Wheelchair user

|
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
A wheelchair user is a person who requires the use a of wheelchair to achieve a degree of mobility. This is typically due to some physical or mental disability that precludes them from walking. People using a wheelchair may be described as ‘disabled’, or a 'person with a disability' or ‘people with health conditions or impairments’. However, some disabled people do not require a wheelchair (ambulant disabled people), while some wheelchair users can walk but with difficulty or cannot walk for long periods unaided, therefore they sometimes require the use of a wheelchair.
NB for guidance on the terminology that should be used see: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/inclusive-communication/inclusive-language-words-to-use-and-avoid-when-writing-about-disability
[edit] Types
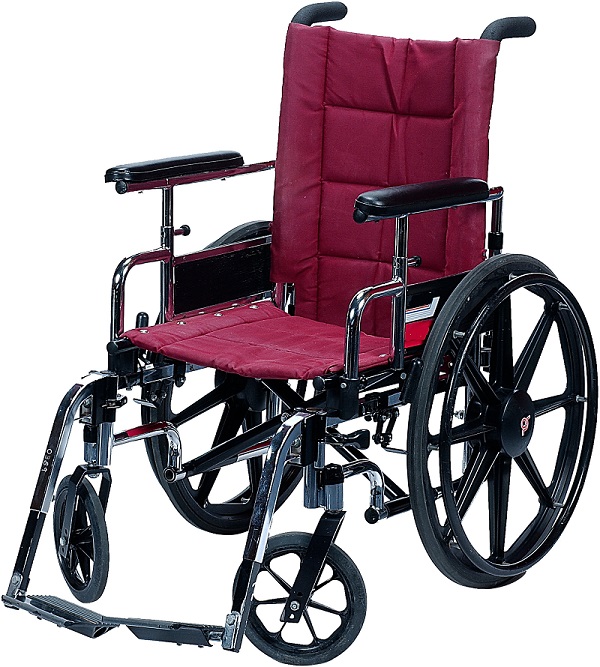
Generally speaking, a wheelchair is a four-wheeled seat (with back, footrests and armrests) that can have either rear- or front-propelling wheels. Manual wheelchairs can be propelled by the user by placing both hands on the wheel hand-rims and applying repeated pushing strokes. Turning may be achieved by pushing just one of the wheels, while reversing is achieved by applying pulling strokes.
Typically, a standard, manual wheelchair will have:
- A foldable steel or aluminium-alloy frame.
- A carry weight of up to 26kg (including footrests).
- A typical maximum user weight capacity of 150kg (23 stone).
- Two small front-propelling wheels.
- Two large 550mm rear wheels (pneumatic tyres) with hand rims.
Propelling a manual wheelchair on average can require between 2,000 and 3,000 strokes per day which may increase the risk of users developing repetitive strain injuries such as carpal tunnel syndrome. The most common injury from repetitive use can occur at the wrist and shoulder. Learning properly to manually control a wheelchair is therefore critical for users, both to minimise the effort required and possible injury, but particularly when they are outdoors and have no assistance.
Stress and strain are reduced – and control can be better – if the wheelchair is battery-powered: forward/rear and left/right movement is usually achieved by moving a joystick located on one of the armrests.
[edit] Wheelchairs in the built environment
Requirements for access to and the use of buildings is set out in Part M of the building regulations, with guidance in Approved Document M.
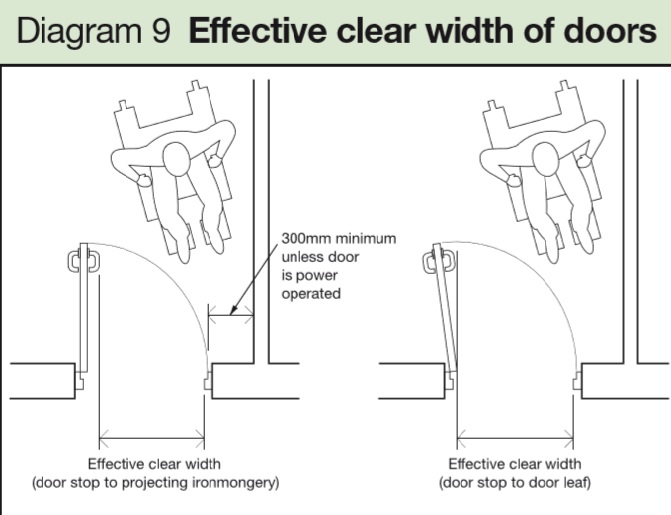
|
| Extract from Approved Document M. Readers should check requirements of the latest version. |
When designing for wheelchair users, it is critical to give proper consideration to the necessary minimal space requirements applicable to the various types of wheelchair and disability. As an illustration:
- Minimum width (large wheelchairs) for forward movement: 790mm (940mm min better).
- Standard chair (rear propelling wheels) may require 1,575mm-diameter turning circle.
- Standard chair (front propelling wheels) may require 1,500mm-diameter turning circle.
- An indoor chair typically requires 1,245mm diameter turning circle.
- Design of disabled WCs
- Typically, recommended dimensions for a wheelchair-user WC cubicle are 1500mm wide by 2000mm deep.
[edit] WC cubicles
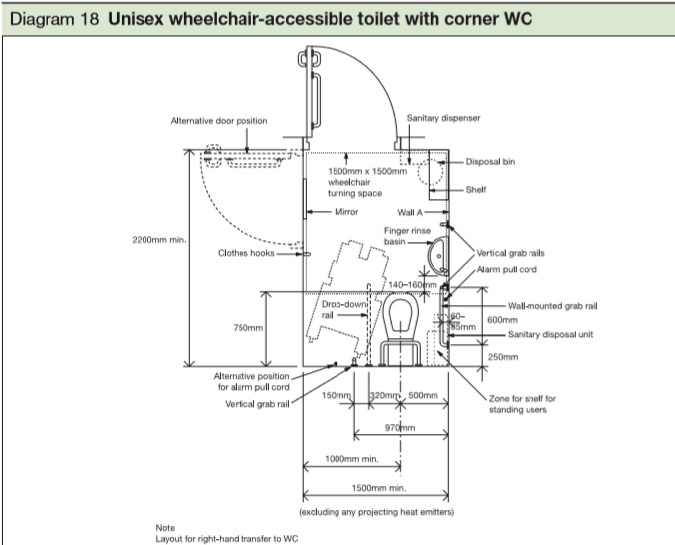
|
| Extract from Approved Document M. Readers should check requirements of the latest version. |
WC cubicles for wheelchair users should accommodate front- or side-transfer from the wheelchair in addition to a wheelchair-accessible unisex toilet, handrails, guardrails, alarm pulls, disabled taps and other special facilities. Furthermore, a wash-hand basin should ideally be easily accessible by a person in a wheelchair and also when sitting on the WC.
Caution: The above dimensions are for illustrative purposes only. Readers should refer to Approved Document M for information.
[edit] Ramps an lifts
Ramps are sloped pathways used both inside and outside buildings used to provide access between vertical levels. Ramps provide an alternative to stairs for wheelchair users, people with mobility issues and people with prams, bicycles and other wheeled items.
For more information see: Ramps.
A lift (or elevator) is a form of vertical transportation between building floors, levels or decks, commonly used in offices, public buildings and other types of multi-storey building. Lifts can be essential for providing vertical circulation, particularly in tall buildings, for wheelchair and other non-ambulant building users and for the vertical transportation of goods. Some lifts may also be used for firefighting and evacuation purposes.
For more information see: Lifts.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- Accessibility in the built environment.
- Approved Document M.
- Balance for Better: Why lack of diversity is an issue for everyone.
- Disability Discrimination Act DDA.
- Equality Act.
- Evacuation chair.
- Inclusive design.
- Lifts and Escalators: A Quality Perspective.
- Lifts for buildings.
- Platforms lifts and how they benefit people.
- Ramps.
- Shopmobility.
- Stairlift.
- Wheelchair housing.
- Wheelchair platform stairlift.





