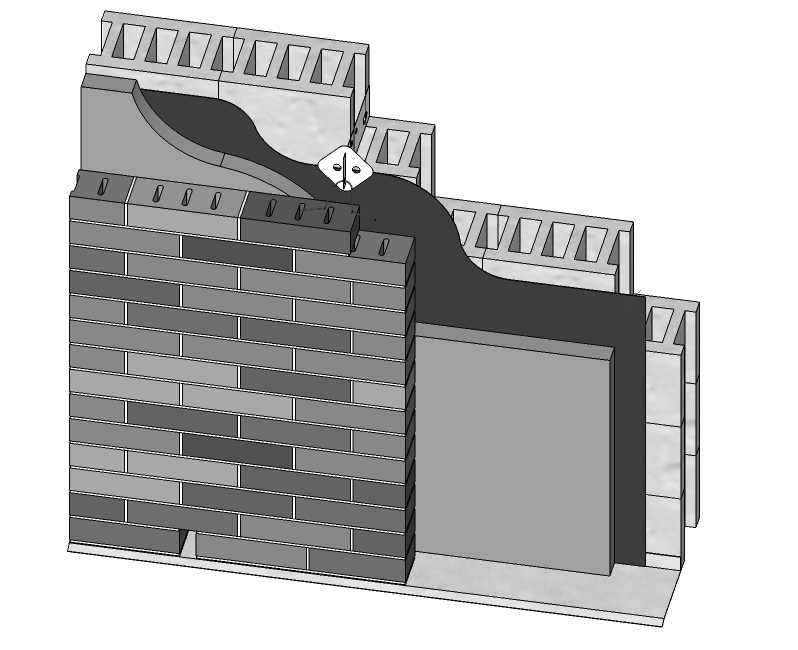
Brick wall
Typically, a brick wall is a vertical element of construction made of bricks and mortar and is used to form the external walls of buildings, parapets, internal partitions, freestanding walls, retaining walls, and so on.
The first walls were made from mud bricks held together by a thin mud slurry, some of which have proved to be surprisingly resilient. A contemporary brick wall is typically made of clay, concrete, or calcium-silicate bricks. The most common brick size is 215mm (L) x 102.5mm (W) x 65mm (H). Bricks are bound together by a cementitious or lime mortar, usually 10mm thick for the horizontal (bedding) joints and 10mm wide for the vertical (perpend) joints.
Brick walls can be straight, curved, zig-zag, and so on in plan form and typically vary in thickness from 102.5 mm upwards. Brick walls can also be sloped but usually require some form of support to achieve this eg from steelwork or a concrete backing.
In modern construction, brick walls (sometimes referred to as brickwork) tend to be used for housing as the external component of cavity wall construction in which they are tied to an inner masonry leaf which can also be brick but is more often blockwork. The cavity will often contain insulation to reduce thermal transmission through the wall. For more information see: Cavity wall.
In contrast, Victorian brick walls were mainly solid brickwork ie, either one-brick-thick (9-inches or 225mm) or one-and-a-half-brick-thick (13 inches or 330mm). However, in some instances they could be thicker depending on the application.
A brick wall usually requires a foundation which can be either a concrete strip or a traditional ‘footing’. In the latter, the base of the brickwork is stepped out either side, usually by a third of a brick width at a time, for three or four courses in order to increase the width and so spread the load over a wider area.
Because clay brickwork undergoes a degree of thermal expansion when temperatures rise, movement joints must be installed, otherwise cracking might occur, possibly leading to instability. Movement joints in clay brickwork are usually placed every 10m-12m around the building perimeter. However, parapets and free-standing walls are less restrained (ie, they are more free to move at their uppermost ends) and so the spacing is usually reduced to 6m-8m. Detailed information is available from The Brick Development Association.
Walls made of concrete or calcium silicate (sand lime) bricks tend to shrink and therefore movement joints must accommodate this.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- Airbrick.
- Aircrete blocks.
- Blockwork.
- Bricklayer.
- Brick strip foundation.
- Brick veneer.
- Cavity tray.
- Cavity wall.
- Crinkle crankle wall.
- Damp-proof course.
- Defects in brickwork
- Efflorescence.
- How to lay bricks.
- Mortar.
- Perpend.
- Pointing.
- Testing bricks.
- Treating brickwork with sealant or water repellent.
- Types of brick bonding.
- Types of bricks.
- Unfired clay masonry: An introduction to low-impact building materials.
- Which way up should you lay a brick?
- Wall tie failure.
Featured articles and news
Repairing historic stone and slate roofs
The need for a code of practice and technical advice note.
UKCW London to tackle sector’s most pressing issues
AI and skills development, ecology and the environment, policy and planning and more.
Managing building safety risks
Across an existing residential portfolio; a client's perspective.
ECA support for Gate Safe’s Safe School Gates Campaign.
Core construction skills explained
Preparing for a career in construction.
Retrofitting for resilience with the Leicester Resilience Hub
Community-serving facilities, enhanced as support and essential services for climate-related disruptions.
Some of the articles relating to water, here to browse. Any missing?
Recognisable Gothic characters, designed to dramatically spout water away from buildings.
A case study and a warning to would-be developers
Creating four dwellings... after half a century of doing this job, why, oh why, is it so difficult?
Reform of the fire engineering profession
Fire Engineers Advisory Panel: Authoritative Statement, reactions and next steps.
Restoration and renewal of the Palace of Westminster
A complex project of cultural significance from full decant to EMI, opportunities and a potential a way forward.
Apprenticeships and the responsibility we share
Perspectives from the CIOB President as National Apprentice Week comes to a close.
The first line of defence against rain, wind and snow.
Building Safety recap January, 2026
What we missed at the end of last year, and at the start of this.