Site constraints
The phrase site constraint normally refers to the physical constraints of a development site, such as the site boundary or surrounding features that may constrain the type of development that is possible. These constraints may also be dictated within planning policy, stating the type of development that is acceptable, known as 'planning constraints'. The development project itself may also be impacted by a number of other types of constraints, which might include legal, regulatory or environmental constraints; utility and infrastructure constraints; as well as budget constraints.
Understanding the site constraints is an important early step when planning a construction or development project, followed by or in tandem with consideration of the wider project constraints. Identifying and analysing such constraintsearly on can help ensure that a project is primarily feasible and compliant with relevant laws and regulations as well as cost-effective. The RIBA Plan of Work section 0 Strategic Definition includes what is referred to as a site appraisal, which includes different actions to be taken at the early stage of a project. These include 'site appraisal of sustainabilityopportunities and constraints of potential sites and building assets'.
Examples of physical constraints of a site might include topography, soil conditions, drainage, existing structures, and access. For example, a steeply sloping site may limit the placement of buildings or require expensive grading and retaining walls. Similarly, poor soil conditions might prevent deep foundations or require soil stabilisation. Access can be a key element in the planning of a project. If the site access is limited, it may be difficult for certain types of development or methods of construction.
Legal and regulatory constraints might include development zones of land classification, relevant building regulations, and boundary or public easements. Planning might dictate the kind of structure that can be built in terms of height, density, overlooking, parking, etc., and may also dictate the uses, such as commercial, residential, etc. Other planningaspects constraining site development could include the site classification, such as 'greyfield, 'greenfield, brownfield' or 'greenbelt. Environmental constraints might also be part of regulatory requirements and include sites with protected species, wetlands, floodplains, contaminated soils, etc.
Utility and infrastructure limitations are another important consideration. A site without access to essential utilities like water, electricity, gas, sewerage, and telecommunications may not be viable for development until those services are extended, often at significant expense. In rural areas, lack of infrastructure can be a significant constraint on residential or commercial growth.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Brownfield Passport.
- Concept design report.
- Construction management: feasibility studies.
- Constrained site.
- Constraints on construction projects.
- Construction site.
- Consultation on proposed reforms to NPPF and other changes to the planning system.
- Deemed discharge of planning conditions.
- Design and access statement.
- Development appraisal.
- Discharge of planning conditions.
- Feasibility studies for construction projects.
- Golden rules for the release of land.
- Grey belt.
- Main statutory considerations and constraints.
- National Planning Policy Framework.
- Planning appeal.
- Planning condition.
- Permitted development.
- Planning enforcement.
- Planning fees.
- Planning objection.
- Planning obligation.
- Planning permission.
- RIBA Plan of Work.
- Site information for design and construction.
- The grey, the brown and the golden rules of housing.
- Traditional contract: feasibility studies.
Featured articles and news
Professional practical experience for Architects in training
The long process to transform the nature of education and professional practical experience in the Architecture profession following recent reports.
A people-first approach to retrofit
Moving away from the destructive paradigm of fabric-first.
International Electrician Day, 10 June 2025
Celebrating the role of electrical engineers from André-Marie Amperè, today and for the future.
New guide for clients launched at Houses of Parliament
'There has never been a more important time for clients to step up and ...ask the right questions'
The impact of recycled slate tiles
Innovation across the decades.
EPC changes for existing buildings
Changes and their context as the new RdSAP methodology comes into use from 15 June.
Skills England publishes Sector skills needs assessments
Priority areas relating to the built environment highlighted and described in brief.
BSRIA HVAC Market Watch - May 2025 Edition
Heat Pump Market Outlook: Policy, Performance & Refrigerant Trends for 2025–2028.
Committing to EDI in construction with CIOB
Built Environment professional bodies deepen commitment to EDI with two new signatories: CIAT and CICES.
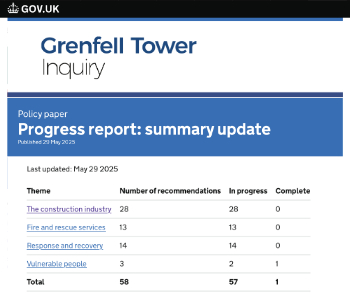
Government Grenfell progress report at a glance
Line by line recomendation overview, with links to more details.
An engaging and lively review of his professional life.
Sustainable heating for listed buildings
A problem that needs to be approached intelligently.
50th Golden anniversary ECA Edmundson apprentice award
Deadline for entries has been extended to Friday 27 June, so don't miss out!
CIAT at the London Festival of Architecture
Designing for Everyone: Breaking Barriers in Inclusive Architecture.
Mixed reactions to apprenticeship and skills reform 2025
A 'welcome shift' for some and a 'backwards step' for others.