Norway could build world-first floating tunnel
The west side of Norway is made up of 1,190 fjords, which, while beautiful, make it very hard to travel along the country’s coastline.
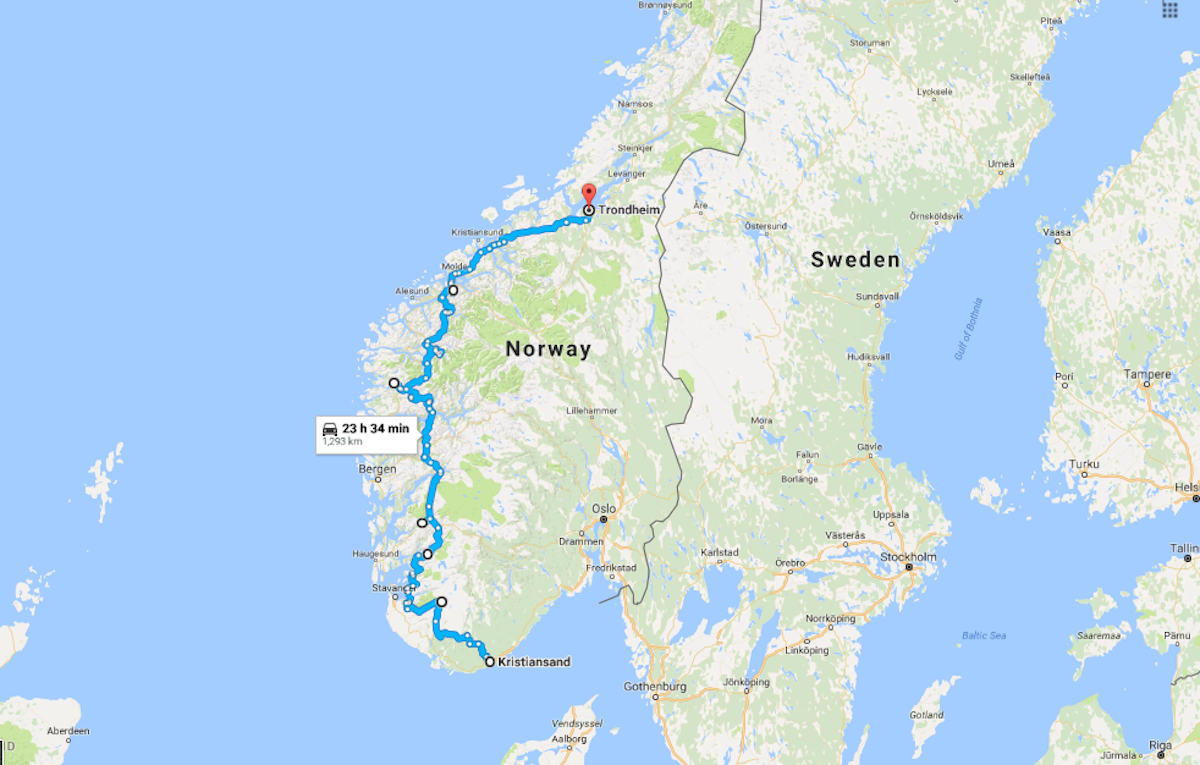
Currently, the drive from the southern city of Kristiansand to Trondheim in the north takes 21 hours and requires seven ferry crossings.
To make that drive easier, the Norwegian Public Roads Administration (NPRA) has proposed the world’s first underwater floating tunnel, which would be submerged in the Norwegian Sea. It is predicted to cost $25bn (around £19m) to build.
The tunnel is part of a series of proposed solutions for the Route E39 coastal highway devised by the NPRA.
[edit] What would it look like?
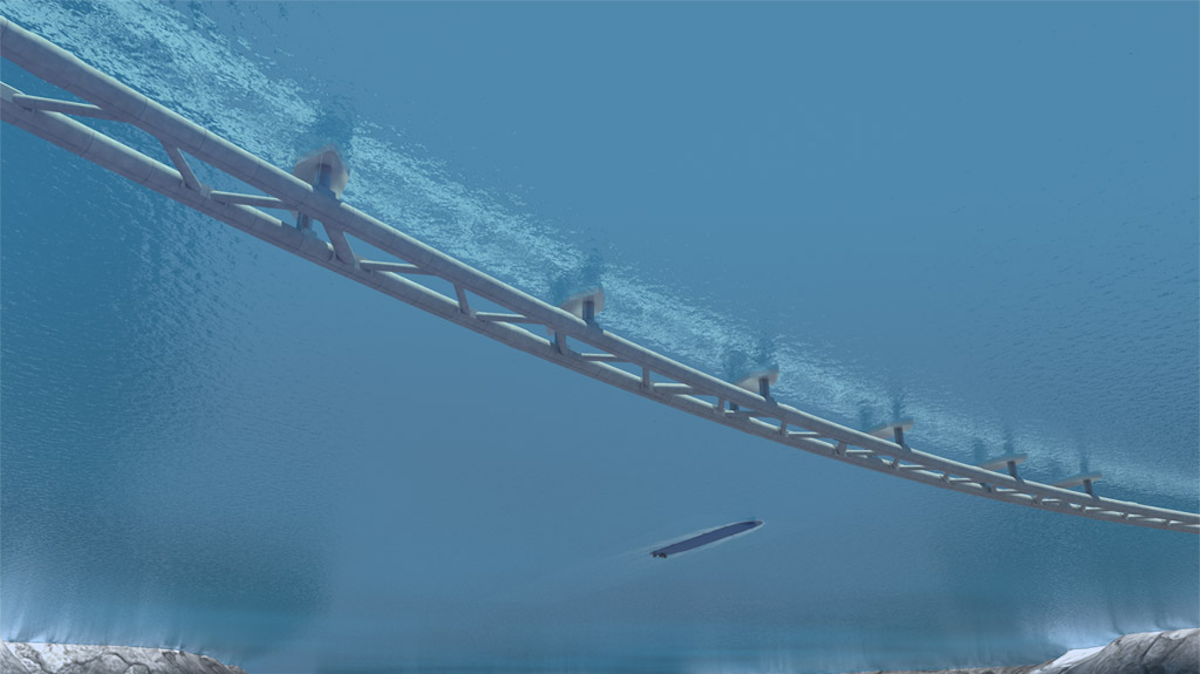
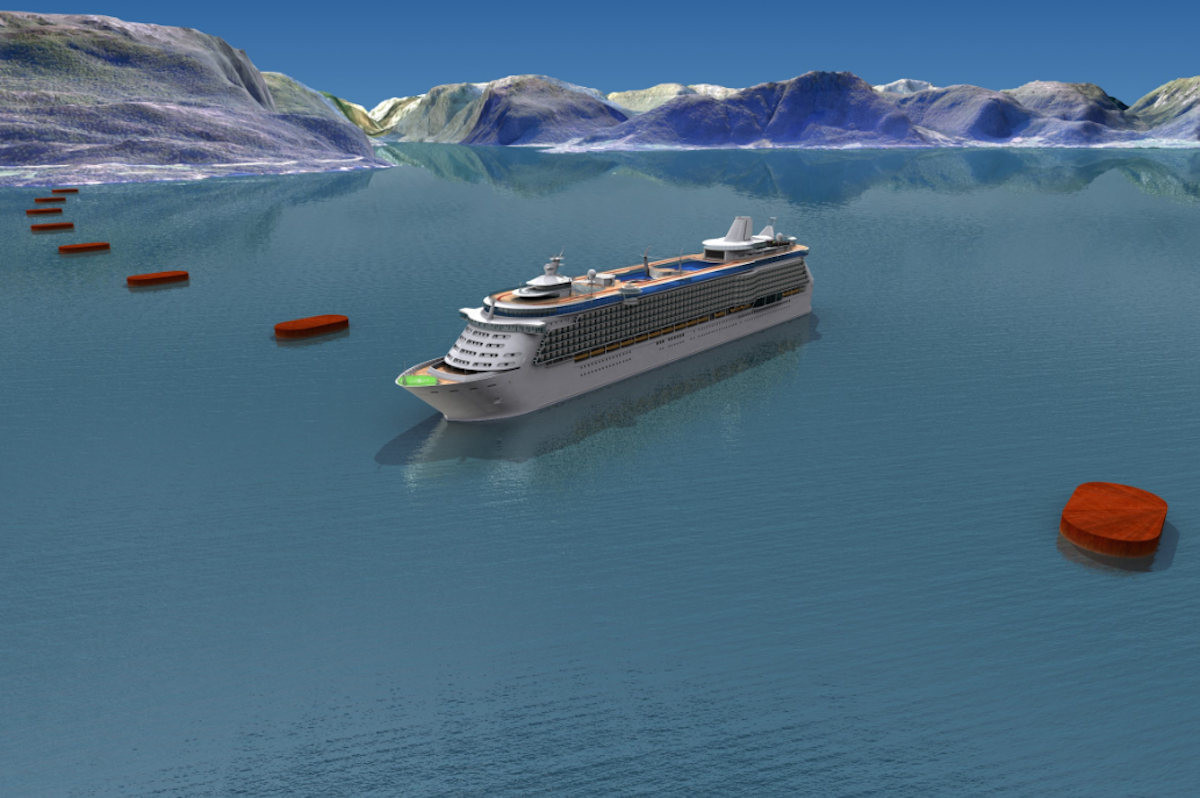
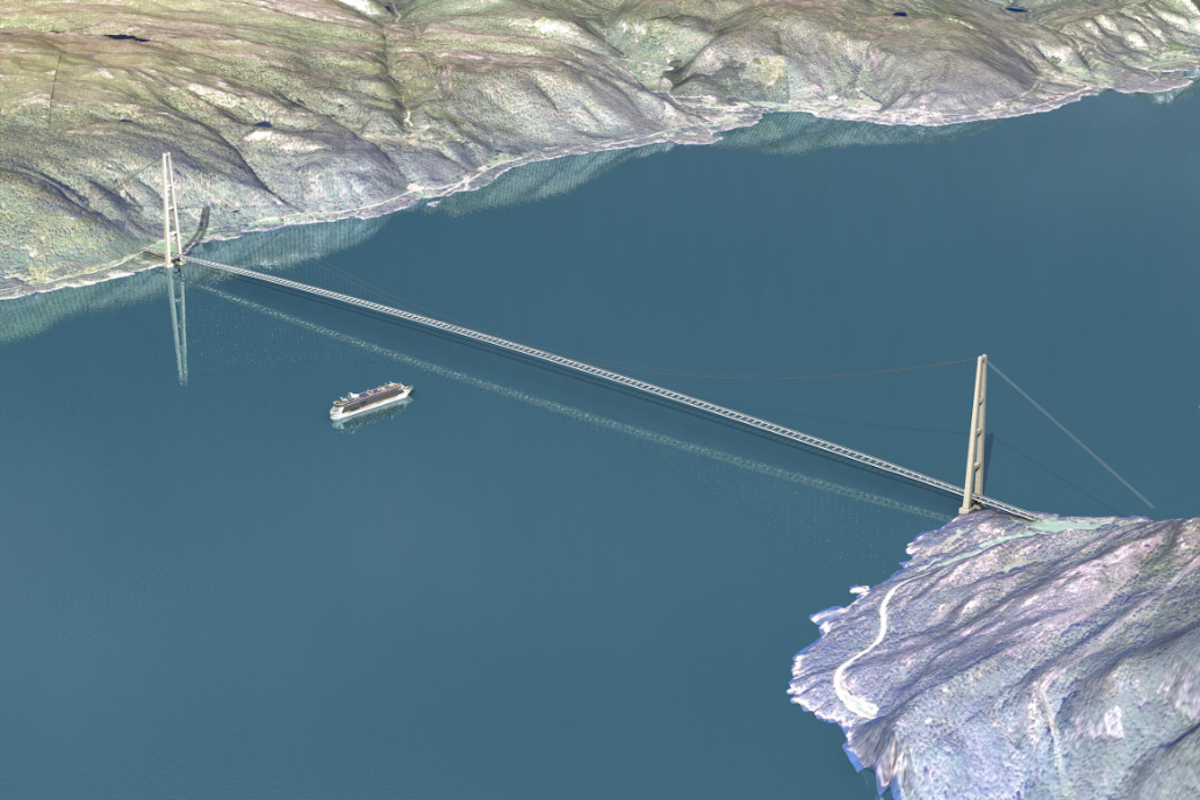
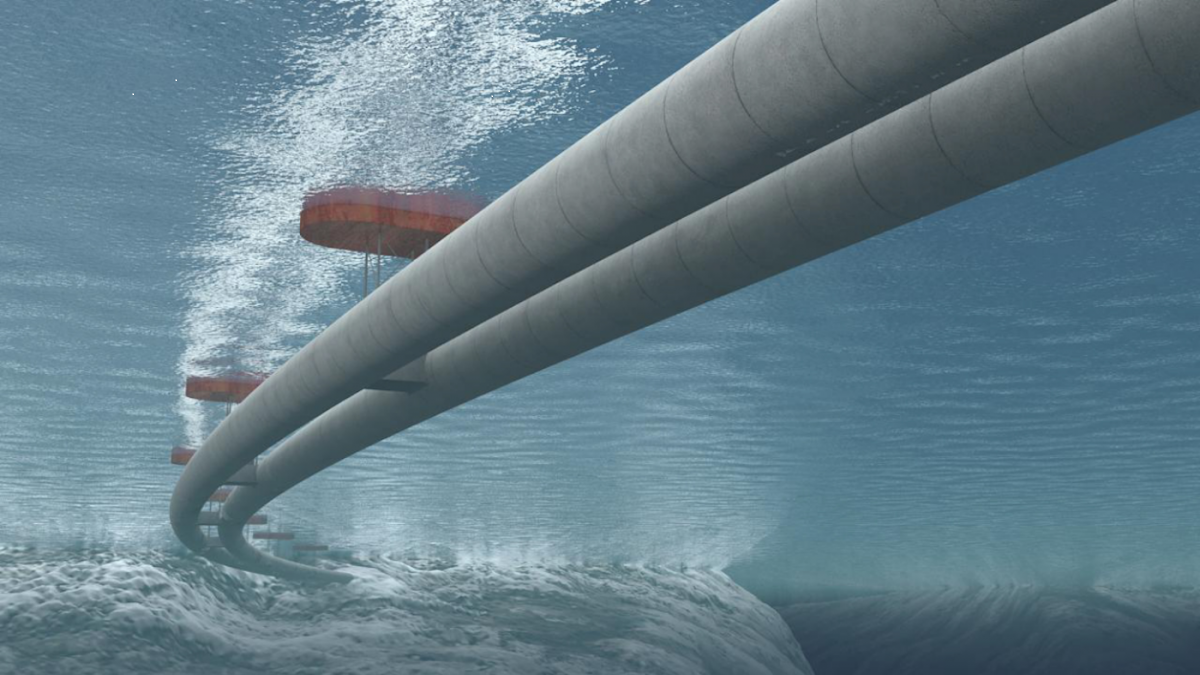
The floating underwater tunnel would consist of two 1,220m-long concrete tubes, submerged 20m below the surface of the Norwegian Sea.
Image: NPRA
Although no floating underwater tunnel like this has ever been built before, a British patent for a similar structure dates back around 100 years.
Image: NPRA
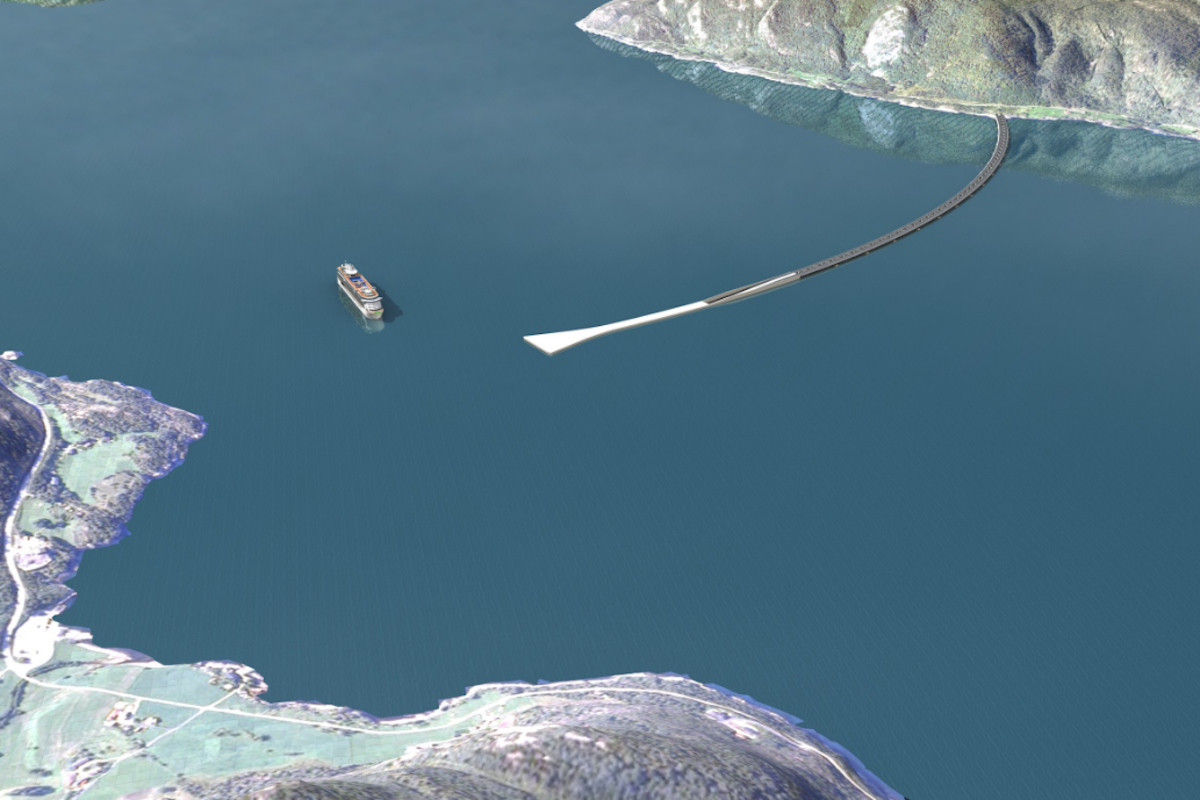
Underwater tunnels could be put in place across the fjords from Kristiansand in the south of Norway to Trondheim in the north.
Image: Google Maps
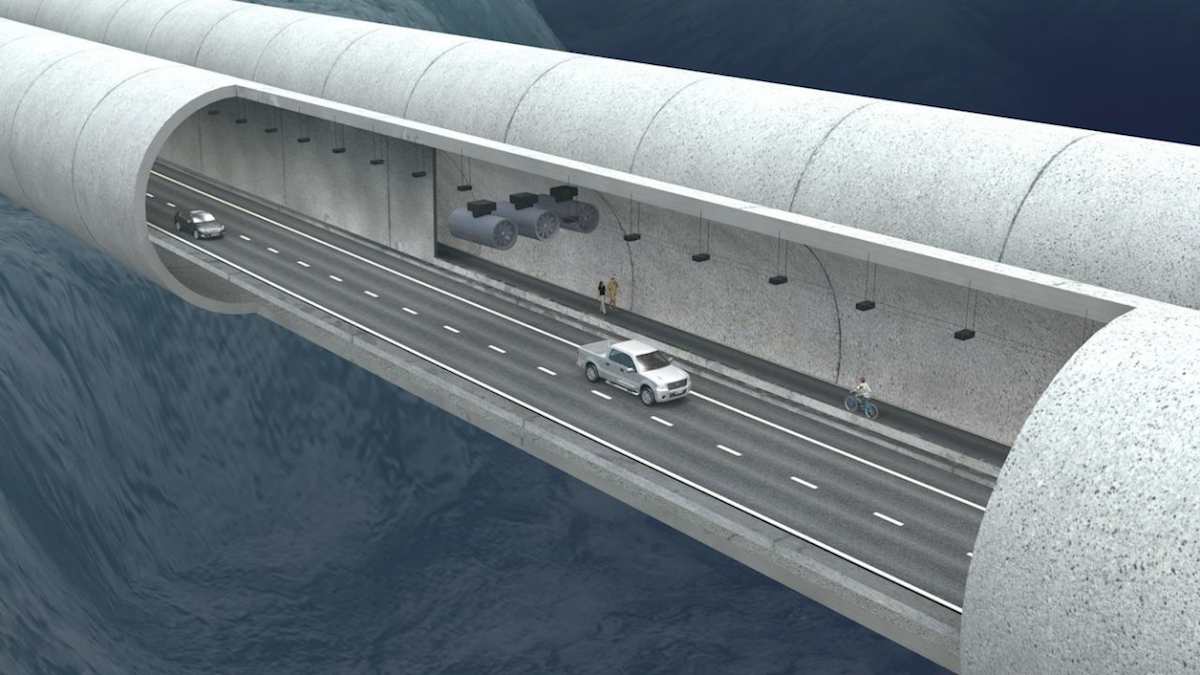
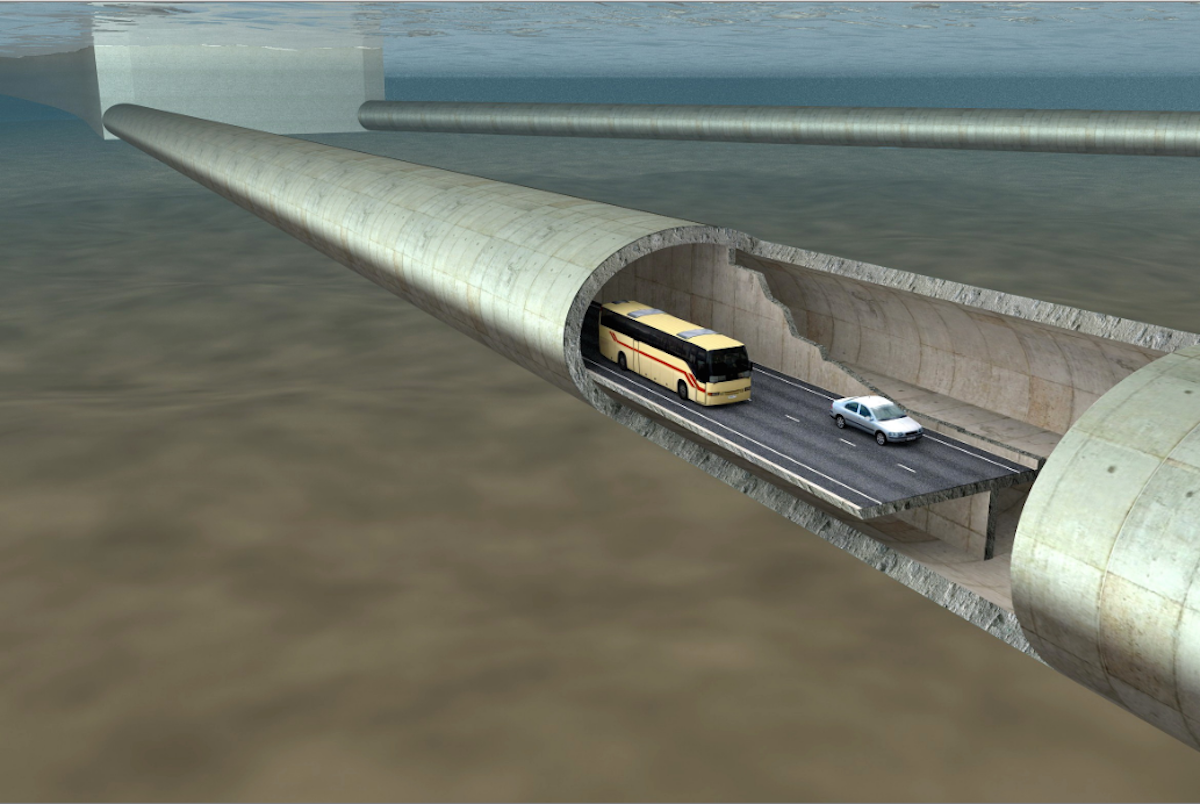
For motorists underwater, the experience would be similar to being in any other tunnel.
Image: NPRA
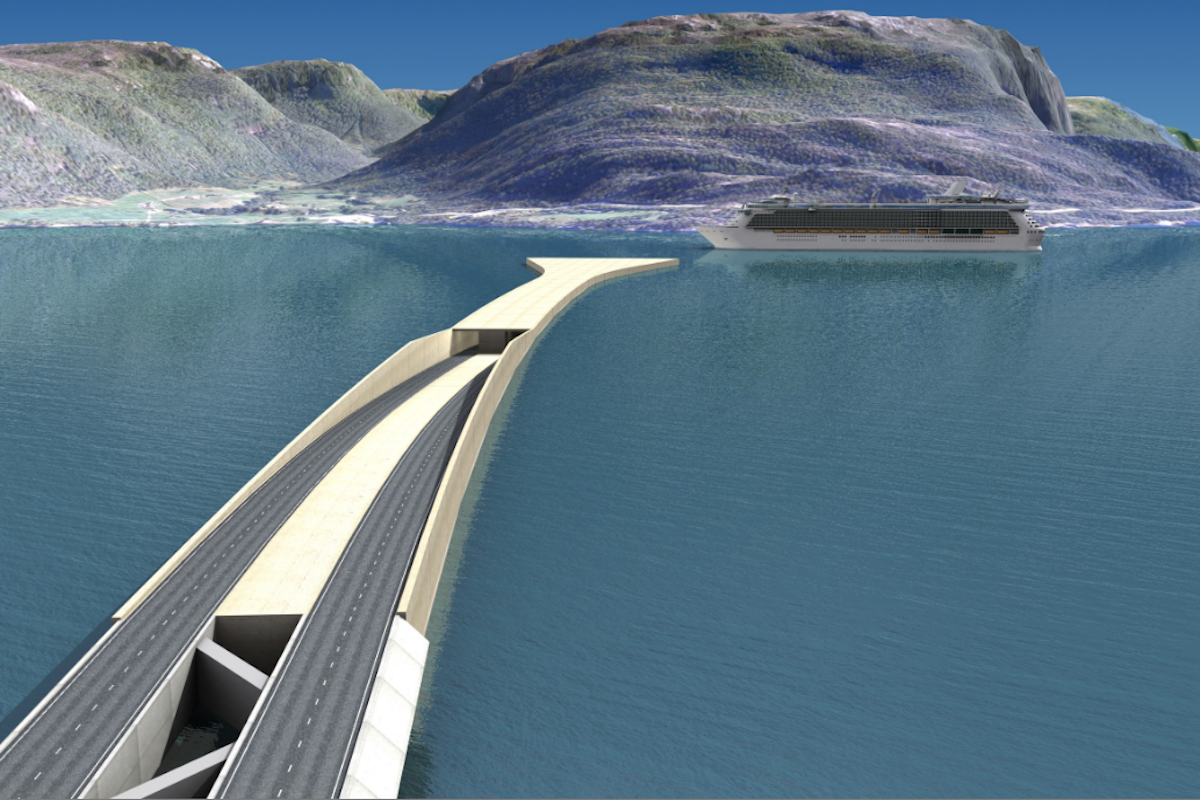
The tunnels would enter the bedrock beneath the fjord on each side.
Image: NPRA
The submerged tubes would be steadied either by being attached to floating pontoons on the surface of the sea or by cables attached to the sea floor..
Image: NPRA
There would be wide gaps between the pontoons to allow ferries to pass through.
Image: NPRA
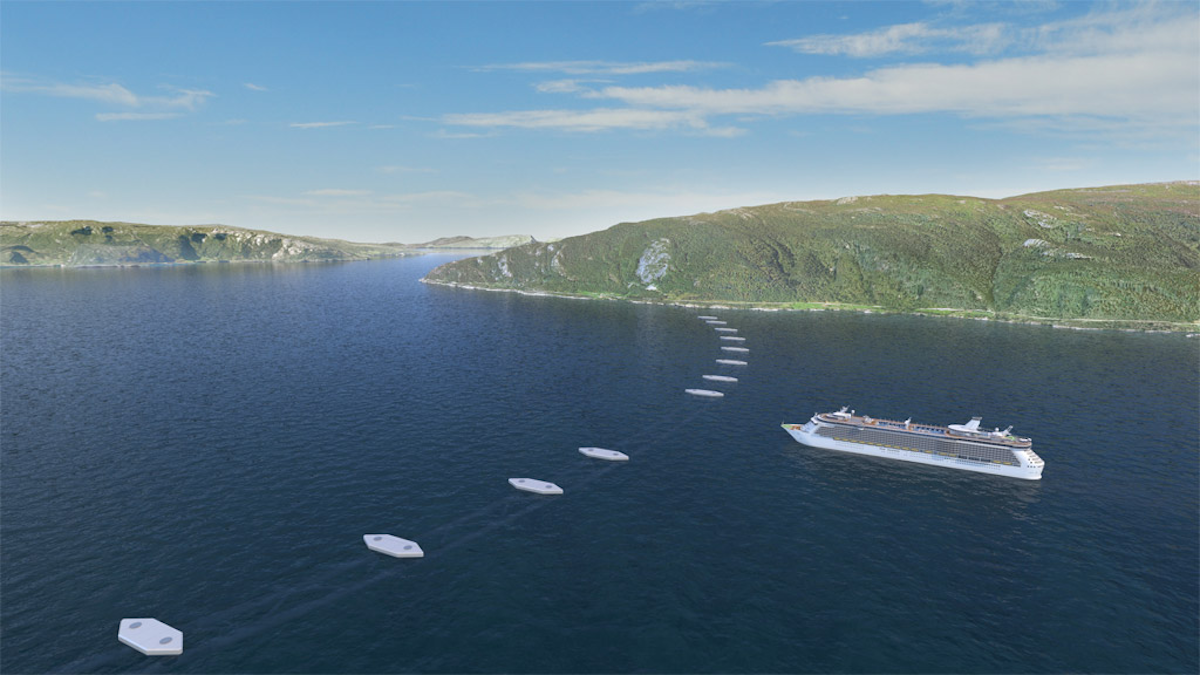
Another option suggested by the NPRA is to combine an underwater tunnel with a bridge.
Image: NPRA
This solution is reminiscent of the Øresund which connects the Danish capital of Copenhagen to the Swedish capital of Malmö.
Image: NPRA
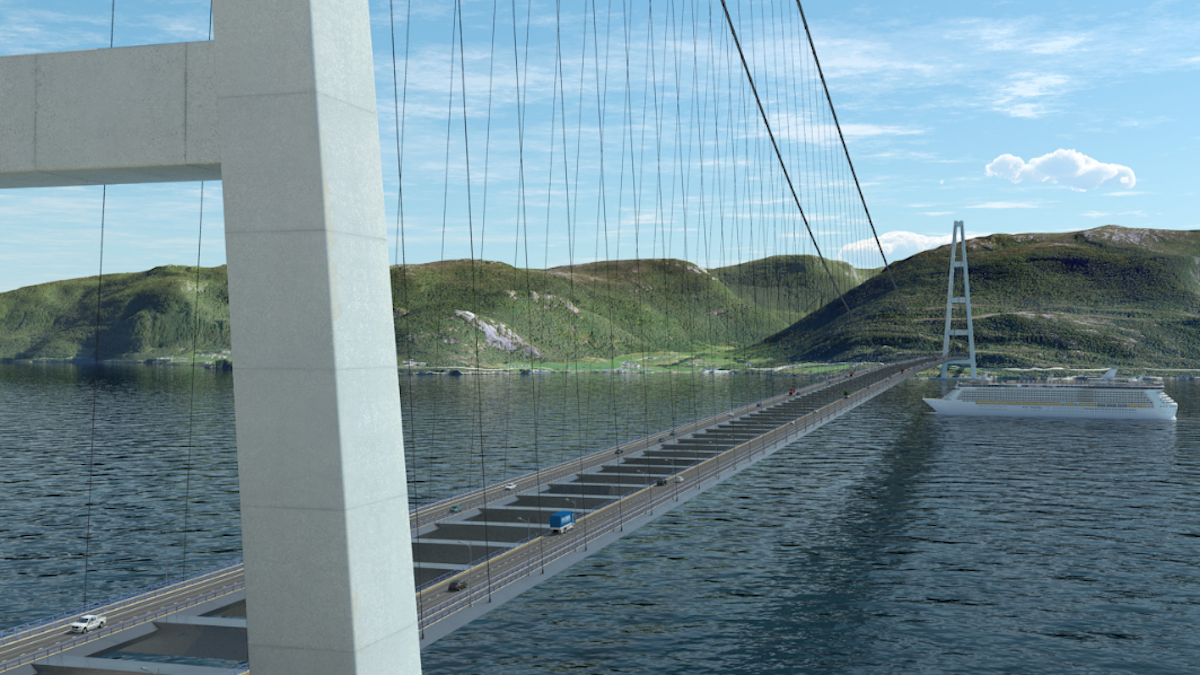
The NPRA is also considering creating a 3,700m-long suspension bridge, which would be three times the length of San Francisco’s Golden Gate bridge and double the current world record for a bridge’s length.
Image: NPRA
The towers on each end of this world-record-breaking suspension bridge would stand at 450m tall — around 150m taller than the Eiffel Tower.
Image: NPRA
The first proposed crossing is for Sognefjord which links up Oppedal with Lavik. By 2035, the crossings are set to be installed between many of the country’s fjords, according to Wired.
Sognefjord. (Image: Shutterstock / S-F)
[edit] About this article
This article was written by Will Heilpern, Features Writer, Business Insider, and is published in collaboration with Business Insider. The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not of the World Economic Forum. It was also published on the Future of Construction Knowledge Sharing Platform and the WEF Agenda Blog.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- At grade.
- Adit.
- Caisson.
- Dredging.
- Excavating plant.
- Excavation.
- Groundworks.
- Ground conditions.
- Grouting in civil engineering.
- Invert.
- Railway engineering.
- Road construction.
- Sewer construction.
- Shotcrete technology.
- Substructure.
- Temporary works.
- Trench support.
- Trenchless technology.
- Tunnels of the world.
- Underpass construction.
- Underpinning.
Featured articles and news
UK Net Zero Carbon Buildings Standard V1 published
Free-to-access technical standard to enable robust proof of a decarbonising built environment.
Prostate Cancer Awareness Month
Why talking about prostate cancer matters in construction.
The Architectural Technology podcast: Where it's AT
Catch up for free, subscribe and share with your network.
The Association of Consultant Architects recap
A reintroduction and recap of ACA President; Patrick Inglis' Autumn update.
The Home Energy Model and its wrappers
From SAP to HEM, EPC for MEES and FHS assessment wrappers.
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.