Time to retrofit to secure a net zero future
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
If the UK is to have any chance of achieving its net zero carbon target by 2050, the existing building stock will have to be improved considerably with a comprehensive retrofit plan to improve thermal performance, reduce energy consumption and upgrade heating systems.
It is well known that Britain's housing stock is some of the oldest and poorest performing in Europe. With nearly six million houses built before 1919, the challenge before us is quite daunting as a good proportion of the UK's 29 million homes will need at least some improvement to reduce the 17% of total carbon emissions that comes from housing. [1]
[edit] Regulatory updates
Whilst higher standards for energy efficiency are being introduced for new build housing – the new and updated Part L of the Building Regulations for England came into force in June 2022, followed by new energy efficiency updates in Scotland and Wales in November and December 2022, and the Future Homes Standard for 2025 will require all new homes and other buildings to be built to ultra-high levels of energy efficiency, there is little to promote and deliver the improvements needed for existing buildings.
The government has a vague aim of upgrading existing homes to EPC C by 2035, but only where 'practical, affordable and cost effective'. This will require more than 15 million homes in England to be upgraded over the next twelve and a half years, but with no real strategy in place it is difficult to see how this can be achieved.
The Heat and Building Strategy published in 2021 expands on the detail of heat in buildings, but there is little on improving energy efficiency, reducing demand or the essential policy needed to support any large-scale approach to mass retrofitting.
If we are to move to a net zero carbon country by 2050 (2045 in Scotland), it will be vital to make improvements to homes and other buildings to reduce emissions. This means installing a whole range of energy saving measures; from better insulation and more efficient appliances, to replacing fossil fuelled boilers with low carbon alternatives such as heat pumps.
[edit] The role of insulation
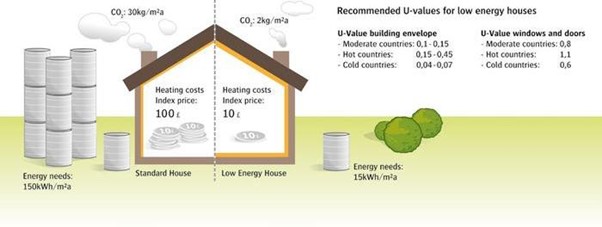
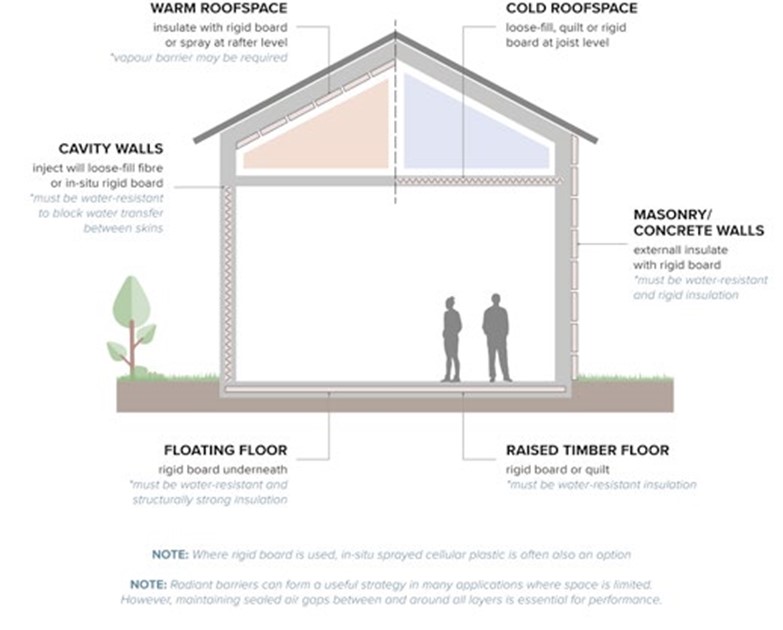
The role of PIR and PUR insulation in upgrading our poorly performing housing stock and ensuring a sustainable future cannot be underplayed. Good insulation is essential and is one of the simplest and most cost-effective ways to reduce energy demand and cut CO2.
The lower the U-values in walls, floors and roofs, the less heat that is lost, resulting in enhanced thermal performance which in turn will help to deliver the standards required.
Highly effective and incredibly versatile, PIR and PUR insulation solutions are available in a range of forms including boards and blocks, cavity injected, composite panels, as well as spray and panel insulation. This with lambda values as low as 0.021 W/mK, PIR insulation performance can be achieved with less thickness than other commonly used insulation materials. Its exceptional insulating properties, high strength and light weight means it is used widely across residential, commercial and refurbishment projects.
Retrofitting insulation such as high-performance PIR is a valuable instrument in reducing heating demand, cutting CO2 emissions whilst addressing fuel poverty and improving comfort and wellbeing. Whether using internal or external insulation, it is vitally important the UK's housing stock is raised to an acceptable standard by making the fabric of the building as energy efficient as possible. Only then will we be able to provide a long-term asset that reduces energy usage and can be confidently passed on to future generations.
[1] Climate Change Committee’s Sixth Carbon Budget
This article first appeared in AT Journal issue 146 and was published on the CIAT website on 19 July 2023. It was written by the Insulation Manufacturers Association (IMA).
--CIAT
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
Featured articles and news
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.
The 2025 draft NPPF in brief with indicative responses
Local verses National and suitable verses sustainable: Consultation open for just over one week.
Increased vigilance on VAT Domestic Reverse Charge
HMRC bearing down with increasing force on construction consultant says.
Call for greater recognition of professional standards
Chartered bodies representing more than 1.5 million individuals have written to the UK Government.