CIOB joins forces to urge Government to regulate embodied carbon
CIOB has joined leading organisations to warn political leaders about the urgent need for regulation of embodied carbon emissions in construction.
The Chartered Institute of Building (CIOB) has teamed up with 10 leading organisations to warn political leaders about the urgent need for regulation of embodied carbon emissions in construction.
Environment experts from CIOB, UK Green Building Council, The Institution of Structural Engineers, the Institution of Civil Engineers, Construction Industry Council, Chartered Institution of Building Services Engineers, UK Architects Declare, RIBA, RICS, Association for Consultancy and Engineering and Part Z have all joined forces to send a clear message to Government.
They warn regulation is necessary because buildings and construction form a substantial part of UK carbon emissions, which are a main driver of climate change. The group believes UK policy has stalled and urgent action is needed.
Amanda Williams, Head of Environmental Sustainability at CIOB, said: “There have been numerous industry initiatives over recent years, calling for government action to reduce the construction industry’s embodied carbon emissions.
“We now join forces as an expert group to pull these proposals together, uniting with one voice for change and asking Government to ensure the UK keeps pace with those who are currently leading this agenda.”
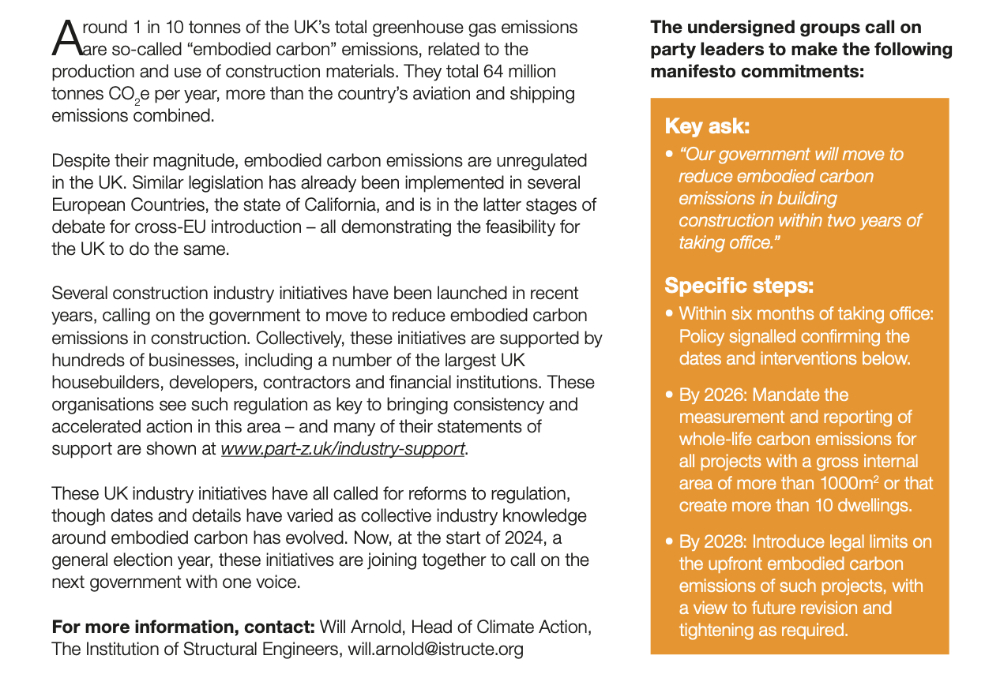
The group of experts has issued a paper to political leaders with a key ask: to include in their manifestoes a commitment to move to reduce embodied carbon emissions in construction within two years of starting government.
Steps for action include:
- In 2024: Policy signalled to confirm the dates and interventions below.
- By 2026: Mandate the measurement and reporting of whole-life carbon emissions for all projects with a gross internal area of more than 1000m2 or that create more than 10 dwellings.
- By 2028: Introduce legal limits on the upfront embodied carbon emissions [those emissions due to the use of materials in the initial construction] of such projects, with a view to future revision and tightening as required.
The group says these actions are essential as around one in 10 tonnes of the UK’s total greenhouse gas emissions are “embodied carbon” emissions. These relate to the production and use of construction materials, which account for a substantial part of the UK’s overall carbon emissions.
Policy recommendations would be complementary to the ‘carbon pricing mechanism’ announced by the government in 2023 and which is due to be introduced in 2027, as well as to existing UK initiatives that incentivise the use of lower carbon cement and steel.
This article appears on the CIOB news and blog site as "CIOB joins forces to urge Government to regulate embodied carbon" dated January 31, 2024.
--CIOB
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- An in-depth look at Environmental Product Declarations EPDs.
- BPIE report urges EU to incorporate the carbon footprint of construction into policy.
- BS EN 15978-1.
- BSRIA Whitepaper on Embodied Carbon NZG 4/2023
- Carbon dioxide.
- Carbon footprint.
- Climate change act.
- Climate change science.
- Climate Emergency Design Guide.
- Cradle to grave.
- Dr. Natasha Watson; UK lead for embodied carbon at Buro Happold.
- Embedded carbon emissions.
- Embodied carbon.
- Embodied energy.
- EN 15804+A1 2012.
- Environmental product declaration EPD.
- Greenhouse gas.
- Life Cycle Carbon Emissions.
- Mandatory and optional environmental impact categories.
- Optional environmental impact categories.
- PHribbon tool calculates embodied carbon of designs.
- Product Environmental Footprint PEF.
- Product category rules PCR.
- RICS launches new global edition of its ground-breaking Whole Life Carbon Assessment standard.
- Sustainable procurement.
- Sustainability in building design and construction.
- The sustainability of construction works.
- Upfront emissions.
- Use stage embodied carbon.
- Wood, embodied carbon and operational carbon.
- Whole life carbon.
Featured articles and news
Repairing historic stone and slate roofs
The need for a code of practice and technical advice note.
UKCW London to tackle sector’s most pressing issues
AI and skills development, ecology and the environment, policy and planning and more.
Managing building safety risks
Across an existing residential portfolio; a client's perspective.
ECA support for Gate Safe’s Safe School Gates Campaign.
Core construction skills explained
Preparing for a career in construction.
Retrofitting for resilience with the Leicester Resilience Hub
Community-serving facilities, enhanced as support and essential services for climate-related disruptions.
Some of the articles relating to water, here to browse. Any missing?
Recognisable Gothic characters, designed to dramatically spout water away from buildings.
A case study and a warning to would-be developers
Creating four dwellings... after half a century of doing this job, why, oh why, is it so difficult?
Reform of the fire engineering profession
Fire Engineers Advisory Panel: Authoritative Statement, reactions and next steps.
Restoration and renewal of the Palace of Westminster
A complex project of cultural significance from full decant to EMI, opportunities and a potential a way forward.
Apprenticeships and the responsibility we share
Perspectives from the CIOB President as National Apprentice Week comes to a close.
The first line of defence against rain, wind and snow.
Building Safety recap January, 2026
What we missed at the end of last year, and at the start of this.