Firefighting shaft
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
In certain buildings, it can be difficult for the fire and rescue service to safely reach and work close to fires. Under such circumstances additional facilities are required to ensure that there is no delay and to provide a secure operating base. This might include:
- Firefighting routes.
- Firefighting lifts.
- Firefighting stairs.
- Firefighting shafts.
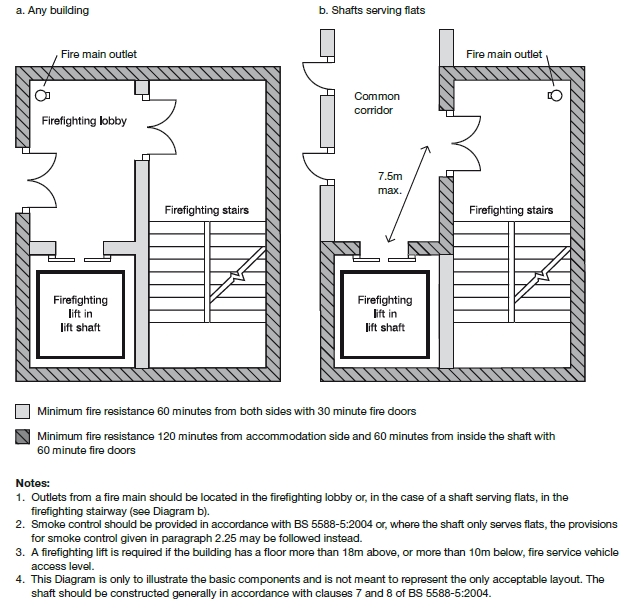
A firefighting shaft provides the fire and rescue service with a safe area from which to undertake firefighting operations. They link all necessary floors of a building, providing at least 2 hours of fire resistance to protect fire crews and are connected to fresh air. A firefighting shaft will typically contain a firefighting main, stairway, lobby and sometimes a lift.
[edit] Provision of firefighting shafts
Fire-fighting shafts should be provided in:
- Tall buildings more than 18m high.
- Buildings with deep basements of more than 10m.
- Commercial, shop, industrial or storage buildings that are more than 7.5m high.
If the building has an automatic sprinkler system, adequate shafts should be fitted so that every part of every storey (over 18m above access level) is no more than 60m from a fire main outlet. If no sprinkler system is fitted, this distance reduces to 45m from an outlet which is inside a protected stairway or 60m if it is in a firefighting shaft.
[edit] Features
In buildings (apart from blocks of flats), the firefighting stairs and lift should be entered from accommodation, through a firefighting lobby. The firefighting shaft should have a fire main with outlet connections and valves on every storey. For blocks of flats, it is not necessary to have a firefighting lobby.
[edit] Further information
Approved Document B (Fire Safety) has further details on the design and layout of firefighting shafts. Additional guidance can be found in BS 9999: Code of practice for fire safety in the design, management and use of buildings.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Approved Document B (Fire Safety).
- BS 9999: Code of practice for fire safety in the design, management and use of buildings.
- Dry riser.
- Escape route.
- Fire and rescue service.
- Fire compartment.
- Fire detection and alarm systems.
- Fire door.
- Fire protection engineering.
- Fire resistance.
- Fire safety design.
- Firefighting lift.
- Firefighting route.
- Inner room.
- Lobby.
- Protected escape route.
- Protected stairway.
- Unprotected escape route.
- Wet riser.
Featured articles and news
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherit assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.
The 2025 draft NPPF in brief with indicative responses
Local verses National and suitable verses sustainable: Consultation open for just over one week.
Increased vigilance on VAT Domestic Reverse Charge
HMRC bearing down with increasing force on construction consultant says.
Call for greater recognition of professional standards
Chartered bodies representing more than 1.5 million individuals have written to the UK Government.
Cutting carbon, cost and risk in estate management
Lessons from Cardiff Met’s “Halve the Half” initiative.
Inspiring the next generation to fulfil an electrified future
Technical Manager at ECA on the importance of engagement between industry and education.
Repairing historic stone and slate roofs
The need for a code of practice and technical advice note.
Environmental compliance; a checklist for 2026
Legislative changes, policy shifts, phased rollouts, and compliance updates to be aware of.
UKCW London to tackle sector’s most pressing issues
AI and skills development, ecology and the environment, policy and planning and more.
Managing building safety risks
Across an existing residential portfolio; a client's perspective.
ECA support for Gate Safe’s Safe School Gates Campaign.
Core construction skills explained
Preparing for a career in construction.
Retrofitting for resilience with the Leicester Resilience Hub
Community-serving facilities, enhanced as support and essential services for climate-related disruptions.