Advanced network planning
Programmes describe the sequence in which tasks must be carried out so that a project (or part of a project) can be completed on time.
Programmes will often identify:
- Dates and durations allocated to tasks.
- A critical path (the sequence of critical tasks upon which the overall duration of the programme is dependent).
- Tasks which can only be carried out after other tasks have been completed.
- Tasks which can be carried out simultaneously.
- 'Float' within tasks that are not on the critical path (that is, delays that can be incurred without affecting the critical path).
- The need for specific resources such as plant, services or materials and their lead time.
Developing a programme for a project can be very complex, as there are a great number of interrelated activities to consider, a change in any one of which may impact on all the others.
Advanced network planning is a process that can be used for planning, scheduling and controlling projects (or programmes – that is portfolios of projects) that consist of a large number of interrelated activities.
Network planning techniques first developed in the 1950s and included techniques such as:
- The Critical Path Method (CPM).
- The Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT).
- The Precedence Diagramming Method (PDM).
- The Graphical Evaluation and Review Technique (GERT).
- Systematic Network Planning (SNP).
Very broadly, these describe projects as a network of tasks, the interrelationships between which can be used to establish the most appropriate moment for their execution in order to complete the overall project on time.
Creating a network includes a number of steps:
- All the project activities are identified and defined.
- The technological sequence between activities is defined.
- A network is constructed which shows the relative priority of those relationships.
- The execution periods for each activity are estimated.
- The critical path is calculated.
- As time goes on and more information is acquired, the network is revised and re-evaluated.
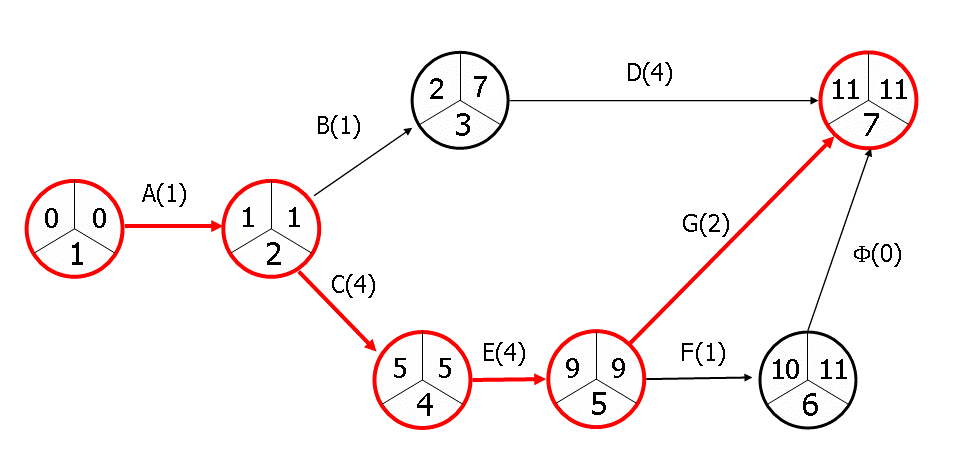
A typical network will include a set of “arrow diagrams” which go from the origin node to the destination node. In this sense, the path is defined as a sequence of connected activities, which flow from the start of the project (node 1) to the end. The time required to follow one of these paths is the sum of the times corresponding to each of the activities. The critical path is that which requires the longest time to progress from inception to completion, and indicates the minimum timeframe required to complete the whole project.
Complex models can be developed that include additional information such as cost information, and may represent:
- Variables: Aspects in the model that can be changed, such as product type.
- Sensitivities: How much performance changes in response to variable changes.
- Scenarios: The range of possible changes to the network.
Advanced network planning can also be used in applications, such as health and safety management, IT asset sourcing, resource allocation, operations and maintenance scheduling and so on.
This is a complex specialist process that is simplified by the use of software that carries out analysis automatically and outputs results in ways that are easier for the project team to digest, such as gantt charts.
On large projects, the client may appoint a programme consultant who specialises in this subject, and suppliers may have their own programmers.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
Featured articles and news
The Home Energy Model and its wrappers
From SAP to HEM, EPC for MEES and FHS assessment wrappers.
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help the homebuilding sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.