Line of balance (LOB)
Line of balance (LOB) is a management control process used in construction where the project contains blocks of repetitive work activities, such as roads, pipelines, tunnels, railways and high-rise buildings. LOB collects, measures and presents information relating to time, cost and completion, and presents it against a specific plan.
LOB assists project management by:
- Comparing a formal objective against actual progress.
- Examining the extent of any deviations from specific plans, in terms of knock-on effects.
- Identifying in advance problematic areas where corrective action may be required.
- Forecasting future performance.
The LOB technique was created by the Goodyear Company in the early 1940s, before being adopted and developed by the U.S. Navy in the early-1950s. It was subsequently developed for industrial manufacturing and production control, as well as the basic concepts behind planning and scheduling in the construction industry.
An LOB diagram shows the repetitive project work as a single line on a graph. It differs from a bar chart which shows a particular activity’s duration, by showing the rate at which the work has to be undertaken to stay on schedule, as well as the relationship of one trade or process to the subsequent trade or process.
The project timeline is represented along the x-axis of the LOB diagram. The work areas that define the project are represented along the y-axis. This is the starting point for the LOB schedule:
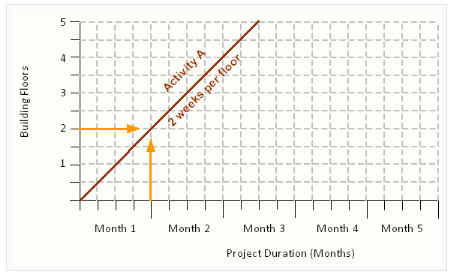
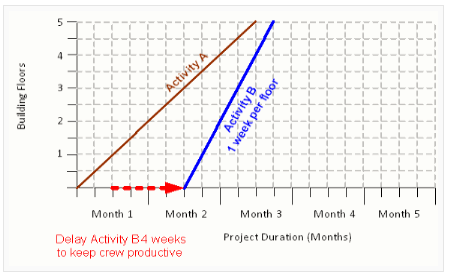
In the figure below, it can be seen that Activity A lasts a 10 weeks. The productivity of A, spread across each of the work areas, is 2 weeks per floor.
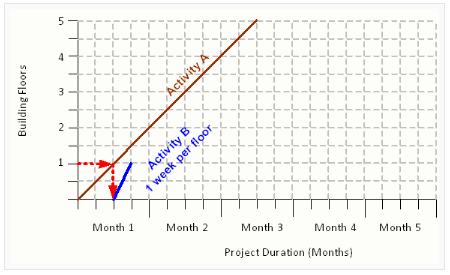
If Activity B has a productivity rate of 1 week per floor, then it can begin work at the end of the second week.
As Activity B continues, at the end of the week 4 work can begin on the second floor; at the end of week 6 work can begin on the third floor, and so on. The horizontal red dashed lines represent the breaks in Activity B work, where the workforce is waiting for Activity A to clear the way for them to continue. In this example, starting Activity B as soon as possible will result in a lost productivity of 4 weeks.
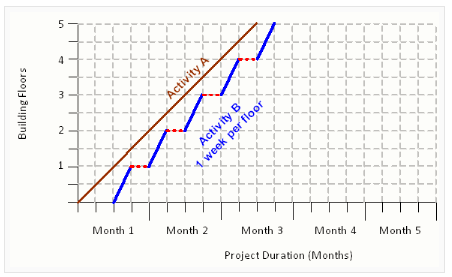
The diagram below shows that by delaying the start of Activity B for 4 weeks, the workforce can continue uninterrupted, and hence are more productive. This enables a better understanding of how workforces follow one another through activities.
The advantages of LOB include:
- Allowing a clearer understanding of the amount of work taking place at a certain time in a specific place.
- Resources can be optimised for a large number of repeated work activities.
- As all information is available for each activity, it allows easier cost and time optimisation analysis.
- It is relatively easy to modify, update and change the schedule.
- It allows better management of subcontractors and resources.
- It allows problem areas to be identified in advance.
[edit] Find out more
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- Activity schedule.
- Advanced manufacturing.
- Block planning.
- Clash avoidance.
- Critical path method.
- Design coordination.
- Gantt chart.
- Key dates.
- Logistics management.
- Milestones.
- Pareto analysis.
- Programme for building design and construction.
- Project manager.
- Resource leveling.
- Scheduling construction activities.
- Time-location chart.
- Time management of construction projects.
[edit] External resources
- CPM Tutor - Line of balance
Featured articles and news
UK Net Zero Carbon Buildings Standard V1 published
Free-to-access technical standard to enable robust proof of a decarbonising built environment.
Prostate Cancer Awareness Month
Why talking about prostate cancer matters in construction.
The Architectural Technology podcast: Where it's AT
Catch up for free, subscribe and share with your network.
The Association of Consultant Architects recap
A reintroduction and recap of ACA President; Patrick Inglis' Autumn update.
The Home Energy Model and its wrappers
From SAP to HEM, EPC for MEES and FHS assessment wrappers.
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.