Line of balance (LOB)
Line of balance (LOB) is a management control process used in construction where the project contains blocks of repetitive work activities, such as roads, pipelines, tunnels, railways and high-rise buildings. LOB collects, measures and presents information relating to time, cost and completion, and presents it against a specific plan.
LOB assists project management by:
- Comparing a formal objective against actual progress.
- Examining the extent of any deviations from specific plans, in terms of knock-on effects.
- Identifying in advance problematic areas where corrective action may be required.
- Forecasting future performance.
The LOB technique was created by the Goodyear Company in the early 1940s, before being adopted and developed by the U.S. Navy in the early-1950s. It was subsequently developed for industrial manufacturing and production control, as well as the basic concepts behind planning and scheduling in the construction industry.
An LOB diagram shows the repetitive project work as a single line on a graph. It differs from a bar chart which shows a particular activity’s duration, by showing the rate at which the work has to be undertaken to stay on schedule, as well as the relationship of one trade or process to the subsequent trade or process.
The project timeline is represented along the x-axis of the LOB diagram. The work areas that define the project are represented along the y-axis. This is the starting point for the LOB schedule:
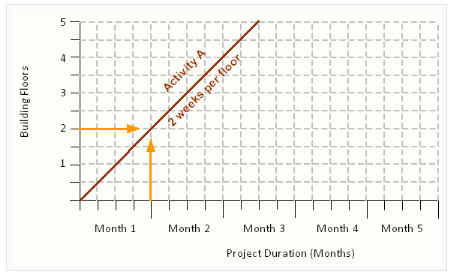
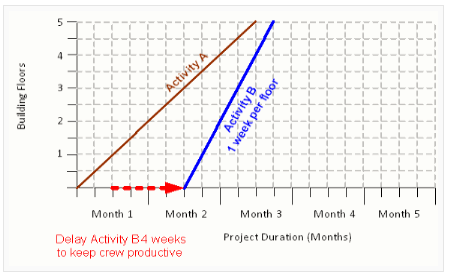
In the figure below, it can be seen that Activity A lasts a 10 weeks. The productivity of A, spread across each of the work areas, is 2 weeks per floor.
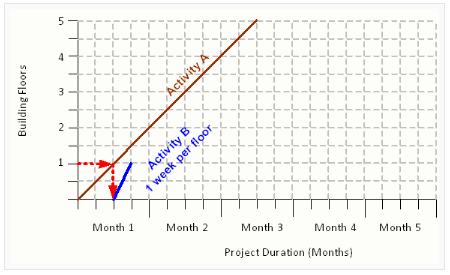
If Activity B has a productivity rate of 1 week per floor, then it can begin work at the end of the second week.
As Activity B continues, at the end of the week 4 work can begin on the second floor; at the end of week 6 work can begin on the third floor, and so on. The horizontal red dashed lines represent the breaks in Activity B work, where the workforce is waiting for Activity A to clear the way for them to continue. In this example, starting Activity B as soon as possible will result in a lost productivity of 4 weeks.
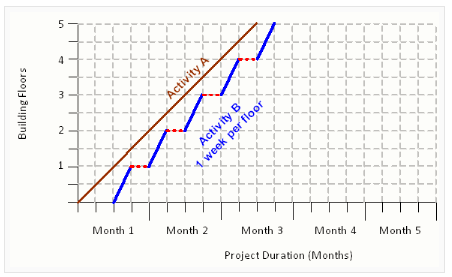
The diagram below shows that by delaying the start of Activity B for 4 weeks, the workforce can continue uninterrupted, and hence are more productive. This enables a better understanding of how workforces follow one another through activities.
The advantages of LOB include:
- Allowing a clearer understanding of the amount of work taking place at a certain time in a specific place.
- Resources can be optimised for a large number of repeated work activities.
- As all information is available for each activity, it allows easier cost and time optimisation analysis.
- It is relatively easy to modify, update and change the schedule.
- It allows better management of subcontractors and resources.
- It allows problem areas to be identified in advance.
[edit] Find out more
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- Activity schedule.
- Advanced manufacturing.
- Block planning.
- Clash avoidance.
- Critical path method.
- Design coordination.
- Gantt chart.
- Key dates.
- Logistics management.
- Milestones.
- Pareto analysis.
- Programme for building design and construction.
- Project manager.
- Resource leveling.
- Scheduling construction activities.
- Time-location chart.
- Time management of construction projects.
[edit] External resources
- CPM Tutor - Line of balance
Featured articles and news
UKCW London to tackle sector’s most pressing issues
AI and skills development, ecology and the environment, policy and planning and more.
Managing building safety risks
Across an existing residential portfolio; a client's perspective.
ECA support for Gate Safe’s Safe School Gates Campaign.
Core construction skills explained
Preparing for a career in construction.
Retrofitting for resilience with the Leicester Resilience Hub
Community-serving facilities, enhanced as support and essential services for climate-related disruptions.
Some of the articles relating to water, here to browse. Any missing?
Recognisable Gothic characters, designed to dramatically spout water away from buildings.
A case study and a warning to would-be developers
Creating four dwellings... after half a century of doing this job, why, oh why, is it so difficult?
Reform of the fire engineering profession
Fire Engineers Advisory Panel: Authoritative Statement, reactions and next steps.
Restoration and renewal of the Palace of Westminster
A complex project of cultural significance from full decant to EMI, opportunities and a potential a way forward.
Apprenticeships and the responsibility we share
Perspectives from the CIOB President as National Apprentice Week comes to a close.
The first line of defence against rain, wind and snow.
Building Safety recap January, 2026
What we missed at the end of last year, and at the start of this...
National Apprenticeship Week 2026, 9-15 Feb
Shining a light on the positive impacts for businesses, their apprentices and the wider economy alike.
Applications and benefits of acoustic flooring
From commercial to retail.
From solid to sprung and ribbed to raised.
Strengthening industry collaboration in Hong Kong
Hong Kong Institute of Construction and The Chartered Institute of Building sign Memorandum of Understanding.
A detailed description from the experts at Cornish Lime.